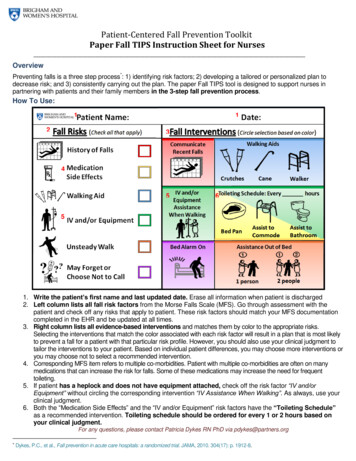
Transcription
FALL PREVENTIONCOMPARE AND CONTRAST SELECT HOSPITALS
MICAH FALLS WITH INJURY2017 - .89 falls per 1000 patients2018 - .76 falls per 1000 patients
WE’RE ALL DOING IT Universal Fall Precautions Bed low and lockedPartial side rails upW/C wheels lockedNon-slip footwearClean and dry surfacesUncluttered areasOrientation to surroundings Call light education Handrails in bathroomPersonal item within reachAppropriate lightingEncourage use of sensory andambulatory items
WE’RE ALL DOING IT Risk assessment upon admission Identifiers on doorway and wristbands Ongoing risk assessment throughout visit Risk Categories (High, Moderate, Low)Environmental factors (clutter, dry floors,lighting) Educate patient and family of risk andinterventions Communication of fall risk across shiftsand departments
FALL RISK ASSESSMENTS Morse Fall Scale STEADI Fall Risk Assessment Observation, judgment, critical thinking with a Fall Risk Assessment tool JACCK AND JILL – Pediatric Fall Injury Risk Assessment - ABCS
DIFFERENT APPROACHES Hourly/Scheduled rounding Every patient vs Moderate to HighRisk Patients Fall Assessment vs Fall AssessmentPLUS Fall Injury Risk Assessment Adult onlyvs Pediatric and OBassessments as well
MISCELLANEOUS ADDITIONS Safe patient handling trainingAppropriately functioning equipmentEarly and progressive mobility if appropriateEducate on activity levelDemonstrate (teach back) use of call lightTransfer time-outList of High Risk medicationsAll employees allowed and expected to assist high risk patients if needed
STORYBOARD COMMON THEMES All CAHs reduced their falls between 15% and 100% Common themes across storyboards were: Safety CultureFront line staff participation in program developmentUp front and ongoing education for staffInterdisciplinary Falls TeamRoot Cause AnalysisDaily Focus on Falls prevention at Safety HuddlesReview each event after it happensHardwire behavior
STORYBOARD METHODS Safety Trumps Privacy initiativePharmacy review of high risk medicationsSupervisor oversight of admission fall risk assessment completionEnvironment – night lights, beds against wallsEquipment – floor mats, wheelchair anti-tip barsPost fall huddlePurposeful Rounding (Person, Plan, Position, Personal Hygiene, Pain, Presence) The 6 P’sPurposeful Rounding Built into EHR
STORYBOARD METHODS Rounding clocksEducation blitz for proper bed alarm settingsEducate ancillary departments on bed alarm activationReport high risk patients at change of shift huddle“Days without a fall” awarenessStock gait belts in bedside table for convenient useEquipment availability and additional trainingVisual cues to identify high risk patients
STORYBOARD METHODS No Pass ZoneGood Catch ProgramSite visits by MHA or other Falls ExpertsRCA on 100% of falls with injuryVarious Falls Risk assessmentsSystem-wide Harms CommitteeFrontline staff work group reviewed falls data and completed gap analysis
QUESTIONS?Group Discussion
Universal Fall Precautions Bed low and locked Partial side rails up W/C wheels locked Non-slip footwear Clean and dry surfaces Uncluttered areas Orientation to surroundings Call light education Personal item within reach Appropriate lighting Encourage use of sensory and ambulatory items Handrails in bathroom