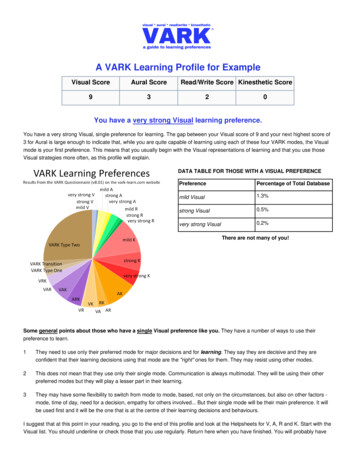
Transcription
International Journal of Learning and Teaching Vol. 4, No. 2, June 2018The VARK Learning Style of the UniversityStudent in Computer CourseVeena Khongpit, Krich Sintanakul, and Thanyarat NomphonkrangFaculty of Technical Education, Department of Computer Education,King Mongkut’s University of Technology North Bangkok, ThailandEmail: kveena@live.com, krich.s@fte.kmutnb.ac.th, thanyaratn@kmutnb.ac.thAbstract—The achievement of teaching and learning processdoesn’t come solely from the teacher or supporting material.It requires the coordination and motivation of the learner aswell. If the teacher realizes the ability of the learner andprovide appropriate learning environment, the learner willbe able learn in accordance with their skills and learningstyle. The VARK learning style process can categorize thelearner’s abilities in to 4 groups: 1) Visual (V), 2) Aural (A),3) Read/Write (R) and 4) Kinesthetic (K). The learner willbe able to learn from direct practice. When the learner hasmany learning options according to their potential, this willlead to motivation of learning. III.The learning style means the physical characteristic,thought and feeling that an individual uses for stablyacknowledging, reacting and interacting with theenvironment. It is important and affects the learningmotivation and efficiency of the learner [3]. There aremany scholars who study the learning style in order tobuild learning motivation in many forms [4].A. Learning Style of KolbThis learning style is applied from the ExperientialLearning Theory that was obtained from the humandevelopment and learning theory of the leading scholarsfrom 20th century including John Dewey, Kurt Lewin,Jean Piaget, William James, Carl Jung, Paulo Freire, CarlRogers and others. The learning style of Kolb divides thelearning style by enquiring the learners into 4 forms:diverging, assimilating, converging and accommodating.It’s found that many people do not know their learningstyle.Index Terms—VARK, learning style, computer education,higher education, computer courseI.INTRODUCTIONIt’s essential for university students to develop theirself-learning potential in order to apply for learningprocess of career. For learning management, the teacherhas to develop teaching style that helps enhance themaximum potential of the learner and support the selfimprovement of the learner in order to achieve thedetermined objectives. There are many factors affectingthe learning organization such as knowledge and abilityof teaching and teaching technique. The successfullearning process also depends on the learner. The learnermust have prominent learning goals that can be appliedwith their career [1]. The researcher also teaches acomputer course. It’s found that the computer learners arereally different. This is normal for university students thatare mostly experienced adults with high individuality.The teaching for university is therefore required goodpreparation that is suitable to the ability of individualdifference [2]. Therefore if the teacher realizes theabilities, existing knowledge, readiness, interests anddiligence of each learner, it will be beneficial to properteaching and potential enhancement organization for thelearner. This method can stimulate and enhance thelearner’s learning.II.B. Learning Style of Peter Honey and Alan MumfordThe concept of this learning style uses the learningstyle and cycle of Kolb to create a survey to categorizethe learners into 4 groups: reflectors, theorists,pragmatists and activists.C. Learning Style of FlemingThe concept of Fleming learning style categorizes thelearning style according to the learner’s perception into 4types called VARK:1) Visual (V): The learner is interested in the visualmaterial. Therefore the teacher must present thecommunicating text.2) Aural (A): The learner who is good at listening suchas lecture, group discussion, conversation and websitechat.3) Read/Write (R): The learner is good at readingdocuments, books, and material by his/her own thensummary what has been read.4) Kinesthetic (K): The learner is good at using his/herexperience and directly practices it.It can be concluded that the learning cycle of Kolbfocuses on the learner to diverge, assimilate, convergeand accommodate their knowledge and transfer theirexperience. However, the learning cycle of Peter HoneyRESEARCH OBJECTIVEThe objective of this study was to the VARK learningstyle of students at Sripatum University-ChonburiCampus and Burapha University in computer course.Manuscript received May 10, 2017; revised November 21, 2017. 2018 International Journal of Learning and Teachingdoi: 10.18178/ijlt.4.2.102-106RELATED THEORY102
International Journal of Learning and Teaching Vol. 4, No. 2, June 2018and Alan Mumford focuses on behavior trend and makethe learner to learn in process in order for them to gainexperience then review and conclude the obtainedexperience which leads to learning planning [5]. Thecategorization of learner type of VARK focuses on thelearner’s abilities, promoting the motivation of the learnerthrough the contents and activities. The VARK method oflearning categorization uses a downloadable survey fromwww.vark-learn.com. The results can be concluded in ashort period. Therefore, this method is widely used inmany countries by university students [6].For this reason, the research selected the VARKlearning style to categorize the learners. It is anappropriate approach for development of teachingmaterial, activities and environment to suit the ability ofuniversity computer students and build their motivation.3) If n1-n2 s meaning the learner has singlepreference of learning style. If the result is less, followstep 4.4) If n2-n3 s meaning the learner has bi-modalpreference. If the result is less, follow step 5.5) If n3-n4 s meaning the learner has tri-modalpreference. If the result is less, it means the learner hasfour-modal preference.F. Single Preference of Learning StyleUse the total scores of VARK of the learner tocompare with Table III.TABLE III. THE STRENGTH OF SINGLE PREFERENCETotalScoresD. Example of VARK QuestionnaireThe VARK questionnaire categorizes the learningquestionnaire in accordance with the perception of thelearners. The Fleming survey contains 16 questions with4 multiple choices. The example of questions andanswers of VARK survey is shown in Table I:TABLE I.QuestionAnswer16-2122-2728-3233 EXAMPLE OF VARK QUESTIONNAIREYou are going to choose food at a restaurant or cafe.You would:V Look at what others are eating or look at picturesof each dish.A Ask the waiter or friends to recommend choices.R Choose from the descriptions in the menu.K Choose something that you have had there before. A R 103 A2 R2K1) Calculate value of stepping distance 12) Calculate the learning style:V (10) – A (3) 7 whereas 7 13) Mr.A has V learning style. He has a very strongvisual preference.Example 2: Mr.B has VARK scores 27.12 6 5 4KKRVA1) Calculate value of stepping distance 22) Calculate the learning style:K (12) – R (6) 6 whereas 6 23) Mr.B has K learning style. He has a strongkinesthetic preference.TABLE II. USE SCORES OF STEPPING DISTANCE TO CALCULATE THESCORE LEVEL OF LEARNING STYLE.G. Bi-modal Preference of Learning StyleExample 3: Mr.C has VARK scores 16.My stepping distance is12345RSteps of learning style calculation:1) Calculate the total scores of VARK to find thestepping distance from Table II. S is used for steppingdistance.2) Sort the VARK points in order from the maximumto minimum. Use n1, n2, n3, n4 respectively. 2018 International Journal of Learning and Teaching VUse the total scores to find the stepping distance fromthe Table II:Table II Use scores of stepping distance to calculatethe score level of learning style.The total of my four VARK scores is14-2122-2728-3232 The strength of single preferenceStrongMildMultimodalPreference PreferenceNo singlepreference4-52-30-15-63-4 36-74-5 47-85-6 5Use the highest VARK scores of each learner tointerpret as shown in the examples 1-4:Example 1: Mr.A has VARK scores 17.E. Interpretation of VARK Learning StyleThe interpretation of VARK learning stylequestionnaire is done by collecting the answers from anindividual learner and interpreted into ability point ofVARK learning style [7]:Calculating the total scores of VARK:VVeryStrongPreference6 7 8 9 5K 3V 3AMr.C has bi-modal preference of learning style: R andK.H. Tri-modal Preference of Learning StyleExample 4: Mr.D has VARK scores 22.103
International Journal of Learning and Teaching Vol. 4, No. 2, June 201887 VA 6 R(V), 2) Aural (A), 3) Read/Write (R) and 4) Kinesthetic(K) as shown on Fig. 2 and Fig. 3.1KMr.D has tri-modal preference of learning style: V, Aand K.I.Four-modal Preference of Learning StyleThe learner has 4 styles of learning: V, A, R and KJ.Learning DesignThe design of learning material in accordance with thelearning style of the learners is done by making thelearners to do the questionnaire in order to categorize thegroup of learners into 4 styles shown on Fig. 1.Figure 2. Online Survey of VARKFigure 3. Example of VARK questionnaireFigure 1. VARK Learning StyleV.The 1st style is visual. The learner is interested invisual material. Using images and colorful content shallstimulate the learners.The 2nd style is aural. The learners of this group like todiscuss and exchange ideas. The suitable learning style islecture and group discussion.The 3rd style is read/write. The learners of this grouplike to read and learn from documents, books andcontents by themselves and summarize what they haveread.The 4th style is kinesthetic. The learners of this grouplike applying the theory into practice [8].IV.RESEARCH RESULTA. Basic Information of the Learner1) There are 145 responders with 55.9% of male and44.1% of female as shown on Fig. 4.RESEARCH METHODOLOGYA. Finding of the Learning Style of the Learners1) Population and sample groupThe sample group of the project consists of 145university students who have registered for computercourse. There are 81 male and 64 female students.2) Research ToolsAn online questionnaire in accordance with the VARKlearning style in Thai language using Google Form. Thequestionnaire is divided into 2 parts. Part of thequestionnaire consists of 1) basic information of theresponders, student ID, name-last name, gender,university, faculty and academic year; 2) questionnaire ofVARK learning style consisting of 16 questions and 4multiple choices. The VARK learning processcategorizes the learner’s abilities in to 4 groups: 1) Visual 2018 International Journal of Learning and TeachingFigure 4. Learner’s sexFigure 5. Learner’s university104
International Journal of Learning and Teaching Vol. 4, No. 2, June 2018Student’s preference2) The learners are from Sripatum UniversityChonburi Campus, Thailand (51%) and BuraphaUniversity, Thailand (49%) as shown on Fig. 5.3) The learners are studying Information Technology,Business Computer and Multimedia Technology 68.3%,25.5% and 6.2% respectively.4) There’s 54.5% of the learners from the 3rd year,18.6% from the 4th year, 16.6% from the 1st year and 9%from the 2nd year. There are other learners as well suchas from external learning scope which is account of 1.3%.B. VARK Learning StyleThe VARK learning style questionnaire resultsthe sample group: The learners chose V learning907 points, A learning style 771 points, R learning757 points and K learning style 911 points. Thepoints are 3,346 points as shown on Fig. .[1][2][3][4][5][6][7]Figure 7. Learning styleThe categorization of learner abilities is shown onTable IV.[8][9]TABLE IV. THE MODEL OF LEARNERTotal15 2018 International Journal of Learning and .344.832.073.454.145.520.68RESEARCH CONCLUSIONREFERENCESConsidering the learning style from the total number of145 responders, it is found that:1) There are 45 learners with single preference oflearning style or 31.03%.2) There are 77 learners with bi-modal preference oflearning style or 53.1%.3) There are 22 learners with tri-modal preference oflearning style or 15.17%.4) There are 1 learner with four-modal preference oflearning style or 0.7% as shown on Fig. 7.Learning styleVTotal58172313136157356811) The learning style of most of the computer learnersis bi-modal preference [9]. There are 53.11% of them.This means the learners are competent in 2 styles: VK,AK, VA, VR, RK and AR especially the VK styles.2) Most of the learners are competent of VK learningstyle or 15.86%. The learners virtually learn from thedemonstration of the teacher and practice in real on thecomputer.3) The research result is found that the teachingmaterial design should be done by creating creativeactivities and environment in consistent with the learningabilities of the learners in order to promote theirmotivation and perception. This approach will enhancethe learning achievement of the learners.Figure 6. Total points of VARK questionnaireStudent’s preferenceSingleLearning 4105Bureau of Education Standard of Ratchathani University.(November 2016). Good Practice Guide Teaching Techniques inHigher Education. [Online]. Available: http://assu.rtu.ac.thS. Rattanathongkom. (November 2016). Learning literature ams.kku.ac.th/aalearnO. Punto and M. Tiantong, “Comparative efficiency ofclassification of VARK learning style using data miningtechniques,” Journal of Industrial Technology Ubon RatchathaniRajabhat University, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 1-11, January 2014.C. Tantarangsee, “Learning styles of full time suan suanandharajabhat university students: A case of general education course;English for communication and study skills,” Fund ResearchReport, Suan Suanandha Rajabhat University, Bangkok, Thailand,2011.S. Wichadee, “Learners’ learning styles: The perspectives fromthe theory of experiential learning,” Executive Journal, v
university, faculty and academic year; 2) questionnaire of VARK learning style consisting of 16 questions and 4 multiple choices. The VARK learning process categorizes the learner’s abilities in to 4 groups: 1) Visual (V), 2) Aural (A), 3) Read/Write (R) and 4) Kinesthetic as shown on Fig. 2 and Fig. 3. Figure 2. Online Survey of VARK : Figure 3. Example of VARK questionnaire . V. R: ESEARCH .