Transcription
Biology 3Transcription, Translation, andMutationsDr. Terence LeeOverview1. DNA and RNA structure2. DNA replication3. Transcription– makes RNA4. Translation– makes proteinJames Watson,Francis Crick,and RosalindFranklindiscovered thestructure ofDNA1
Image of DNADNA Structure Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) isa type of nucleic acid Three parts:1. Sugar group (deoxyribose)2. Phosphate group3. Nitrogenous base AdenineGuanineThymineCytosine2
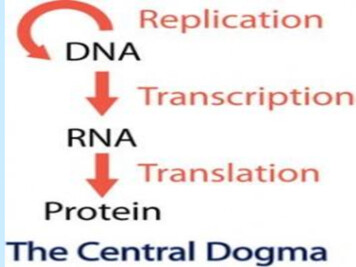
DNA provides the instructions for buildingvirtually every organism on earth!The protein, influenced by the environment and in somecases other genes, then produces the trait.CentralCentralDogma of Biology3
DNA Replication Process by which a cell makes another copyof its DNA Pairing Rules:– A T– G C The structure of DNA is adouble helix Shaped like a twisting ladder4
RNA Structure Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a type of nucleic acid Three parts1. Sugar group (ribose)2. Phosphate group3. Nitrogenous base AdenineGuanineUracilCytosineHow is RNA different from DNA?1.2.3.4.5.Ribose has –OH groupRNA has uracil instead of thymineRNA is a single strandDNA stays in nucleusRNA is made from DNA in nucleus and thenmoves to cytoplasm.5
HOW GENES WORK: AN OVERVIEWInside nucleusTRANSCRIPTIONThe sequence for a geneis copied from DNA to amiddleman moleculecalled mRNA.CytoplasmmRNADNATRANSLATIONThe sequence for agene, now encoded inmRNA, is used to directthe production of aprotein.GenesProtein moleculeNuclearporeGrandmother’scookbookCopying cookierecipe to index cardIndex cardwith recipeCombining andbaking ingredientChocolatechip cookiesTranscription Transcription is the process of using DNAas a template to synthesize RNA.– 1.) The DNA strands separate.– 2.) RNA Polymerase reads the DNA and buildsthe RNA strand.– 3.) Three types of RNA can be made:1. mRNA – messenger RNA2. rRNA – ribosomal RNA3. tRNA – transfer RNA6
Promoter sequence – specific sequences of DNA thatthe RNA Polymerase recognizes. Protein code – the DNA sequence that holds the geneticmaterial to create each protein. Termination sequence – Tells the RNA Polymerase tostop transcription.TRANSCRIPTIONDNA1 RECOGNIZE and BINDOnce RNA polymeraserecognizes a promoter site,it binds to one strand of theDNA and begins readingthe gene’s message.RNApolymerase3 TERMINATE2 TRANSCRIBEAs the DNA strand is processedthrough the RNA polymerase,the RNA polymerase builds asingle-strand copy of the gene,called the mRNA transcript.When the RNA polymeraseencounters a code signalingthe end of the gene, it stopstranscription and releasesthe mRNA transcript.RNApolymeraseRNApolymeraseTermination sitePromoter sitemRNA transcriptmRNAtranscriptUNWIND and REWINDAs the RNA polymerasemoves down the strand ofDNA, the helix unwinds sothat the DNA can be read. Atthe same time, the DNA thathas already been transcribedrewinds back to its originaldouble-helix form.Helix unwindsHelix unwinds4TailCapNon-protein-codingregions of mRNACAPPING and EDITINGBefore the mRNAtranscript can betranslated into a protein,a cap and tail are oftenadded for protection andto promote recognition,and non-coding sectionsare removed.mRNA transcript leaves nucleusto be translated into a protein.Translation Translation is the process of using the information inmRNA to direct protein synthesis. Relies on sets of 3 nucleotides called codons. Each codon codes for a specific amino acid.7
Translation Ribosome– 2 subunit non-membraneorganelle– Holds the mRNA and tRNAduring protein formation tRNA– Transfer RNA– Reads the codons and findsthe correct amino acids.Translation1. Initiation2. Elongation3. TerminationTranslation Initiation:1. Ribosome small subunit binds to mRNA2. Finds the start codon3. The tRNA binds to the codon and brings the firstamino acid4. The large subunit joins the small subunit andprotein formation can begin.8
Translation Elongation:1. A new tRNA arrives and reads the codon.2. The next amino acid arrives and binds to theprevious amino acid.3. The process continues until a polypeptide(protein) is formed.9
Translation Termination:– Occurs when the ribosome reaches a stop codon.– The two subunits come apart.– The mRNA is released.Summary of Protein Synthesis10
5.4 Not all DNA contains instructionsfor making proteins.The Proportionof the DNAThat Codes forGenes11
Introns and Exons Portions of the mRNA are removed beforetranslation.Mutations Point Mutation – change in a single nucleotide of theDNA sequence. Insertions and Deletions – changes one or morenucleotides in the DNA sequence.12
A “fastflush”response13
Transcription Transcription is the process of using DNA as a template to synthesize RNA. - 1.) The DNA strands separate. - 2.) RNA Polymerase reads the DNA and builds the RNA strand. - 3.) Three types of RNA can be made: 1. mRNA - messenger RNA 2. rRNA - ribosomal RNA 3. tRNA - transfer RNA