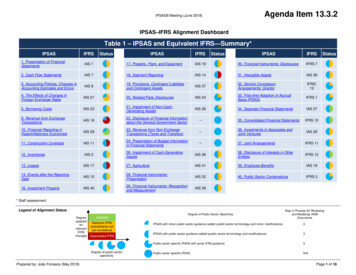
Transcription
Wider Fields: IFRS 9credit impairmentmodellingActuarial Insights Series2016Presented by Dickson Wong and NiniKung
Presenter BackgroundsDicksonWongNini Kung Actuary working in financial risk management: creditrisk, market risk, stress testing, regulatory capital,model validation PwC Singapore (previously PwC Australia) Actuary working in financial risk management:credit risk, stress testing, IAS 39 auditing,regulatory capital PwC Singapore (previously PwC South Africa)2
AgendaOverview of IFRS 9Stress Testing inBankingImpairment modellingapproachesWhat’s NextInsights inMalaysiaChallenges3
Banking for ActuariesThe Banking Industry presents a large opportunity for actuariesDemand forskill setRegulatoryChangeEducationCredit Risk Modelling rolesrequire similar modellingand programming skillsActuaries are applying theirskill set in different bankingareas: Pricing, Treasury,Stress TestingIntroduction of IFRS 9requires a significant increasein modelling skillsetNew Basel requirements areproviding more technicalrisk management andmodelling opportunitiesIntroduction of the Bankingspecialist courses as part ofthe Part 3 education systemFocus on wider fieldpresentations coveringbanking4
The Need for ProvisionsBanks issue loansto a variety ofcustomersScorecard modelsScore credit riskinessof customersA portion ofthe loans willdefaultDefaulted loansmay incur a lossto be written offExpected CreditLossLGD and EADmodelsPD modelsPredict defaultprobabilityBanks musthold provisionsfor these lossesECL PDxLGDxEADPredict final lossamountBest estimate forexpected lossesRequirements stipulated by Accounting StandardsIFRS 9IAS 39(current)(2018)5
Overview of IFRS 9In response to the financial crisis: Existing IAS 39 considered “too little too late” Regulators developed a new principles-basedStandards IFRS 9IFRS 9 contains 3 parts: P1: Classification and measurement P2: ImpairmentFocus P3: Hedge AccountingBanks are facing challenges with P2: Impairment: Sufficient data Complexity Impairment calculation Interpretation of requirements6
IFRS 9 P2 Impairments StagesStage 2Lifetime expectedcredit lossesStage 3Lifetime expectedcredit lossesChallenge:Lifetime ECLIFRS 9 Provision12 months expectedcredit lossesForward-looking adjustmentsPerformingYStage 1UnderperformingCredit impairedNNon-performingSignificant deterioration incredit risk since :Forward-looking7
IFRS 9 ECL Model ComponentsAlignment RequiredPDEAD12 months ForwardLookingAdjustment12 monthsForward LookingPDLife-time DefinitionLifetime ForwardLookingAdjustmentLifetime ForwardLooking PDAmortisationprofile12 month/Lifetime FLAdjustment12 month /Lifetime ForwardLooking EADBasel IIIFRS 912 Month PD12 Month PDLife-time PD termstructureCurrent balanceand limitCurrent collateralvalueLGDCurrent LGDBucket 1 and Bucket 2DefinitionsMacroeconomicModelIFRS 9 PD for allaccountsIFRS 9 EAD for allaccountsForecast collateralvalues12 month/Lifetime FLAdjustment12 month /Lifetime ForwardLooking LGDIFRS 9 LGD for allaccounts8
EADBasel IIIFRS 912 Month PD12 Month PDLife-time PDstructureLife-time DefinitionCurrent balanceand limit12 months ForwardLookingAdjustment12 monthsForward LookingPDLifetime ForwardLookingAdjustmentLifetime ForwardLooking PD12 month/Lifetime FLAdjustment12 month /Lifetime ForwardLooking EADAmortisationprofileCurrent collateralvalueForecast collateralvaluesCurrent LGD12 month/Lifetime FLAdjustmentLGDECL model component - PDBucket 1 and Bucket 2DefinitionsMacroeconomicModelAlignment RequiredPD12 month /Lifetime ForwardLooking LGDKey Challenge: Lifetime PD Term StructureMethod 1: Cohort Analysis Conditional for survival Kaplan-Meier estimate ofhazard functions to removepotential biases in the data𝑓𝑠,𝑿 𝑡𝑆𝑠,𝑿 𝑡 1ℎ 𝑡, 𝑠 𝑡, 𝑋 default hazard of a customer 𝑡months after observationℎ 𝑡, 𝑠 𝑡, 𝑿 𝑓𝑠,𝑿 𝑡 P(account defaults exactly 𝑡 monthsafter observation )Years From Origination𝑆𝑠,𝑿 𝑡 P(default does not occur within thefirst 𝑡 months)Marginal Default RateMarginal Default RateCumulative Default RateCumulative Default RateYears From OriginationConsiderations Requires a long time series of data (loan lifetime; segmentation and a full economic cycle Impacted by calendar based events (e.g. change in business policy) Develop lifetime PD given Stage 29IFRS 9 PD for allaccountsIFRS 9 EAD for allaccountsIFRS 9 LGD for allaccounts
EADBasel IIIFRS 912 Month PD12 Month PDLife-time PDstructureLife-time DefinitionCurrent balanceand limitECL model component - PDAmortisationprofile12 months ForwardLookingAdjustment12 monthsForward LookingPDLifetime ForwardLookingAdjustmentLifetime ForwardLooking PD12 month/Lifetime FLAdjustment12 month /Lifetime ForwardLooking EADCurrent collateralvalueForecast collateralvaluesCurrent LGD12 month/Lifetime FLAdjustmentLGDBucket 1 and Bucket 2DefinitionsMacroeconomicModelAlignment RequiredPD12 month /Lifetime ForwardLooking LGDKey Challenge: Lifetime PD Term StructureMethod 2: Regression Modelling Relationship between historical PDs and behavioural factorsAnalyse statistical significance and business intuitiveness of factorsLinear regression with logistic transformln𝑃𝑿1 𝑃𝑿 𝛽0 𝑝𝑖 1 𝛽𝑖 𝑋𝑖 ,where𝑃𝑿 𝑃 𝐷𝑿 1 and𝐷𝑿 0 𝑖𝑓 𝑑𝑒𝑓𝑎𝑢𝑙𝑡 𝑑𝑜𝑒𝑠 𝑛𝑜𝑡 𝑜𝑐𝑐𝑢𝑟.1𝑖𝑓 𝑑𝑒𝑓𝑎𝑢𝑙𝑡 𝑜𝑐𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑠Cox regression for survival function𝑝𝑆𝑿 𝑡 𝑒 ℎ0𝛽 𝑋𝑡 𝑒 𝑗 1 𝑗 𝑗where ℎ0 𝑡 is the empirical hazard function, estimatednon-parametrically. Under this model, the probabilityof default at outcome period 𝑡 is given by:𝑃𝑿 𝑡 1 𝑆𝑿 𝑡 .Considerations Consider transforms of variables to ensure stationarity Different regression formats (linear regression with logistic transform preferred by most banks) Term structure developed through including a month on book variable10IFRS 9 PD for allaccountsIFRS 9 EAD for allaccountsIFRS 9 LGD for allaccounts
EADBasel IIIFRS 912 Month PD12 Month PDLife-time PDstructureLife-time DefinitionCurrent balanceand limitECL model component - PDAmortisationprofile12 months ForwardLookingAdjustment12 monthsForward LookingPDLifetime ForwardLookingAdjustmentLifetime ForwardLooking PD12 month/Lifetime FLAdjustment12 month /Lifetime ForwardLooking EADCurrent collateralvalueForecast collateralvaluesCurrent LGD12 month/Lifetime FLAdjustmentLGDBucket 1 and Bucket 2DefinitionsMacroeconomicModelAlignment RequiredPD12 month /Lifetime ForwardLooking LGDKey Challenge: Lifetime PD Term StructureMethod 3: Transition matricesTransition matrixFrom/toAAABBB Cumulative Default RateB-CCCDMarginal Default Rate60%30%50%25%AAAAAA87.0% 0.0%0.0%0.1%0.0%40%20%BBB 0.0% 73.9% % 52.6% 11.4% 7.5%0.1%9.1% 43.9% 26.4%Source: S&P Average One-Year Transition Rates For GlobalCorporates By Rating Modifier (1981-2014) (%)BBB B BCCC/CConsiderations Extrapolation assumes a memoryless process Alternative method considered where cohort data is not available11IFRS 9 PD for allaccountsIFRS 9 EAD for allaccountsIFRS 9 LGD for allaccounts
EADBasel IIIFRS 912 Month PD12 Month PDLife-time PDstructureLife-time DefinitionCurrent balanceand limitAmortisationprofile12 months ForwardLookingAdjustment12 monthsForward LookingPDLifetime ForwardLookingAdjustmentLifetime ForwardLooking PD12 month/Lifetime FLAdjustment12 month /Lifetime ForwardLooking EADCurrent collateralvalueForecast collateralvaluesCurrent LGD12 month/Lifetime FLAdjustmentLGDECL model component - EADBucket 1 and Bucket 2DefinitionsMacroeconomicModelAlignment RequiredPD12 month /Lifetime ForwardLooking LGDKey Challenge: Lifetime EADAmortising products(e.g. term loans and mortgages)Loan Repayment PatternEstimating prepaymentsPrepaymentContractual repayment𝑃𝑟𝑒𝑝𝑎𝑦𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑡 ��𝑖𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝐵𝑎𝑙𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒𝑛Expected Out. BalanceActual Out. Balance𝑃𝑟𝑒𝑝𝑎𝑦𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑡 𝛼 𝑚𝛽𝑖 𝑥𝑖 𝑖 1𝛾𝑗 𝑦𝑗 𝜖𝑖𝑗 1𝛽𝑖 coefficient for macroeconomic variable𝑥𝑖 macroeconomic variable𝛾𝑗 coefficient for loan level characteristic𝑦𝑗 loan level characteristicConsiderations Loan level characteristics (product type, borrower income level, loan-to-value) Macroeconomic economic variables (interest rates, unemployment rates, GDP, inflation) Additional loan features such as refinancing12IFRS 9 PD for allaccountsIFRS 9 EAD for allaccountsIFRS 9 LGD for allaccounts
EADBasel IIIFRS 912 Month PD12 Month PDLife-time PDstructureLife-time DefinitionCurrent balanceand limit12 months ForwardLookingAdjustment12 monthsForward LookingPDLifetime ForwardLookingAdjustmentLifetime ForwardLooking PD12 month/Lifetime FLAdjustment12 month /Lifetime ForwardLooking EADAmortisationprofileCurrent collateralvalueForecast collateralvaluesCurrent LGD12 month/Lifetime FLAdjustmentLGDECL model component - EADBucket 1 and Bucket 2DefinitionsMacroeconomicModelAlignment RequiredPD12 month /Lifetime ForwardLooking LGDKey Challenge: Lifetime EADRevolving products(e.g. credit card, line of credit)123 200180%75%68%74%200285%80%81%200388%81%200481% Development patternprojection techniquesTime to default0Origination year0Projected utilisation rate𝑂𝑢𝑡𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑛𝑔 ��𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝐴𝑚𝑜𝑢𝑛𝑡𝑡Time to defaultOrigination yearHistorical utilisation rate𝑈𝑡𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑠𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑅𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑡 123 0481%79%75%74% Considerations Aggregation of data into homogenous risk groups Stability of development patterns and representativeness of historical experience Alternative methods such as developing regression models13IFRS 9 PD for allaccountsIFRS 9 EAD for allaccountsIFRS 9 LGD for allaccounts
EADBasel IIIFRS 912 Month PD12 Month PDLife-time PDstructureLife-time DefinitionCurrent balanceand limitBucket 1 and Bucket 2DefinitionsMacroeconomicModelAlignment RequiredPD12 months ForwardLookingAdjustment12 monthsForward LookingPDLifetime ForwardLookingAdjustmentLifetime ForwardLooking PD12 month/Lifetime FLAdjustment12 month /Lifetime ForwardLooking EADAmortisationprofileCurrent collateralvalueForecast collateralvaluesCurrent LGD12 month/Lifetime FLAdjustmentLGDECL model component – Forward Looking12 month /Lifetime ForwardLooking LGDKey Challenge: Forward LookingLeveraging Existing Stress Testing Process:Current Stress Testing Process:Additional modification:Determine Stress ScenariosUnbiased best estimateforecastMonte Carlo Simulationfor MEV forecastEconomic Linkage ModelLinkages for non-stressperiodsLinkages for areas notcoveredDetermine Stress OutcomesSensitivity and backtestingOverlay FrameworkConsiderations Lack of data required to build a statistical model Require multiple year of Macro-economic forecast Shift in mentality from stress testing to forward looking14IFRS 9 PD for allaccountsIFRS 9 EAD for allaccountsIFRS 9 LGD for allaccounts
ECL model component – TriggersKey Challenge: Relative and Absolute Credit QualityRelative credit qualityAbsolute credit qualityDoes the financial asset meet the definitionof “low credit risk” at the reporting date?noHas the credit risk increased significantly since initialrecognition? If more than 30 days overdue yes (rebuttable presumption) Financial asset is below investment grade- likely yes but significance of increasehas to be determinednoyesyesCredit-impairedDoes the financial asset meet the credit-impaired definition(same definition as in IAS 39)?no1Performing2Deterioration of credit qualityyes3Credit-impaired 12-Months-EL EL over Lifetime EL over Lifetime(interest revenue on gross basis)(interest revenue on gross basis)(interest revenue on net basis)15
ECL model component – TriggersKey Challenge: Definition of significant increase in credit riskQuantitative Triggers:Changes in credit ratings Drop in external credit ratings Drop in internal credit ratingsChanges in internal priceindicators of credit riskChanges in external marketindicators Significant deterioration of loan tovalue ratio Breaches in financial covenants Drop in borrower’s bond prices Increase in credit default swapprices for borrowerChanges in operating resultsOther qualitative inputs Actual or expected decline inrevenues/margins Working capital deficiencies Trading suspension of listed shareson exchange Litigations likely to have materialimpact Profit warningsQualitative Triggers:Changes in business, financialor economic conditions Industry downturn Increase in unemployment rates16
Challenges to comply with IFRS 9Banks face a number of challenges in meeting their desired level of IFRS9 complianceIFRS 9 RequirementsChallengesDesired level ofcomplianceRange of data requirementsSophisticated modellingexpectationsExpert judgement baseddecisionRegulatory expectationLack of dataCorrect modelsExpert JudgementPeoples and skillsImplementationUncertainty inexpectationSystems andprocessesInterpretation ofthe StandardTimelinesCross-borderexposureHolistic governance processIndustry PracticeAuditor expectationHigh qualityimplementation17
Results from Latest SurveyThere is still a significant amount of work to be done in APAC.Understanding IFRS 9Detailed Design14201215108106452000% - 20%20% - 40%40% to 60%60% - 80%80% - 100%0%0% - 20%20% - 40% 40% to 60% 60% - 80% 80% - 100%Model DevelopmentTest / Implementation2025201515101055000%0% - 20%20% - 40% 40% to 60% 60% - 80% 80% - 100%0%0% - 20%20% - 40% 40% to 60% 60% - 80% 80% - 100%18
Results from Latest SurveyThe industry view currently varies on the best approach to adopt when itcomes to incorporating forward looking in their models25Approach to incorporate Forward LookingAPACOthers20151050Bottom-up modelBottom-up expert Top-down quantitativelydriven enhancements tojudgement basedassessed overlayPD, LGD and EADenhancements to PD,LGD and EADTop-down expertjudgement overlayA combination of theaboveTo be determined19
Further Reading and Q&AIFRS 9: Impairment, Globalbanking industry benchmarkAvailable on RequestIFRS 9: Expected Credit reditlosses.pdf20
IFRS 9 12 Month PD Bucket 1 and Bucket 2 Definitions IFRS 9 ECL Model Components IFRS 9 EAD for all accounts Amortisation profile Current balance EAD and limit 12 month / Lifetime Forward Looking EAD 12 month/ Lifetime FL Adjustment IFRS 9 LGD for all accounts Forecast collateral values Current LGD Lifetime FL 12 month / Lifetime Forward .