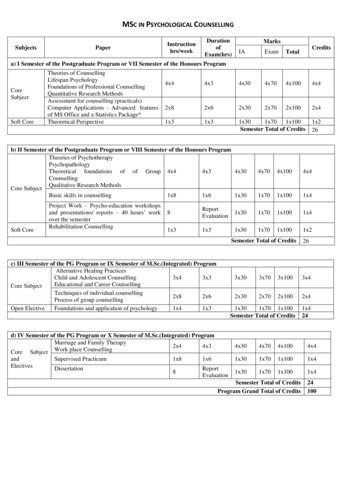
Transcription
FACT SHEET 3: CounsellingWHAT IS COUNSELLING?Counselling is when we meet with someone who is a qualifiedcounsellor trained in listening and talking. In counsellingwe can talk about things that might be worrying us or aboutchanges we might want to make in our life. This is done in astructured way.Counselling can be helpful for people with mental healthproblems. It is also helpful for people looking for ways ofmanaging better in their lives.Counselling is confidential.It is a safe place. In counselling youare free to talk about your thoughtswithout being criticised.People trained in counselling areusually psychologists. They can alsobe from other professions.Copyright Scope (Vic) Ltd 20081
FACT SHEET 3: Counselling2TYPES OF COUNSELLING:All counsellors use the same skills for listening. There aredifferent types of Counselling used.The type of counselling depends on the counsellors training.It also depends on what may be the best way to help.There are a lot of things that are the same in all types ofcounselling. The differences are in what they pay attention to.These are the most used and helpful types of counselling andwhat they pay most attention to;Cognitive Behaviour TherapyYour thinkingInterpersonal TherapyYour relationshipsPsychodynamic TherapyYour pastFamily TherapyYour familySolution Focussed TherapyYour strengthsPerson Centred TherapyWhat you payattention toCopyright Scope (Vic) Ltd 2008
FACT SHEET 3: Counselling3WHAT DO PEOPLE GO TO COUNSELLING FOR?:People go to counselling for help with many issues such as;DepressionStressRelationship difficultiesAnxiety and fearsDealing with loss or traumaSelf esteemIntimacy and sexualityconcernsDealing with conflictCopyright Scope (Vic) Ltd 2008
FACT SHEET 3: Counselling4Coping with health problemsProblems with alcohol anddrug usePersonal growthCareer planningLiving with a disabilityAnger controlPainCopyright Scope (Vic) Ltd 2008
FACT SHEET 3: Counselling5WHAT WILL HAPPEN IN COUNSELLING?Counselling may occur as -Counselling sessions are usually 1 hourCounselling sessions can occur weekly,fortnightly or monthly depending on whatworks best for you.One to oneAs a couple or familyAs a group of people with thesame concernsCopyright Scope (Vic) Ltd 2008
FACT SHEET 3: Counselling6In the first session you will;Meet the counsellorLearn about what will happen incounsellingHave a chance to ask questions aboutcounsellingTalk about the things you want help within counsellingCopyright Scope (Vic) Ltd 2008
FACT SHEET 3: Counselling7In other sessions you may;Make goals that you want to achieve incounsellingAnswer assessment questions that helpthe counsellor plan with you how to besthelp you.Answer assessment questions that helpyou to understand how you may bemeeting your goals in counselling.Be given things to read or look at.Be given activities to do between sessionssuch as keeping a diary.REMEMBERYou can always end counselling when youwant to.You are always able ask questions aboutwhat is happening in the counsellingprocess.Copyright Scope (Vic) Ltd 2008
FACT SHEET 3: Counselling8HOW DOES COUNSELLING HELP?Counselling can help you in these ways:To learn new skills and better ways to copeTo understand what you are experiencingTo learn new ways of looking at what ishappening to youTo solve problems and make decisionsTo learn about your strengths and how touse themCopyright Scope (Vic) Ltd 2008
FACT SHEET 3: Counselling9PREPARING FOR COUNSELLINGYou don’t have to but it can be helpful to think about and do thefollowing before you go to counselling:What do you want from counselling?What are the things that are important foryou to talk about in counselling?Are you ready to talk a lot about yourself,your feelings and your experiences?Practice thinking about your feelings andhow to describe them.Practice noting how much you feel at anygiven time. Perhaps you could give yourfeelings a rating from a little to a lot.Copyright Scope (Vic) Ltd 2008
FACT SHEET 3: Counselling10COUNSELLING AND DISABILITY:People with disabilities may experience any of the issues thatpeople go to counselling for.Also people with disabilities sometimes have more stressfulthings in their lives than people without disabilities. Some ofthese stressful things may be:Not being able tocommunicateNot being understoodHaving few friendsNot having much to doNot feeling in controlBeing discriminated againstCopyright Scope (Vic) Ltd 2008
FACT SHEET 3: Counselling11Unhappy life experiencesNot feeling included in thingsMoney problemsHealth problemsFrustrationsCounselling can be one way to help cope with these stressful things.REMEMBER that everyone is different.Just because there are a lot of stressfulthings in someone’s life, it doesn’t meanthat that person needs counselling.Copyright Scope (Vic) Ltd 2008
FACT SHEET 3: Counselling12WHERE TO GO TO FOR COUNSELLING:You can first speak to your doctor who will be ableto refer you to a psychologist.You can also find a psychologist by contacting theAustralian Psychological Society referral service.In an emergency you can do one of these things Call your DoctorCall Lifeline if youlive in Australiaon 13 11 14Go to a hospitalPeople who are deaf or have a hearing orspeech impairment can call Lifeline throughtthe National Relay Service (NRS);TTY users phone 13 36 77 then ask for theLifeline number which is 13 11 14.Speak and Listen (speech - to - speech relay)users phone 1300 555 727 then ask for theLifeline number which is 13 11 14.Internet relay users connect to the NRSwebsite (http://www.relayservice.com.au)and then ask for the Lifeline number whichis 13 11 14.Copyright Scope (Vic) Ltd 2008
FACT SHEET 3: CounsellingThis Fact Sheet is linked to the work of theBridging Project. The Bridging Project isbeing undertaken by Scope in collaborationwith the Centre for Developmental DisabilityHealth Victoria, Monash University. Themission of the Bridging Project is to progressthe knowledge and resource base to ensurethat people with complex communication andmental health needs have access to qualityservices. The project has two complementarystreams, Building Evidence (increasing theevidence base in relation to individuals withcomplex communication and mental healthCopyright Scope (Vic) Ltd 200813needs through research and related activities)and Building Capacity (building the capacityof services to address the mental health needsand preferences of individuals with complexcommunication needs). The project is designedaround the needs of people who are 18 yearsor older.More information regarding The BridgingProject can be found at the Scope Web Page,http://www.scopevic.org.au
Answer assessment questions that help you to understand how you may be meeting your goals in counselling. Be given things to read or look at. Be given activities to do between sessions such as keeping a diary. REMEMBER You can always end counselling when you want to. You are always able ask questions about what is happening in the counselling .