Transcription
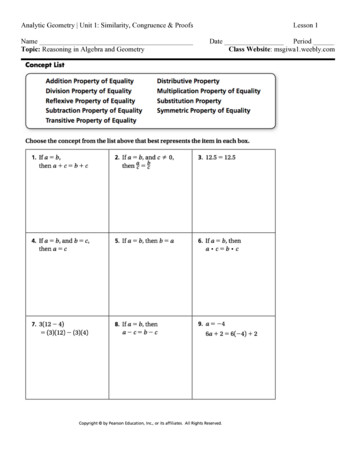
NameclassdateGeometry Unit 3 PracticeLesson 17-13. Triangle X(1, 6), Y(5, 22), Z(25, 21) is mappedonto XʹYʹZʹ by a dilation with center (1, 22) anda scale factor of 3. Which function represents thisdilation?1. Find the image of each point after the2 3transformation (x, y) x , y . 3 2 a. (6, 6)A. (x, y) (x 1 3(x 1 1), y 1 3(y 1 2))B. (x, y) (x 1 3(x 2 1), y 1 3(y 2 2))C. (x, y) (x 1 3(x 2 1), y 1 3(y 1 2))b. (12, 20)D. (x, y) (x 1 3, y 2 6)4. Make use of structure. In the diagram shown, adilation maps each point (x, y) of the preimage PQR to (1 1 2(x 2 1), 22 1 2(y 1 2)).c. (23, 10)yd. 1 , 21 3 P (23, 4)5e. (0.15, 1.50)525xR (2, 24)Q(24, 23)2. Attend to precision. Quadrilateral A(23, 3),B(4, 5), C(6, 0), D(24, 24) is mapped ontoAB2AʹBʹCʹDʹ by a dilation in which5 .A B 3The center of dilation is (0, 0).25a. What is the scale factor?y5A (23, 3)B (4, 5)b. Is the dilation an enlargement or a reduction?x5 C (6, 0)25c. What is the center of dilation?D(24, 24)25a. What is the scale factor for this dilation?d. What are the coordinates of the vertices of PʹQʹRʹ?b. What are the coordinates of AʹBʹCʹDʹ? 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.1SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
Nameclass5. What are the coordinates of the image of rectangleABCD after the figure undergoes a dilation with ascale factor of 0.75 centered at the origin?8. The sequence of similarity transformations belowis applied to PQR to get STV.(x, y) (2x, 2y) (2x, 3 2 2y)y10A (24, 10)dateWhat are the coordinates of the vertices of STV?B (4, 10)y55P (23, 2)Q (1, 2)52521052510xR(1, 23)C (4, 22)D (24, 22)x25259. A figure is transformed by the dilation Do, 1 and4then by another dilation. The composite of the twodilations is the same as the single dilation Do, 3.What is the second dilation?Lesson 17-26. What single dilation produces the same image asthe composition D 3 (Do ,40 (Do ,4 ))?o,A. D3o,1604B. Do, 33C. Do, 90D. Do, 1207. Model with mathematics. Write the sequence ofsimilarity transformations that maps ABC to XYZ.10. Construct viable arguments. Is a dilation a rigidtransformation? Explain your answer.y10A (26, 9)5X (5, 3)210525Z (4, 22)B(26, 26 )10xY(5, 22)25C (23, 26 )210 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.2SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
Nameclass14. Figure ABCD is similar to figure WXYZ. Whichproportion CANNOT be used to find side lengthsin the two figures?A. AB 5 DAWX ZWAB WXB.5BCYZBCXYC.5AD WZCDYZD.5AB WXLesson 17-311. Reason quantitatively. The two rectangles shownare similar. What is the value of x?x164212. Consider the two pairs of similar figures shown.202015. Construct viable arguments. In isosceles ABC,AB 5 AC. AʹBʹCʹ is a dilation of ABC by a scale1factor of .2a. Is AʹBʹCʹ isosceles? Explain.2525121210101212yyzzdate66Find the values of y and z.b. What is the ratio of the perimeter of ABC to AʹBʹCʹ?13. The vertices of a triangle are A(21, 4), B(4, 5),and C(6, 22). After a dilation with center (0, 0)and a scale factor of 3, the vertices are translatedT(22, 5).a. Is the image congruent to the original triangle?Is the image similar to the original triangle?Lesson 18-116. Reason quantitatively. Consider the trianglesshown. Are any of the triangles similar? Explain.858II258Ib. What are the vertices of AʹBʹCʹ, the finalimage?458358708III 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.3858708IV358SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
Nameclass17. Use triangles ABC and XYZ.19. Construct viable arguments. Using the diagramshown, what information is needed to concludethat PQR PST using each criterion?A78.6 date16P12TCS18BRX78.6 20Q15a. AA similarityZYa. Show that ABC and XYZ are similar by theSAS similarity criterion.b. SAS similarityb. Find YZ. Explain your steps.20. In the diagram shown, AB DE and m ACB 5 35 .A18c. Using the definition of similarity, explain whythe two triangles are similar.358CDB16d. Complete this statement: BCA E.a. If m A 5 (5x 1 3) and m B 5 (15x 1 2) , findm D and m E.18. Which of the following is NOT an abbreviation fora statement that can be used to conclude that twotriangles are similar?b. If AC 5 20, find EC to the nearest tenth.A. AA similarityB. SAS similarityC. SSA similarityD. ASA similarity 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.4SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
NameclassLesson 18-224. Persevere in solving problems. The length of thesides of Triangle I are 6 units, 10 units, and 8 units.One side of Triangle II has a length of 12 units.21. Reason quantitatively. In the diagram shown,RS XY , m X 5 25 , XY 5 30, RS 5 26, andZY 5 20.a. Find the lengths of the other two sides ofTriangle II if the sides with lengths 6 units and12 units are corresponding sides.XRZdateYSb. Find the other two lengths in Triangle II if thesides with lengths 10 units and 12 units arecorresponding sides.a. What is m SRZ?b. Complete this statement: ZYX c. Find the other two lengths in Triangle II if thesides with lengths 8 units and 12 units arecorresponding sides.XZexpressed as aRZreduced fraction? Expressed as a decimal to thenearest hundredth?c. What is the value of the ratiod. Triangle III is similar to the other two triangles,and its longest side has a length of 3 units.What are the lengths of the other two sides ofTriangle III?d. If ZY 5 20, what is SY to the nearest hundredth?25. In the diagram shown, AB BC, BD AC, and A CBD. Therefore, the two small trianglesare similar to each other, and to the large triangle,by AA similarity. Which proportion is NOT true?e. If XR 5 2, find RZ and XZ.B22. Find DE in the diagram shown. Write your answeras a decimal rounded to the nearest tenth.AAD11ADDC11AC BC5BC DCDB DCB.5DA DBAB ACC.5AD ABAD DCD.5ABBCA.CC1414BBEE1010FF23. Triangle I has side lengths 8, 9, and 6 units.2Triangle II has side lengths 8 units, 10 units, and312 units. Show that the two triangles are similar. 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.5SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
NameclassLesson 18-3date29. Reason quantitatively. In the diagram shown,XY ZW QR. Use the given measurements tofind each length.26. In the diagram shown, DE FG. Which proportionis NOT true?PF10DHXEG16YdRa. PXVW36Qb. XQ27. Make use of structure. Use the diagram shown towrite a proportion to illustrate the TriangleProportionality GDFFDGED.5DHEHYc. XYbd. ZWZc30. In the diagram shown, CD 5 7, DB 5 8, AE 5 5,and m C 5 62 .28. In the diagram shown, ED CB.AA75 m30 mE5DEB62 25 mC7x D8BCa. If AC DE , what is AB?a. Complete this statement using segments fromthe diagram: 30 5.25b. If AC DE , what is the value of x?b. Find AD and DB, each to the nearest tenth. 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.6SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
NameclassLesson 19-1date33. Attend to precision. In the diagram shown,SP PT , PM ST , PS 5 13, and SM 5 5.31. In the diagram shown, SP PT and PM ST .PP13SMTSa. Name two angles that are congruent to SMP.b. Find MT.c. Name an angle that is congruent to S.c. Find ST.d. How many right triangles appear in thediagram?d. Find PT.34. In DEF, DE 5 DF and DG is a segment fromvertex D. Which of the following statements isNOT true?32. Make sense of problems. This diagram shows arectangle ACJG and its two diagonals. Points B, F,H, and D are midpoints of the sides.DGBECEHTa. Find PM.b. Name an angle that is congruent to SPM.A5 MDFGFJa. Which segment is an altitude of ACE?A. If DG is a median in isosceles triangle DEF, thenDG forms two right triangles.b. Which segment is an altitude of CGJ?B. If DG is an angle bisector in isosceles triangleDEF, then DG forms two right triangles.c. Which segment is an altitude of CEJ?C. If G is a point on EF , then DG forms two righttriangles.D. If DG is a perpendicular bisector of EF , thenDG forms two right triangles.d. Which triangles have AG as an altitude? 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.7SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
Nameclass35. Write a similarity statement comparing the threetriangles in the diagram shown.Mdatec. Find m 1 n if t 5 4 and n 5 4.Jd. Find t if m 5 4 and m 1 n 5 13.LK38. Use the diagram shown. If necessary, round youranswers to the nearest tenth.Lesson 19-236. Use the segments in the diagram shown. Whichproportion does NOT represent Corollary 1 orCorollary 2 of the Right Triangle AltitudeTheorem?asprbqdcA.B.C.D.ea. Find q if r 5 4 and s 5 12.b. Find r if q 5 10 and r 1 s 5 50.a 1b c5caa d5d bc d5d ea 1b e5ebc. Find s if q 5 8 and r 5 3.d. Find p if r 5 s 5 6 and q 5 8.39. Determine the positive geometric mean of eachpair of values. Simplify any radicals.37. Express regularity in repeated reasoning. Usethe diagram shown. If necessary, round youranswers to the nearest tenth.ta. 25 and 100b. 27 and 36c. 1 and 45nmd. 100 and 200a. Find t if m 5 2 and n 5 8.e. a and bb. Find m if t 5 5 and n 5 6. 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.8SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
NameclassdateLesson 20-140. Persevere in solving problems. In the diagramshown, BC CA and CD BA .41. Which three numbers do NOT form a Pythagoreantriple?CA. 5, 12, 13aB. 6, 8, 10bfC. 6, 10, 14B4d16eDD. 8, 15, 17Ac42. A supporting wire is attached to a tree at a heightof 45 feet from the ground. If the length of the wireis 51 feet, what is the distance between the base ofthe tree and the foot of the wire?a. Use a corollary of the Right Triangle AltitudeTheorem to find f.wire45 ftb. Use the base AB and altitude CD to find thearea of ABC. Show your work.51 ft?43. Attend to precision. The length of a rectangularrug is 18 feet and the length of its diagonal is 22 feet.c. Use a corollary of the Right Triangle AltitudeTheorem to find a and b.18 ft22 ftd. Using a and b as the base and height of ABC,find the area of ABC. Show your work.a. What is the width of the rug, to the nearest foot?b. What is the perimeter of the rug, to the nearestfoot?c. What is the area of the rug, to the nearest squarefoot?d. A second rectangular rug has side lengths thatare the same as the width and diagonal of theoriginal rug. What is the length of the diagonalof the second rug to the nearest foot?e. What do you notice about your answers to Partsb and d? 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.9SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
NameclassLesson 20-244. Reason quantitatively. An isosceles triangle hasside lengths 15 units, 15 units, and 8 units.15hdate46. Tell whether the three lengths are the sides of anacute triangle, a right triangle, or an obtusetriangle.a. 8, 11, 1215ab. 24, 45, 518a. What is the length of the altitude h from thevertex angle, to the nearest tenth?c.3 2 1, ,10 5 2d. 12, 14, 20b. What is the area of the triangle, to the nearesttenth?e. 9, 11, 13c. What is the length of the altitude a from one ofthe base angles?47. Construct viable arguments. Tell whether or noteach triangle is a right triangle. Explain youranswers.d. Find the sum of the lengths of the threealtitudes of the triangle.a.23.815.145. Two sides of a right triangle have lengths 15.1 cmand 30.6 cm.18.4a. Find the length of the third side if the givenlengths represent the legs of the triangle.b.b. Find the length of the third side if the givenlengths represent the hypotenuse and one leg ofthe triangle.18.511.313.5 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.10SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
Nameclassdate50. For Parts a–e, the last number represents the lengthof the hypotenuse of a right triangle and the othertwo numbers represent the lengths of the legs. Findeach missing length.48. Reason quantitatively. Two sides of a triangle are8.6 cm and 10.5 cm.a. What is an inequality that represents the lengths of the shortest side of the triangle?a. 10 , ? , 15b.b. What is an inequality that represents the lengthl of the longest side of the triangle?8 , ? , 10c. 100 , ? , 101d. 19 , ? , 25c. What is the length of the third side if it is the legof a right triangle?e.n , ? , n13Lesson 21-151. Use appropriate tools strategically. Find thelength of the hypotenuse of an isosceles righttriangle given the length of a leg. Write each answeras an exact value and as a decimal rounded to thenearest hundredth.d. What is the length of the third side if it is thehypotenuse of a right triangle?a. 12 in.49. Four students wrote the following statements abouttwo given positive numbers. Which statement isalways true?b. 25 cmA. If I select any number between the two givennumbers, the three numbers can be the sides ofa right triangle.c. 7a ftB. If the two numbers are the lengths of two sidesof a triangle, then the sum of the two numberscan be the length of the third side of thetriangle.d.52. Find the length of the leg of an isosceles righttriangle given the length of a hypotenuse. Writeeach answer as an exact value and as a decimalrounded to the nearest hundredth.C. If I select any number between the two givennumbers, the three numbers can be the lengthsof the sides of a triangle.D. If the two numbers are lengths of two sides of atriangle, the length for the third side can be anyone of these three choices: it can be less than thesum of the two numbers, it can be greater thanthe difference of the two numbers, or it can bebetween the two numbers. 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.aunitsb11a.22 in.b.19 cmc.5a ftd.cunitsdSpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
Nameclass53. In an isosceles right triangle, the length of thehypotenuse is 8 units. Which measurement is NOTassociated with the triangle?dateLesson 21-256. Express regularity in repeated reasoning. Findthe length of the longer leg and the length of thehypotenuse given the length of the shorter leg of a30 -60 -90 triangle.A. 4 2 unitsB. 8 2 unitsa. 15 in.C. 45 D. 90 b. 8 3 cm54. Find the length in each isosceles right triangle.a. Find the leg if the hypotenuse is 6 2 units.c. a ftb. Find the hypotenuse if the leg is 13 2 cm.d. 3 5 unitsc. Find the hypotenuse if the leg is (1 1 3) cm.57. Find each length for a 30 -60 -90 triangle.d. Find the leg if the hypotenuse is1unit.2a. the shorter leg and the longer leg if thehypotenuse is 25 cm55. Make sense of problems. For an isosceles righttriangle, find the length of the leg and thehypotenuse with the given criterion.b. the shorter leg and the hypotenuse if the longerleg is 12 in.a. The perimeter is (14 1 7 2 ) units.c. the shorter leg and the hypotenuse if the longerleg is 10 ftb. The perimeter is (20 1 10 2 ) units.d. the shorter leg and the longer leg if the2hypotenuse isunits3c. The area is 12.5 square units.d. The area ismsquare units.2 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.12SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
NameclassdateLesson 22-158. In a 30 -60 -90 triangle, one of the legs has a lengthof 30 cm. Which of the following measurements isNOT associated with this triangle?61. Model with mathematics. Identify the indicatedside in the right triangle shown.A. 10 3MB. 20 3C. 30 3D. 60 3NTa. the leg that is opposite angle N59. In a 30 -60 -90 triangle, find the lengths of thelegs and the hypotenuse with the given criterion.b. the leg that is adjacent to angle Ma. The perimeter of the triangle is (15 1 5 3 ) cm.c. the leg that is adjacent to angle Nb. The area is 36 3 square units.d. the leg that is opposite angle M62. Find the indicated measures in the triangle shown.c. The triangle is half of an equilateral trianglewith sides that measure 30 units.Q8d. The perimeter is (3a 1 a 3 ) units.R17Sa. QS60. Make use of structure. Find a, b, c, and d in thediagram shown.b. m SSc. Draw and label a triangle XYZ so XYZ QRSand the scale factor from QRS to XYZ is 7 : 2.Indicate the measures of all sides and angles.d60861.98Pc5Rabd. Explain how you found the measures of thesides and angles of XYZ.Q63. In a right triangle, the hypotenuse is 15 cm and aleg is 11 cm. In a similar right triangle, thehypotenuse is 9 cm. Find the lengths of the legs ofthe smaller triangle. Write your answers to thenearest tenth. 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.13SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
Nameclass64. Right triangle DEF is similar to right triangle HJK. DEF is larger than HJK, and the length of HKis 7.5 cm. Which statement describes how tocalculate the length of DF?date67. Using the triangle shown, write each ratio insimplest form.M48NA. Add 7.5 to the length of HK .B. Subtract 7.5 from the length of HK .55C. Multiply the length of HK by 7.5.73D. Divide the length of HK by 7.5.T65. Make use of structure. Find the scale factor andthe unknown angle measures and side lengths forthe pair of similar right triangles shown.b. tan TCACF86Fc. sin T81761.9861.98a. tan N28.18D628.18BE68. Use appropriate tools strategically. Use acalculator to find each value. Round your answersto the nearest hundredth.Lesson 22-2a. sin 57.3 66. Model with mathematics. Use the triangle shownto write a fraction for each trigonometric ratio.rPqd. cos Te. sin NEBDb. cos 42.8 Qc. tan 89.6 pd. cos 90 Ra. sin Pe. tan 45 b. tan Q69. Which trigonometric ratio can be greater than 1?c. cos QA. sineB. cosined. sin QC. tangente. tan P 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.D. all three ratios14SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
Nameclass70. Which statement is NOT true?73. In right triangle XYZ, m Y 5 37 and XY 5 27.Which of the following is NOT a method you canuse to find XZ?yA. Solve sin Y 5 .zyB. Solve tan Y 5 .xxC. Solve cos Y 5 , and then use the PythagoreanzTheorem.A. sin 45 5 cos 45 B. sin 20 1 sin 50 5 sin 70 C. cos 74.7 5 sin 15.3D. sin 35 5 cos 55 Lesson 22-371. Use trigonometric ratios to find the indicated sidelengths in the diagram shown. Show your work andwrite your answers to the nearest tenth.D. Find m X, and then solve cos X 5MA688bPy.z74. Use appropriate tools strategically. The diagonalof rectangle ABCD is 42.3 cm, and it forms an angleof 53 with the shorter side AD of the rectangle.150adateBN538a. aDT42.3 cmCa. Find the length and width of the rectangle.Show your work.b. bb. Use the area of ABD to find the length of AT ,the altitude from vertex A in ABD. Show yourwork.72. Use appropriate tools strategically. Find theperimeter and area of each triangle. Showyour work.a.6287mc. Use a trigonometric ratio in ADT to find AT.27.6d. Compare your results for Parts b and c. Whichmethod do you prefer?b.17.8p438q 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.15SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
Nameclass75. A campsite at point P is 600 meters from a river.One group of campers hikes to the river on a paththat forms a 68 angle with the direct route to theriver, and gets to the river at point A. Anothergroup of campers hikes to the river at a path thatforms a 40 angle with the direct path to the river,and gets to the river at point B.date77. Model with mathematics. A ramp is being designedso that wheelchairs can go up the distance AB, whichis 2.5 feet. Write each answer to the nearesthundredth of a degree.A2.5 ftPC688408a. If CB is 30 feet, what is the measure of ACB?600 mARiverRBBb. If CA is 30 feet, what is the measure of ACB?a. What is the length of the path from P to A?b. What is the length of the path from P to B?78. Find all the missing sides and angles for thetriangle shown.c. How far apart are points A and B?Ad. How much longer is the distance from A to P toB than the straight-line distance from A to B?41816Lesson 22-476. Use appropriate tools strategically. Use acalculator to find each angle measure. Be sure yourcalculator is in degree mode.Ca. sin A 5 0.5736B79. Find the missing sides and angles for the triangleshown.b. tan D 5 0.9657D23c. cos B 5 0.1994Fd. tan21 (4.0108)25E 15 e. sin21 17 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.16SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
Nameclassdate82. Write the three-part statement of the Law of Sinesfor the triangle shown.80. For the right triangle shown, which statement isNOT true?Mcanx8tb b A. x 5 90 2 tan21 a a B. x 5 tan21 b b C. x 5 cos21 c a D. x 5 cos21 cTmN83. Use appropriate tools strategically. Find eachmeasure to the nearest tenth.U83815.2Lesson 23-1W81. Construct viable arguments. Complete the stepsbelow to derive a part of the Law of Sines.588VPrQa. VWqhTb. UVp84. The Law of Sines CANNOT be applied to which ofthe following?Ra. In PQT, write an expression for sin Q.A. acute trianglesB. obtuse trianglesb. In PRT, write an expression for sin R.C. right trianglesD. triangles where no angle measures are knownc. Solve for h in Parts a and b.d. In Part c, there are two expressions for h. Setthem equal to each other.e. Starting with your equation in Part d, divideeach side by rq. 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.17SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
Nameclassdate87. Consider the triangles below.85. Which measure for ABC can be found using theLaw of Sines?SPA105812151512C13Q388RT388V17.8a. Use the Law of Sines in PQR to find m Q.Show your work.BA. ACB. the altitude from vertex Ab. Use the Law of Sines in STV to find m T.Show your work.C. m CD. m BLesson 23-2c. Compare your answers to Parts a and b with thetriangles in the illustration. What do youconclude?86. Which diagram indicates two sides and thenonincluded angle?A.d. How can you find the actual measure of Tin STV?B.88. Consider DEF with m F 5 40 , DF 5 32, andDE 5 25. Find two possible values, each to thenearest whole number, for each expression.C.a. m Eb. EFD.89. Make sense of problems. Sketch two possibilitiesfor WXY if m W 5 45 , YW 5 10, and YX 5 8. 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.18SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
Nameclassdate94. Attend to precision. Consider the triangle shown.Find YZ to the nearest tenth.90. Reason quantitatively. Use your triangles fromItem 89, where m W 5 45 , YW 5 10, andYX 5 8.Xa. Find the two possible values for m Y, each tothe nearest tenth.41823.5 cm11.2 cmb. Find the two possible values for XW, each to thenearest tenth.ZY95. In an isosceles triangle, the legs are 12 cm and thebase is 5 cm.Lesson 23-391. Which one of the following is a statement of theLaw of Cosines for PRQ?a. Find the measure of the vertex angle.Prqb. Find the measure of the base angles.QpRA. p2 5 q2 1 r2 2 2pq cos PB. q2 5 p2 1 r2 1 2pr cos QLesson 23-4C. r2 5 p2 1 q2 2 2pq cos R96. Suppose you know the measures of three parts of atriangle. Which combination of known sides andangles is NOT sufficient to let you use the Law ofSines to find other parts of the triangle?D. r2 5 p2 1 q2 2 2rp cos P92. Use appropriate tools strategically. Consider MNT. Find m N to the nearest tenth of a degree.15.7 cmA. the length of two sides and the measure of anangle opposite one of the sidesB. the measures of three sides of the triangleNC. the measures of two angles and the length of theside between the angles14.8 cmM26.1 cmD. the measures of two angles and the length of aside that is not between the anglesT93. Which set of known measures is NOT enough touse the Law of Cosines?A. the three sides of the triangleB. two sides and one angle of the triangleC. two sides and three angles of the triangleD. one side and two angles of the triangle 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.19SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
Nameclass97. Consider triangle PQR.date99. Make use of structure. Consider triangle HJK.PH11.79.518.7R12.3938Q23.9Ka. What combinations of sides and angles are shown?Ja. What combinations of sides and angles areshown?b. Which law can you use to find anothermeasurement, the Law of Sines or the Law ofCosines?b. Which law can you use to find anothermeasurement, the Law of Sines or the Law ofCosines?c. What is m P to the nearest tenth?d. What is m Q to the nearest tenth?c. What is HK to the nearest tenth?e. What is m R to the nearest tenth?d. What is m K to the nearest tenth?98. Consider triangle DEF.De. What is m H to the nearest degree?100. Attend to precision. Two surveyors at points Aand B are exactly 100 meters apart. The diagramshows the angle measures from the surveyors totheir supply truck at point T.13.21128428FETa. What combinations of sides and angles are shown?b. Which law can you use to find anothermeasurement, the Law of Sines or the Lawof Cosines?A258298100 mBWhich surveyor is closer to the supply truck?How much closer (to the nearest tenth)? Showyour work.c. What is DE to the nearest tenth?d. What is FE to the nearest tenth?e. What is m D to the nearest tenth? 2015 College Board. All rights reserved.20SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice
Triangle X(1, 6), Y(5, 22), Z( 5, 1) is mapped . SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice LeSSon 19-1 31. In the diagram shown, SP PT and PM ST. P S M T a.Name two angles that are congruent to . SpringBoard Geometry, Unit 3 Practice 8 15 b. c. d.,, answers., ? , .