Transcription
CALIFORNIA GROCERS ASSOCIATIONHazardous Waste Presentationpresented byClif McFarlandandLeila BrudererMay 22, 2013
Hazardous WasteWhy should grocers and otherretailers care about hazardouswaste?– Hazardous waste regulations applyto grocers and other retailers
Big Box andHome Improvement Stores
Drug Stores
Grocery Stores
Enforcement Actions Wal-Mart– Wal-Mart To Pay 27.6 Million InCalifornia Dumping Case Target– Target to pay 22.5 million to settlehazardous-waste dumping case
Enforcement Actions Home Depot– Home Depot Pays 10 Million To SettleHazardous Waste Case Walgreens– Walgreens to Pay 16.57 Million forHazardous Waste Disposal Violations
Enforcement Actions CVS– CVS retail giant must pay 13.75million in fines over waste disposalviolations Save-Mart– Save Mart pays 2.6M in WasteComplaint
Hazardous Waste EPA increased focus on grocer/ retailers as well. EPA looking at potential regulations/ revisions toregulations this year
Hazardous WasteFocus of Enforcement Storage, handling,transportation and disposalof returned, damaged,recalled, used, anddiscarded products that arehazardous materials.
Hazardous WasteFocus on the Larger Players More Waste at issueSets an exampleTrophyAttention will spread to others in theindustry
Hazardous WasteBackground RCRA (1976)Hazardous Waste regulations (1980)Not designed with retailers in mindParadox: Household waste exemptionKey definitions: Waste, hazardouswaste
Hazardous WasteWaste or Solid Waste Seemingly simple: any discardedmaterial But, in the end, very slippery concept Storage: No longer used for itsintended purpose Recycling: Legitimate or Sham Subject to reverse distribution
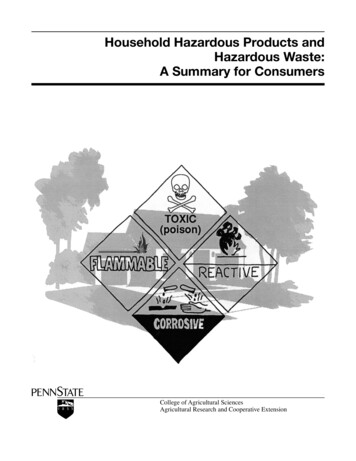
Hazardous WasteHazardous Waste Listed veToxic
Hazardous WasteBasic Triage Perfect World: Life is good Real World: Returns, breaks, shelf life Question 1: Subject to reversedistribution? Question 2: If not, is it hazardous?
Hazardous WasteIgnitableIgnitable wastes are wastes thatcan easily catch on fire andsustain combustion. Can beliquids, gas or solid.Examples: lighter fluid, charcoal,rubbing alcohol, nail polish, nail polishremover, motor oil, etc.
Hazardous WasteCorrosiveCorrosive wastes are acidic or alkaline(basic) wastes that can readily corrodeor dissolve materials they come intocontact with.Examples: drain cleaner, ammonia, lime/scaleremovers.
Hazardous WasteReactiveReactive wastes are wastes thatreadily explode or undergoviolent reactions.Examples: pool chemicals, chlorine,hair dyes, bleach, hydrogen peroxide.
Hazardous WasteToxicToxic wastes are wastes thatcause deleterious health orenvironmental effects.Examples: soaps, fertilizers, batteries,insect repellant, cosmetics, antifreeze,pharmaceuticals.
Hazardous WasteFundamental Problem Generator Duty to determine if waste ishazardous waste Based on testing Or, based on process knowledge No process knowledge Too many products/waste streams
Hazardous WasteThree Main Challenges1. Identifying products that arehazardous materials2. Understanding when a hazardousmaterial becomes a hazardous waste3. Training employees to managehazardous waste
Hazardous WasteIdentifying hazardous materials Why? These are the products that arehazardous waste when discarded. There are tens of thousands of commonretail products that are hazardousmaterials under applicable federal andCalifornia law.
Hazardous WasteIdentifying hazardous materials:––––MSDSManufacturer3rd party serviceAisles or categories of products
Hazardous WasteMSDS– Available from manufacturer– Proprietary information
Hazardous WasteManufacturer Contract with manufacturer Disclosure
Hazardous WasteThird Party Services Information for a fee Risk involved
Hazardous WasteAisles or categories Household cleanersCosmeticsPersonal hygienePesticides/fertilizersPhoto processingPharmacy
Hazardous WasteHazardous material to hazardous waste Hazardous waste:– A waste that exhibits any of the characteristicsof hazardous waste or a waste that is listed inthe regulations.(22 CCR §66261.3)
Hazardous WasteUniversal Wastes Not fully regulated CA includes: certain types of batterieselectronic devicesmercury-containing equipment,lampscathode ray tubescathode ray tube glassaerosol cans(22 CCR §66261.9)
Hazardous WastePharmacy Wastes RCRA hazardous waste– P-listed (Warfarin, Nicotine)– U-listed (Warfarin, Lindane),– Characteristic (ignitable, corrosive, toxic,reactive)- e.g. vaccines containingthimerosal
Hazardous WastePharmacy Wastes Non-RCRA (California only)hazardous waste (covered byMedical Waste Management Act)– Segregate into containers labeled“incinerate only”, transport by medicalwaste transporter Medical waste: sharps, vials fromlive vaccines
Hazardous WasteHazardous Material to HazardousWaste When it is discarded and/or can no longerbe used for its intended purpose. (See 22CCR §66261.2)
Hazardous WasteReturned Products Options? Donation – Must ensure thatproducts are being used, and notdiscarded. Surplus material
Hazardous WasteSurplus Materials Exempt from hazardous wasteregulations Requirements:––––––No major damage to the containerNot leaking and/or deterioratedMinor dings, dents, scratches are okayProduct label in good conditionProduct has real valueEnd user will use material how it iscommonly used
Hazardous WasteDamaged Products What kind of damage? Can the product be re-sold (onsiteor to 3rd party)? Donated? (condition of label,leaking/deteriorated)
Hazardous WasteObsolete Products Return to manufacturer to be usedor reclaimed? (Potentially excludedrecyclable material (“ERM”))
Hazardous WastePast shelf life Return to manufacturer? (ERM) Donation if still valuable? Disposal as hazardous waste?
Hazardous WasteSpills/Releases Spilled hazardous materials arewastes Need to consider condition ofcontainer to determine how tomanage unspilled material. Empty containers
Hazardous WasteManaging Hazardous WasteKey: Ease of Implementation1. Written hazardous wastemanagement program2. Hazardous waste managementarea3. Spills/releases
Hazardous WasteHW Managemenet Program Employee training: Only thoseemployees whose responsibilitiesinclude hazardous material/wastemanagement– Initial training upon hire– Periodic refresher training
Hazardous WasteHW Management Program Quick reference materials– Signs in hazardous waste managementarea– Signs near spill cleanup materials– Signs in Store returns area
Hazardous WasteHW Management Area Designated area for storage ofhazardous waste absorbent anddamaged/leaking product (segregationof incompatible wastes) Sealable containers for storage ofhazardous waste
Hazardous WasteHW Management Area Multiple containers to keepincompatible wastes separated Labels for containers to recordcontents, CA EPA ID number,accumulation start date Arrange for transport/disposal ofhazardous waste
Hazardous Waste One option -- Bucket system Bucket colors identify thehazardous waste properties(e.g., red for flammables)
Spills
Hazardous WasteSpills/Releases Characterize the waste (cleanup mayvary based upon type of hazardouswaste) Have spill cleanup materials readilyavailable (absorbent, broom, PPE,gloves) Training for employees on how torespond to a spill
Hazardous WasteHazardous Materials Business Plans Who is required to have one?– Owner/operator of a facility that handles ahazardous material that has a quantity at onetime during the reporting year equal to orgreater than 55 gallons, 500 pounds, or 200cubic feet at standard temperature andpressure.– Exemption for hazardous materials containedsolely in a consumer product for distribution to,or use by, the general public.
Hazardous WasteWhat is a HMBP Inventory of hazardous materials at facility Emergency response plans in event of areportable release of a hazardous material Training for all employees in safetyprocedures in event of a reportablerelease of a hazardous material
Hazardous WasteHMBP Submission Local Certified Unified Program Agency(“CUPA”) Forms are available online from mostCUPAs After initial submission, need to reviewannually for changes.
Hazardous WasteInspections Yes Review local CUPA procedures tounderstand how often they inspect
Hazardous WasteQuestions/Comments?
Hazardous Waste Corrosive Corrosive wastes are acidic or alkaline (basic) wastes that can readily corrode or dissolve materials they come into contact with. Examples: drain cleaner, ammonia, lime/scale removers. Hazardous Waste Reactive Reactive wastes are wastes that readily explode or undergo violent reactions.