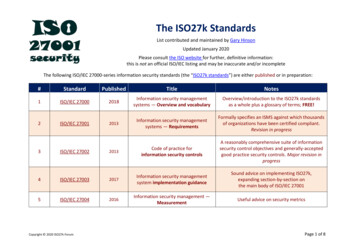
Transcription
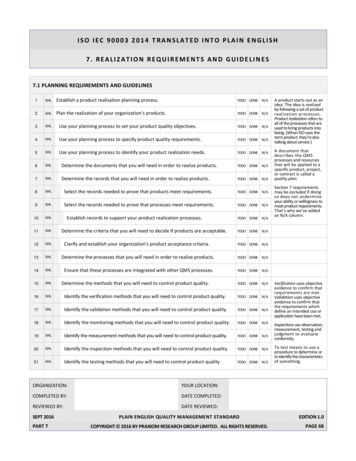
ISO IEC 90003 2014 TRANSLATED INTO PLAIN ENGLISH7. REALIZATION REQUIREMENTS AND GUIDELINES7.1 PLANNING REQUIREMENTS AND GUIDELINES1SHLEstablish a product realization planning process.TODO DONE N/A2SHLPlan the realization of your organization’s products.TODO DONE N/A3SHLUse your planning process to set your product quality objectives.TODO DONE N/A4SHLUse your planning process to specify product quality requirements.TODO DONE N/A5SHLUse your planning process to identify your product realization needs.TODO DONE N/A6SHLDetermine the documents that you will need in order to realize products.TODO DONE N/A7SHLDetermine the records that you will need in order to realize products.TODO DONE N/A8SHLSelect the records needed to prove that products meet requirements.TODO DONE N/A9SHLSelect the records needed to prove that processes meet requirements.TODO DONE N/A10SHL11SHL12SHLClarify and establish your organization's product acceptance criteria.TODO DONE N/A13SHLDetermine the processes that you will need in order to realize products.TODO DONE N/A14SHLEnsure that these processes are integrated with other QMS processes.TODO DONE N/A15SHL16SHLIdentify the verification methods that you will need to control product quality.TODO DONE N/A17SHLIdentify the validation methods that you will need to control product quality.TODO DONE N/A18SHLIdentify the monitoring methods that you will need to control product quality.TODO DONE N/A19SHLIdentify the measurement methods that you will need to control product quality.TODO DONE N/A20SHLIdentify the inspection methods that you will need to control product quality.TODO DONE N/A21SHLIdentify the testing methods that you will need to control product quality.TODO DONE N/AEstablish records to support your product realization processes.Determine the criteria that you will need to decide if products are acceptable.Determine the methods that you will need to control product quality.ORGANIZATION:YOUR LOCATION:COMPLETED BY:DATE COMPLETED:REVIEWED BY:DATE REVIEWED:SEPT 2016PART 7TODO DONE N/AA product starts out as anidea. The idea is realizedby following a set of productrealization processes.Product realization refers toall of the processes that areused to bring products intobeing. (When ISO uses theterm product, they’re alsotalking about service.)A document thatdescribes the QMSprocesses and resourcesthat will be applied to aspecific product, project,or contract is called aquality plan.Section 7 requirementsmay be excluded if doingso does not undermineyour ability or willingness tomeet product requirements.That’s why we’ve addedan N/A column.TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/APLAIN ENGLISH QUALITY MANAGEMENT STANDARDCOPYRIGHT 2016 BY PRAXIOM RESEARCH GROUP LIMITED. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.Verification uses objectiveevidence to confirm thatrequirements are met.Validation uses objectiveevidence to confirm thatthe requirements whichdefine an intended use orapplication have been met.Inspections use observation,measurement, testing andjudgment to evaluateconformity.To test means to use aprocedure to determine orto identify the characteristicsof something.EDITION 1.0PAGE 68
ISO IEC 90003 2014 TRANSLATED INTO PLAIN ENGLISH7. REALIZATION REQUIREMENTS AND GUIDELINES22SHL23SHL24SHL25SHLDetermine the resources that you will need to realize products.Produce product realization planning outputs.TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/APrepare outputs that are suitable and consistent with your organization's methods.Develop your product realization processes.TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/AA note to section 7.1says that you may usethe approach describedin section 7.3 to developyour product realizationprocesses (if you find ithelpful).7.1.1 USE LIFE CYCLE MODELS TO PLAN WORK26SHDSelect suitable life cycle models to manage software design and development.TODO DONE N/A27SHDConsider the nature of your project when you select models and methods.TODO DONE N/A28SHDConsider project size and complexity when you select models and methods.TODO DONE N/A29SHDConsider tasks and activities when you select models and methods.TODO DONE N/A30SHDConsider the nature of your product when you select models and methods.TODO DONE N/A31SHDConsider risks and safety concerns when you select models and methods.TODO DONE N/A32SHD33SHDMake sure that design specifications address potential software failure conditions.TODO DONE N/A34SHDSpecify requirements that expect immunity from potential failure conditions.TODO DONE N/A35SHDSpecify requirements that expect a response to potential failure conditions.TODO DONE N/A36SHD37SHD38SHD39SHD40SHD41SHD42SHDConsider software products that could cause injury, damage, or destruction.Use suitable life cycle models to plan and perform software design and development.Use suitable life cycle models to plan your processes, activities, and tasks.Use your life cycle models to develop software development plans.Use your plans to describe the software products that will be developed.Specify who will develop them and when this work will be done.Use your plans to describe how software products will be developed.Use your plans to describe how products will be assessed.ORGANIZATION:YOUR LOCATION:COMPLETED BY:DATE COMPLETED:REVIEWED BY:DATE REVIEWED:SEPT 2016PART 7TODO DONE N/ASection 7.1.1 says:“ISO 9001:2008 isintended for applicationirrespective of the lifecycle models used and isnot intended to indicatea specific life cycle modelor process sequence.”ISO 9001:2008 doesnot force you to use aparticular software lifecycle model or expectyou to follow a particularprocess sequence. Youmay use any suitableapproach.Section 7.1.1 says:“Design and developmentcan be an evolutionaryprocess and proceduresmay therefore need to bechanged or updated asthe project progresses,after consideration ofchanges to relatedactivities and tasks.”TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/APLAIN ENGLISH QUALITY MANAGEMENT STANDARDCOPYRIGHT 2016 BY PRAXIOM RESEARCH GROUP LIMITED. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.EDITION 1.0PAGE 69
ISO IEC 90003 2014 TRANSLATED INTO PLAIN ENGLISH7. REALIZATION REQUIREMENTS AND GUIDELINES43SHD44SHDUse your plans to describe how products will be maintained.Use suitable life cycle models to perform processes, activities, and tasks.TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/A7.1.2 CARRY OUT SOFTWARE QUALITY PLANNINGPlan software projects, products, and contracts.45SHDTODO DONE N/A46SHD47SHDClarify product oriented quality needs and requirements.TODO DONE N/A48SHDClarify process oriented quality needs and requirements.TODO DONE N/A49SHD50SHD51SHD52SHD53SHD54SHDUse procedures and instructions that respect the scope of your quality manual.TODO DONE N/A55SHDUse procedures and instructions that acknowledge any official exclusions.TODO DONE N/A56SHDAddress the need to have project-specific procedures and instructions.TODO DONE N/A57SHDAddress the need to have project-specific software test specifications.TODO DONE N/A58SHD59SHD60SHD61SHD62SHDEmploy reusable tools, methods, and life cycle models.TODO DONE N/A63SHDEmploy reusable programming language conventions.TODO DONE N/AClarify quality needs and requirements.TODO DONE N/AFigure out how QMS should be tailored.TODO DONE N/AFigure out how QMS can be applied to projects, products, and contracts.Address quality needs and requirements.TODO DONE N/AAddress the need to have suitable procedures.TODO DONE N/AAddress the need to have appropriate QMS procedures and instructions.Use suitable project-specific test plans, designs, cases, and procedures.Use suitable unit, integration, system, and acceptance testing procedures.Address the need to have effective configuration management procedures.Address the need to employ reusable assets.YOUR LOCATION:COMPLETED BY:DATE COMPLETED:REVIEWED BY:DATE REVIEWED:PART 7TODO DONE N/AYour quality planningactivities will generatea quality plan. Your plancould be a single document,several documents, or partof another larger document.Also see ISO/IEC 12207section 6.3.1 on projectplanning and section 7.2on software support.ISO/IEC 12207 treatsquality planning andproduct developmentplanning as a singleplanning activity whichresults in the creation of aproject management plan.TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/ASee section 7.5.3, below.TODO DONE N/AORGANIZATION:SEPT 2016TODO DONE N/AThe purpose of yourquality planning shouldbe to figure out howto apply your qualitymanagement system toyour software projects,products, and contracts.PLAIN ENGLISH QUALITY MANAGEMENT STANDARDCOPYRIGHT 2016 BY PRAXIOM RESEARCH GROUP LIMITED. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.EDITION 1.0PAGE 70
ISO IEC 90003 2014 TRANSLATED INTO PLAIN ENGLISH7. REALIZATION REQUIREMENTS AND GUIDELINESEmploy reusable software libraries and D72SHD73SHD74SHDEstablish specific software review methods and procedures.TODO DONE N/ASee section 7.3.4, below.75SHDEstablish specific software verification methods and procedures.TODO DONE N/ASee section 7.3.5, below.76SHDEstablish specific software validation methods and procedures.TODO DONE N/ASee section 7.3.6, below.77SHD78SHDAddress the need to manage and control resource changes.TODO DONE N/A79SHDAddress the need to manage and control schedule changes.TODO DONE N/A80SHDAddress the need to manage and control contractual changes.TODO DONE N/A81SHD82SHD83SHD84SHD85SHD86SHDTODO DONE N/AAddress the need to perform monitoring activities.TODO DONE N/AAddress the need to carry out suitable measurement activities.Address the need to approve process outputs.TODO DONE N/AMake people responsible for approving outputs for subsequent use.Address the need to use competent personnel.Clarify your software training needs and requirements.TODO DONE N/ASchedule suitable training before skills are needed.TODO DONE N/ATeach people how to use tools and techniques.TODO DONE N/AAddress the need to control software quality.TODO DONE N/AAddress the need to manage and control changes.TODO DONE N/AAddress the need to maintain suitable records.TODO DONE N/AEstablish software quality objectives.See section 4.2.4, below.TODO DONE N/AClarify limited quality objectives for limited-purpose software.Plan the testing of this software to ensure that it fulfils its limited purpose.Define each software development stage.TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/ADefine each design and development stage before you begin work on that stage.YOUR LOCATION:COMPLETED BY:DATE COMPLETED:REVIEWED BY:DATE REVIEWED:PART 7TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/AORGANIZATION:SEPT 2016TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/APLAIN ENGLISH QUALITY MANAGEMENT STANDARDCOPYRIGHT 2016 BY PRAXIOM RESEARCH GROUP LIMITED. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.EDITION 1.0PAGE 71
ISO IEC 90003 2014 TRANSLATED INTO PLAIN ENGLISH7. REALIZATION REQUIREMENTS AND GUIDELINESEstablish criteria that determines when each project stage starts and finishes.87SHD88SHD89MAYInclude or refer to generic or project, product, or contract-specific procedures.TODO DONE N/A90SHDInclude or refer to your product development plans, procedures, and policies.TODO DONE N/A91MAY92MAY93MAY94MAYInclude all related plans and procedures.TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/AReview plans for projects, products, and contracts.TODO DONE N/AAsk all participating organizations to review your software quality plans.Approve plans for projects, products, and contracts.TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/AAsk all participating organizations to agree before work is carried out.For more information,see ISO/IEC 25010:2011on systems and softwarequality requirements andevaluation (SQuaRE), andsystem and softwarequality models; ISO/IEC25001:2007 on systemsand software qualityrequirements andevaluation (SQuaRE),and planning andmanagement; andISO/IEC 16326:2009 onlife cycle processes, andproject management.TODO DONE N/A7.2 CUSTOMER REQUIREMENTS AND GUIDELINES7.2.1 DETERMINE REQUIREMENTS RELATED TO PRODUCTSDetermine your customers' requirements.95SHLTODO DONE N/A96SHLIdentify your customers’ product requirements.TODO DONE N/A97SHLIdentify your customers’ delivery requirements.TODO DONE N/A98SHLIdentify your customers’ post-delivery requirements.TODO DONE N/A99SHL100SHL101SHLIdentify customers’ contractual requirements.TODO DONE N/A102SHLIdentify supplementary service requirements.TODO DONE N/A103SHLIdentify customers’ recycling requirements.TODO DONE N/A104SHLIdentify customers’ final disposal requirements.TODO DONE N/A105SHLDetermine your intended use requirements.TODO DONE N/A106SHLDetermine your legal product requirements.TODO DONE N/AIdentify customers’ warranty requirements.TODO DONE N/AIdentify customers’ maintenance requirements.TODO DONE N/AORGANIZATION:YOUR LOCATION:COMPLETED BY:DATE COMPLETED:REVIEWED BY:DATE REVIEWED:SEPT 2016PART 7PLAIN ENGLISH QUALITY MANAGEMENT STANDARDCOPYRIGHT 2016 BY PRAXIOM RESEARCH GROUP LIMITED. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.EDITION 1.0PAGE 72
ISO IEC 90003 2014 TRANSLATED INTO PLAIN ENGLISH7. REALIZATION REQUIREMENTS AND GUIDELINES107SHLIdentify product requirements imposed by regulators.TODO DONE N/A108SHLIdentify product requirements imposed by statute.TODO DONE N/A109SHLDetermine your organization's requirements.TODO DONE N/A7.2.1.1 DETERMINE CUSTOMER-RELATED REQUIREMENTSEstablish methods for managing software requirements.110MAYTODO DONE N/A111MAY112MAY113MAYEstablish methods for identifying your customer's software requirements.TODO DONE N/A114MAYEstablish methods for clarifying the customer's operational environment.TODO DONE N/A115MAYEstablish methods for identifying your organization's software requirements.TODO DONE lish methods for ensuring that requirements are clearly specified.TODO DONE N/A123MAYEstablish methods for ensuring that misunderstandings are avoided.TODO DONE N/A124MAYEstablish methods for defining terms and providing background information.TODO DONE N/A125MAYEstablish methods for ensuring that specifications facilitate product acceptance.TODO DONE N/A126MAY127MAYEstablish methods for developing software requirements.TODO DONE N/AEstablish methods for identifying software requirements.TODO DONE N/AEstablish methods for clarifying your organization's operational environment.Establish methods for allocating software requirements.TODO DONE N/AEstablish methods for allocating requirements for system specifications.Establish methods for allocating requirements between software and hardware.Establish methods for ensuring that interface specifications are formulated.Establish methods for formulating software requirements.Establish methods for evaluating software requirements.Establish methods for evaluating software prototypes or demonstrations.YOUR LOCATION:COMPLETED BY:DATE COMPLETED:REVIEWED BY:DATE REVIEWED:PART 7TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/AORGANIZATION:SEPT 2016TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/APLAIN ENGLISH QUALITY MANAGEMENT STANDARDCOPYRIGHT 2016 BY PRAXIOM RESEARCH GROUP LIMITED. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.EDITION 1.0PAGE 73
ISO IEC 90003 2014 TRANSLATED INTO PLAIN ENGLISH7. REALIZATION REQUIREMENTS AND GUIDELINESEstablish methods for reviewing software requirements.128MAY129MAY130MAY131MAYEstablish methods for agreeing on software requirements.TODO DONE N/A132MAYEstablish methods for obtaining official customer approval.TODO DONE N/A133MAYEstablish methods for authorizing changes in requirements.TODO DONE Y142MAY143MAY144MAY145MAYClarify relevant operational environments.TODO DONE N/A146MAYClarify legal obligations for your software.TODO DONE N/A147MAY148MAY149MAYClarify software reliability requirements.TODO DONE N/A150MAYClarify software efficiency requirements.TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/AEstablish methods for reviewing requirements and recording results.Establish methods for approving software requirements.TODO DONE N/AEstablish methods for tracking changes in software requirements.Establish methods for tracking changes during iterative development.Establish methods for controlling software requirements.Establish methods for controlling changes to software requirements.Establish methods for controlling changes during development projects.Establish methods for amending contracts whenever requirements change.Establish methods for tracing software requirements.TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/AEstablish methods for tracing requirements throughout development life cycle.Establish methods for tracing software requirements to final software products.Manage your organization's software requirements.TODO DONE N/ASee section 7.5.3, below.TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/AClarify requirements for your software.TODO DONE N/AClarify regulatory and statutory requirements.TODO DONE N/AClarify required software characteristics.TODO DONE N/AYOUR LOCATION:COMPLETED BY:DATE COMPLETED:REVIEWED BY:DATE REVIEWED:PART 7TODO DONE N/ATODO DONE N/AORGANIZATION:SEPT 2016TODO DONE N/APLAIN ENGLISH QUALITY MANAGEMENT STANDARDCOPYRIGHT 2016 BY PRAXIOM RESEARCH GROUP LIMITED. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.EDITION 1.0PAGE 74
ISO IEC 90003 2014 TRANSLATED INTO PLAIN ENGLISH7. REALIZATION REQUIREMENTS AND GUIDELINES151MAYClarify software functionality requirements.TODO DONE N/A152MAYClarify software maintainability requirements.TODO DONE N/A153MAYClarify software traceability requirements.TODO DONE N/A154MAYClarify software portability requirements.TODO DONE N/A155MAYClarify software usability requirements.TODO DONE N/A156MAYClarify software security requirements.TODO DONE N/A157MAYClarify software safety requirements.TODO DONE N/A158MAYSpecify requirements for your software.TODO DONE N/A159MAYSpecify requirements for software that will be developed as part of a contract.TODO DONE N/A160MAYSpecify requirements for software that will be produced for a market sector.TODO DONE N/A161MAYSpecify requirements for software that will be used to support processes.TODO DONE N/A162MAYSpecify requirements for software that will be embedded in a system.TODO DONE N/A163MAYApprove requirements for your software.TODO DONE N/A164MAYControl requirements for your software.TODO DONE N/ANow that you've seen a sample of our approach, please considerpurchasing ISO IEC 90003 2014 Translated into Plain English (Title 75).If you purchase our publication, you'll find that it's detailed, exhaustive,and easy to understand. We guarantee it. Title 75 is 146 pages longand comes in both pdf and MS Word file formats.ORGANIZATION:YOUR LOCATION:COMPLETED BY:DATE COMPLETED:REVIEWED BY:DATE REVIEWED:SEPT 2016PART 7PLAIN ENGLISH QUALITY MANAGEMENT STANDARDCOPYRIGHT 2016 BY PRAXIOM RESEARCH GROUP LIMITED. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.EDITION 1.0PAGE 75
of another larger document. Also see ISO/IEC 12207 section 6.3.1 on project planning and section 7.2 on software support. ISO/IEC 12207 treats quality planning and . 73 SHD Address the need to control software quality. TODO DONE N/A 74 SHD Establish specific software revi ew methods and procedures. TODO DONE N/A See section 7.3.4, below.