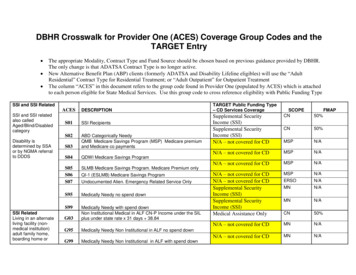
Transcription
ACES & OPIATESConnecting the Impact ofAdverse Childhood Experienceson Addiction
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) Study Adverse Childhood Experiences Categories Measuring the correlation of health risk behaviors anddiseases to exposure to childhood emotional, physical,or sexual abuse and household dysfunction.(American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 1998)
Study Design Largest scientific research study of its kind Initiated in 1995 Requested participation of 26,000 consecutive patientsseeking medical treatment at Kaiser Permanente inSan Diego ; 71% agreed Over 17,500 participants mostly middle-classAmerican Adults
What is an Adverse Childhood Experience?1. Physical Abuse2. Emotional Abuse3. Sexual Abuse4. Incarcerated Relative5. Mother treated violently6. Substance Abuse7. Mental Illness8. Loss of a Parent9. Physical Neglect10. Emotional Neglect(Adverse Childhood Experiences, Overcoming ACEs in Alaska, 2015)
Toxic StressToxic Stress occurs when a child experiences strong and/orprolonged adversity, including trauma, parental neglect orexposure to violence.Many of these experiences have been closely associated withparental or caregiver use of various substances includingalcohol, opioids or amphetamines.This can result in a child with attachment problems, a lessdeveloped and smaller brain, and fewer neuralconnections which can lead to cognitive deficits(Adverse Childhood Experiences, Overcoming ACEs in Alaska 2015)
How Does Exposure to Toxic Stress EffectBrain Development ? It can result in smaller brain size. It can disrupt the development of brain circuits. The individual then develops a low threshold for stressand becomes overly reactive to adverse experiencesthroughout the lifetime.(Adverse Childhood Experiences, Overcoming ACESs in Alaska, 2016)
What Else Effects Brain Development ?Introduction of foreign chemicals into the maternalblood stream, including alcohol, drugs andenvironmental factors.Introduction of maternally produced adrenal steroidsproduced by external stressIn addition to one time external stressors that produceadrenal responses, some mothers may be in aconstant state of hyper-arousal.
What causes a state of maternalhyper-arousal? Domestic violenceLow socio-economic statusLack of social supportHistory of violence and abuse as a childPoor parenting skills
The higher the number of incidentsof childhood exposure to abuseand violence the greater the risk ofan early death.
Childhood Exposure to Toxic Stress Effects in Adulthood(American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 1998)
Childhood Exposure to Toxic Stress Effects in Adulthood(Finkelhor& Dziuba-Leatherman, 1994)
How is Toxic Stress Different ThanOther Types of Stress?
Now that we have an understandingof how ACE’s affect our brains let’stalk about how drugs affect ourbrains and behaviors.
Brain OverviewBrain Stem- Controls Basic Functions of Life. Heart Rate BreathingCerebral Cortex See, hear ,feel, taste Thought Processing, Problem Solving,Decision MakingLimbic System The reward/pleasure part of the brain Activated by life sustaining activities andalso by abusive drugs Responsible for emotions both positive andnegative
DopamineMost drugs of abuse target the brain’sreward system by flooding it withdopamine Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that activatesthe natural reward system Drugs such as heroin overstimulate the rewardsystem producing a euphoric effect The use of this drug is then reinforced leadingto high levels of tolerance and addiction( Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: the Science of Addiction, National Institute on Drug Abuse, 2016)
Within Us“In our detailed study of over 17,000 middle-classadults of diverse ethnicity, we found the compulsiveuse of nicotine, alcohol and injected street drugsincreases proportionately in a strong graded, dose –response manner that closely parallels the intensity ofadverse life experiences during childhood Ourfindings are disturbing to some because they imply thatthe basic causes of addiction Lie Within Us and theway we treat each other, not in drug dealers ordangerous chemicals.”(Felitti VJ The Origins of Addiction, Evidence from the Childhood Experience Study, 2004)
500% increase in adult alcoholism is related in a strong, gradedmanner to (four or more) adverse childhood experiencesFelitti, VJ, The Origins of Addiction: Evidence from the Adverse Childhood Experiences Study, 2004
Male child with an ACE score of six has a 4,600%Increased likelihood of becoming an injection drug user.Felitti, VJ, The Origins of Addiction: Evidence from the Adverse Childhood Experiences Study, 2004
What Does ACES Look Like in Alaska?Source: Alaska data from the 2013 Alaska Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, AK DHSS, Divisionof Public Health, Section of CDPHP
What are the most common ACEsamong Alaska Adults?
How do ACEs compare between Men& Women in Alaska?
What data is there about the Bristol Bay Region?Researchers from the Nurses’ Health Study II “ found that women who were exposed to trauma and had at least four PTSDsymptoms were 60% more likely to have a heart attack or stroke than women who reported having no l)
How childhood trauma affectshealth across a lifetime
Treatment, Prevention and Resilience Treatment for addictions can be social,therapeutic or medically assisted. Prevention activities generally includeeducation, systemic awareness activities,early screening and community organization. Creation of protective factors to buildresilience, positive coping skills, clinical care,Spirituality, positive family and social supports,positive role models and healthy inter-personalrelationships.
(Adverse Childhood Experiences, Overcoming ACEs in Alaska, 2015) What is an Adverse Childhood Experience? 1. Physical Abuse 2. Emotional Abuse . Mental Illness 8. Loss of a Parent 9. Physical Neglect 10. Emotional Neglect . Toxic Stress Toxic Stress occurs when a child experiences strong and/or prolonged adversity, including trauma, parental .