Transcription
WHITE PAPERIFRS 17Implementation:A Solution Approachfor InsurersAbstractThe International Accounting Standards Board's(IASB) International Financial Reporting Standard17 (IFRS 17) for insurance contracts takes effectfrom January 1, 2021. With little time to prepare,insurance companies must quickly get their acttogether to understand the implementationchallenges and develop a project plan forimplementation. The new standard impacts notonly the pro ts, equity, insurance obligations, and nancial reporting of the insurers but also theactuarial models and IT architecture. This isbecause of the changes suggested in the standardaround consistent accounting treatment ofinsurance contracts, measurement of insurancecontracts, and disclosure requirements.An ideal solution approach to addressing IFRS 17requirements would be to use an agileimplementation methodology for enhanced exibility and communication between crossfunctional teams. In addition, automating theprocess of grouping contracts, deploying analyticsto determine onerous contracts, and building astrong database for granular reporting can helpinsurers drive timely compliance.
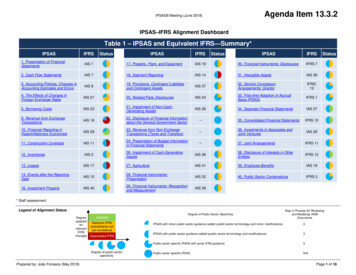
WHITE PAPERIFRS 17 Contract Accounting andMeasurement RequirementsIFRS 17 requires companies to report insurance contracts onthe balance sheet as a total of the ful lment cash ows (usingcurrent estimates of the amount, timing, and uncertainty ofcash ows and discount rates) and contractual service margin(CSM) at each reporting date. It also requires them todistinguish between groups of contracts expected to makepro ts and groups of onerous contracts. The expected pro t forproviding insurance coverage is recognized in the pro t or loss(P&L) statement over time. Once the company determines thatlosses are expected from onerous contracts, the losses areaccounted for in the P&L statement. In addition, IFRS 17requires insurers' to disclose additional information to enablethe users to understand the risks that company faces fromissuing insurance contracts. So what are the IFRS 17implementation challenges and possible solutions for insurers?IFRS 17 Implementation ChallengesInsurers face two major implementation challenges in additionto incurring implementation costs.1) Short run up to implementation: Given that the newstandard is to be implemented on or before January 1,2021, now is the time for insurers to start with an impactanalysis and prepare a project plan for the next three years.The project plan should consider aspects such as gapanalysis, budgeted costs, IT architecture changes, resourceplanning, data collection, data mapping, data conversion,and storage issues.2) Data gathering and analysis: IFRS 17 will have a majorimpact on the way data is collected, stored, and analyzed.Currently, under IFRS 4, insurers store data according tothe insurance product groups for measurement purposes.IFRS 17 requires insurers to analyze the data with suf cientgranularity to identify and consistently segregate the groupsof contracts right at inception. This helps determine andaccrete interest on CSM, and store information on inceptiondates and the coverage period of the group of contracts,historical cash ows, discount rates, and risk adjustmentsfor each group of contracts. This level of granularity willhave a major impact on actuarial modelling and nancialreporting systems, as well as supporting data requirements.
WHITE PAPERAgile is the Way ForwardA structured implementation approach can help insurers drive asmooth and timely implementation of IFRS 17.Methodology: Considering the complexity involved, theagile methodology is best suited for project implementationrather than the traditional waterfall approach. Theimplementation project will likely span three years andinvolve changes in the accounting systems, actuarialmodels, and IT systems along with multiple milestones. Anagile methodology enables insurers to be exible andinteractive across different phases of implementation tobetter overcome the implementation challenges. Agile alsoreduces the risk of developing wrong solutions and speedsup delivery.Technical requirements: The existing insurance databasemight not be equipped to meet IFRS 17 requirements due tothe complex calculations and reporting requirements of itsbuilding blocks, as well as the need to maintain discountingrates and historical data. This means insurers will need tochange the data architecture to include the requirements ofIFRS 17. The database management systems must becapable of maintaining a high level of granularity, grouping,calculation, and data reporting requirements. The databaseshould also be exible and ef cient to support the reportingchanges as well as integrate necessary automation toreduce overall costs involved. Each insurance contract is tobe tested at inception to check if it is onerous or not, andaccordingly grouped for measurement. Arti cial intelligence(AI) and robotics can play a major role here. They can helpanalyze each contract for accurate grouping andmeasurement to determine if it is onerous or not, and alsoef ciently handle the huge volume of data.Resource planning: Implementing IFRS 17 requiresexperts from different functions to work together. Theactuarial function and risk management teams need to workwith the nancial reporting function to ensure that complexcalculations required for CSM and Solvency II are processedaccurately and in a timely manner. Resource planning mustbe carried out at the initial stages to include the expertsfrom various functions who need to work together. Expertsfrom different teams such as actuarial, nance, IT, andlearning and development need to come together tounderstand the changes required and plan the
WHITE PAPERimplementation strategy. These experts will rst need toundergo training to understand the expectations andrequirements of IFRS 17. They will also need to perform agap analysis to identify the changes required in the existingprocesses and systems, while collaborating to nalize theimplementation plan. With the agile methodology, thetechnical and functional teams can easily come together toimplement the plan through enhanced and goal-orientedcollaboration.Benefits Outweigh Costs with IFRS 17Implementation of IFRS 17 requires changing the existing nancial systems of insurers and gathering new information,which in turn, requires signi cant investments in terms of time,money, and effort. However, once implemented, IFRS 17addresses a number of inadequacies in IFRS 4 and existinginsurance accounting practices such as inconsistent accountingpolicies across insurers, usage of inappropriate discount ratesand older estimates of the contracts, as well as riskadjustments in insurance contracts that are not explicit. Inaddition, it addresses challenges such as non-recognition ofonerous insurance contracts in a timely manner and inadequatecomparability of nancial information.The result: IFRS 17 will put insurers on a rmer footing todrive long term growth.ReferencesI]The Accountant, IASB Issues IFRS 17 in Insurance Accounting Shake Up, May 2017, accessedDecember 2017, es-ifrs-17-in-insuranceaccounting-shake-up-5817902
WHITE PAPERAbout The AuthorRajesh PatilRajesh Patil is the Finance andAccounting Delivery Lead withthe Business Process Servicesunit at TCS. He has 17 years ofexperience in the insurance,finance, and accounting domain,and has worked for major globalinsurance organizations in theindustry. Rajesh currentlymanages the statutory andregulatory reporting function foran Australian financial servicesclient for TCS. He is a postgraduate in commerce fromPune University and holds aDipIFRS degree from Associationof Chartered CertifiedAccountants Institute, UK.ContactVisit the Insurance Service page on www.tcs.comEmail: global.insurance@tcs.comSubscribe to TCS White PapersTCS.com RSS: http://www.tcs.com/rss feeds/Pages/feed.aspx?f wFeedburner: http://feeds2.feedburner.com/tcswhitepapersTata Consultancy Services is an IT services, consulting and business solutionsorganization that delivers real results to global business, ensuring a level ofcertainty no other firm can match. TCS offers a consulting-led, integrated portfolioof IT and IT-enabled, infrastructure, engineering and assurance services. This isdelivered through its unique Global Network Delivery ModelTM, recognized as thebenchmark of excellence in software development. A part of the Tata Group,India’s largest industrial conglomerate, TCS has a global footprint and is listed onthe National Stock Exchange and Bombay Stock Exchange in India.For more information, visit us at www.tcs.comAll content / information present here is the exclusive property of Tata Consultancy Services Limited (TCS). The content / information contained here iscorrect at the time of publishing. No material from here may be copied, modified, reproduced, republished, uploaded, transmitted, posted or distributedin any form without prior written permission from TCS. Unauthorized use of the content / information appearing here may violate copyright, trademarkand other applicable laws, and could result in criminal or civil penalties. Copyright 2018 Tata Consultancy Services LimitedTCS Design Services I M I 01 I 18About Tata Consultancy Services Ltd (TCS)
Benefits Outweigh Costs with IFRS 17 Implementation of IFRS 17 requires changing the existing nancial systems of insurers and gathering new information, which in turn, requires signi cant investments in terms of time, money, and effort. However, once implemented, IFRS 17 addresses a number of inadequacies in IFRS 4 and existing