Transcription
MINISTRY OF ROADSREPUBLIC OF KENYACost Estimation ManualFor Road Maintenance WorksNovember, 2011in association withJAPAN INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION AGENCYStrengthening of Capacity on Road Maintenance Management through Contracting
Cost Estimation Manual for Road Maintenance Works 2011FOREWORDRoads are among the most valuable public assets in the country. This investment thereforerequires an organized and balanced maintenance program to realize the maximum service lifeof the road-network. The approach is based on maintenance of road network in fair or goodcondition rather than adopting a “worst-first” methodology which means spending hugeamounts of the road budget on full reconstruction.This manual provides roads Authorities a scientific index on the approximate price ofmaintenance works for the tendered works by factoring in input components comprisinglabour, salaries and wages, materials, plant and equipment. This is derived from a survey thatevaluates the condition of the segment of the road in need of preventive maintenance toprotect capital investments.The development of this manual is indicative of the serious attention the government ispaying to the road maintenance works in the country. The government now has laidemphasize on preventive maintenance of road network to allow it live its lifespan and providethe intended utility of improved access to schools, markets, health facilities, improvedcomfort and travel time and safety, and lower cost of vehicle operating expenses.The government has continued to make a lot of capital investment in the construction ofroads in all geographical regions of the country which have different topographical setup. Thevarious regions have varied source of materials and climatic condition that may affect roadmaintenance pricing. This manual will allow tender participants to use the document toconstruct their own biding price while considering unique cost settings.Cognizant that the market trends are dynamic, the government will monitor price movementsof inputs to road maintenance for appropriate review to reflect the prevailing situation.It is therefore instructive that compliance with this manual is mandatory for all cost estimatesprepared for preventive road maintenance programs by project engineers, project managers,technical officers and consultants. All parties must follow these procedures when preparingcost estimates to minimize escalation of cost and provide value for money for the tax payer.HON. FRANKLIN BETT, EBS, MPMINISTER FOR ROADS1 Page
Cost Estimation Manual for Road Maintenance Works 2011MESSAGE BY THE PERMANENT SECRETARY; MINISTRY OFROADSThe Ministry of Roads has undergone major reforms in the last few years, all geared towardsimproving service delivery and realising value for money.Roads infrastructure is a critical component to our economy which is expected to experiencerapid growth that would stimulate and enable the country achieve middle level income status.It is therefore prudent for our country to invest heavily in its roads sector among otherinfrastructure that will catalyse growth of all other sectors such as trade, industry, Agriculture,Transport, Health among others.By recognising this importance, the government has invested heavily in the road sectorsteadily increasing the budgetary allocation to roads to Ksh 100 billion in the currentfinancial year-2010/2011 representing an increase of 8 fold over the last eight years.To achieve value for money in our roads construction and maintenance, it is found necessaryto standardise the cost estimation of road maintenance countrywide.The introduction of this manual is noble since it will contain instructions for estimating priceof maintenance works for bidding price in any part of the country. This manual will alsoguide the respective Authorities formulate the annual work plans and serve as a tool forauditing the various maintenance works that have been awarded.In this regard, the Government with the technical and financial assistance from JapaneseInternational Cooperation Agency (JICA) has developed cost estimation manuals for roadmaintenance works.Thank You.ENG. M. S. M. KAMAU, CBS, HSCPERMANENT SECRETARY2 Page
Cost Estimation Manual for Road Maintenance Works 2011MESSAGE BY THE CHIEF REPRENTATIVE; JAPANINTERNATIONAL COOPERATION AGENCY (JICA)The road sector reforms have progressed steadfastly with first the introduction of theRoad Maintenance Levy Fund and the establishment of Kenya Roads Board (KRB) .This was followed by the establishment of Kenya National Highways Authority(KeNHA), Kenya Rural Roads Authority (KeRRA) and Kenya Urban RoadsAuthority (KURA). Throughout this sector reform process, the Ministry of Roads(MoR) has shown great commitment and leadership. The ministry has emphasisedon road maintenance in order to safeguard the on-going heavy investment intransport infrastructure in line with Kenya Vision2030. This is laudable.Currently, there is need to have the road management system work smoothly andeffectively. Therefore, the development of this Cost Estimation Manual (CEM) is amilestone in the “next generation” road maintenance administration system inKenya. The CEM assist the Road Authorities to develop the Engineers’ Estimatesand formulate annual Work Plans. The contractors can use the Manual to preparetheir bids. It is an indispensable management tool for all.I call upon all practitioners in the road sector to start using this manual and laterreview it objectively in order to make it a dynamic road management tool.I appreciate the continued cooperation between JICA and Ministry of Roads. It is amodel in our international development work.MASAAKI KATO3 Page
Cost Estimation Manual for Road Maintenance Works 2011CHIEF REPRENTATIVE, JICA KENYA OFFICETable of ContentsAbbreviations and Acronyms51. Introduction1.1 Purpose of the Manual1.2 Application of the Manual6662. Glossary of Terms73. Contents of the Manual3.1 Work Items and Coding3.2 Cost Configuration3.3 Price List and Source3.4 Haulage Cost3.5 Unit Quantity and Productivity3.6 Indirect Work Costs3.7 Overheads and Profit1313171821222222Appendix 1. Unit Calculation TablesAppendix 2. References4 Page
Cost Estimation Manual for Road Maintenance Works 2011Abbreviations and AcronymsAASHTOAmerican Association of State Highway and TransportationOfficialsACAsphalt ConcreteCBRCalifornia Bearing RatioJICAJapan International Cooperation AgencyKeNHAKenya National Highways AuthorityKeRRAKenya Rural Roads AuthorityKNBSKenya National Bureau of StatisticsKRBKenya Roads BoardKURAKenya Urban Road AuthorityKWSKenya Wildlife ServiceM&TMechanical and Transport Department, Ministry of RoadsMDDMaximum Dry DensityMoRMinistry of RoadsPPOAPublic Procurement Oversight AuthorityPVCPolyvinyl ChlorideRMMSRoad Maintenance Management SystemVATValue-added Tax5 Page
Cost Estimation Manual for Road Maintenance Works 20111. Introduction1.1 Purpose of the ManualThis manual gives instructions for estimating the cost of roadmaintenance works, by considering all inputs. This is to provide astandardized procedure of pricing road activities in Kenya, to ensureuniformity in public and private procurement practice.1.2 Application of the ManualThis manual is to be applied in the preparation of Engineer’s Estimate fortender documentation by procurement entities and provides a benchmarkfor evaluation of bidding prices.The manual shall also be used for the formulation of annual work plansby the roads authorities and as an auditing tool for ongoing road works.It can also be used as a reference for bidders to prepare their biddingdocuments while considering their unique cost settings.6 Page
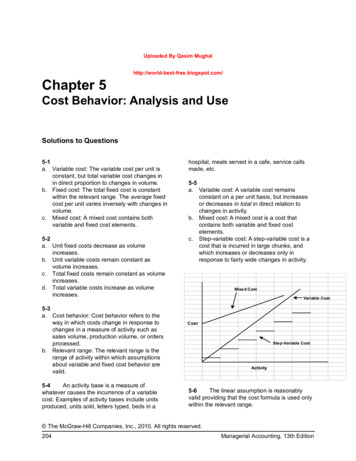
Cost Estimation Manual for Road Maintenance Works 20112. Glossary of TermsThis chapter contains a glossary of terms that are used in this manual.Cross SectionThe typical cross sections of paved, unpaved and urban roads are as follows;Paved RoadUnpaved Road1. Roadway 2. Carriageway 3. Shoulder 4. Surfacing 5. Base 6. Subbase 7. Camber (Cross Fall)8. Cut 9. Embankment 10. Subgrade 11. Cut Slope 12. Embankment Slope 13. Berm 14. Side Ditch15. Benching 16. Natural Ground Level 17. Centre-line 18. Marking 19. Grave 20. Footpath21. Road Reserve 22. Pavement 23. Side Ditch 24. Boundary Stone7 Page
Cost Estimation Manual for Road Maintenance Works 2011Glossary of TermsAbutmentStructure support to bridge deck and retains the road embankmentAdhesionSticking quality, for example, holding aggregate to the binder in chip sealingAggregateCrushed local rock or stoneApronFloor of concrete, masonry or stone at the inlet or outlet of a culvert or waterway to prevent scour.Asphalt ConcreteRoad construction material usually comprising a mixture of bitumen and aggregate, also known as hot-mix orhot-rolled asphalt.Base CourseThe main structural element of the pavement, between surface course and subbase.BenchingA stepped platform cut in an embankment to prevent earth slipping. Can also be used as stepping to provide alevel base for additional fill material.BermA low ridge or bund of soil to collect or redirect surface water.BinderAn adhesive material, usually bitumen or bitumen emulsion, used to seal the road surface, also providing awaterproof layer to receive and hold aggregate. The most common binders are bitumen based. A binder is alsoused to hold aggregate together in bituminous mixtures.Binder CourseThe layer forming part of the bituminous surfacing immediately below the wearing course.BitumenBitumen (called asphalt cement in the US) is a black to dark brown sticky material composed principally ofhigh-molecular-weight hydrocarbons. Most bitumen is derived from the distillation of crude oil. Bitumen is athermoplastic material that gradually liquefies when heated.Borrow PitAn excavation outside the road limits from which suitable material is obtained, usually for earthwork orregravelling operations.Box CulvertA culvert of rectangular cross-section, usually constructed in reinforced concrete.BridgeA structure with a span of 6 metres or more providing a means of transit above land and/or water or above anobstruction, whether natural or artificial.Camber (Cross Fall)The transverse slope applied to the carriageway on a section of straight alignment.8 Page
Cost Estimation Manual for Road Maintenance Works 2011CausewayLow-level structure constructed across streams or rivers with openings to permit water to pass below road level.CarriagewayThe part of the road used by vehicular traffic.Catchment AreaThe area from which water runs off by gravity to a collecting point.CatchpitA covered, accessible chamber with a sump for collection of silt forming part of the drainage system andpermitting inspection and maintenance of underground drainage pipes.Centre-lineThe middle of the carriageway, normally marked with a yellow dashed line on a paved road.CompactionCompacting embankment by roller to increase density of soil what composes embankment body. It causes toimprove mechanical properties of soil.Cross-fallThe transverse gradient or fall across a formation or pavement.Cross-sectionSection through the road construction at right angles to the centre-line.CrownThe highest part of a cambered surface, usually on or near the centreline.CulvertA duct, usually rectangular or circular, for carrying surface water under the road.Cut (Cutting)Excavation in natural ground usually with graded slopes.Cut-off DrainA drain cut to intercept surface water flowing from adjacent land and to prevent it reaching a pavement or otherprepared surface.Cut SlopeA soil plane constructed at an angle to the horizontal.CyclewayThe track which is mainly used for bicycle traffic. The track is separated with other parts of road by kerb stoneor its similar structures.Ditch (Drain)A long narrow excavation designed or intended to collect and drain off surface water.DrainageThe interception and removal of ground and surface water by artificial or natural means.Drainage ChannelA waterway or gutter to carry away surface water.9 Page
Cost Estimation Manual for Road Maintenance Works 2011Drift or FordA stream or river crossing at bed level over which the stream or river water can flow.EarthworksGeneral term of construction works involving soil and rocks(e.g. excavation, loading, hauling, spreading andcompaction).Embankment SlopeAn artificially constructed soil plane at an angle to the horizontal.Fill (Embankment)Earthworks constructed below the pavement raising the road above the surrounding natural ground level.FootbridgeThe overpass bridge crossing carriageway/railway to ensure the safety of pedestrian and smoothvehicle traffic.FootpathThe track which is mainly used for pedestrian. The track is separated with other parts of road by kerb stone or itssimilar structures.GabionThe steel mesh cage filled with cobble stone or crushed stone. This is mainly used for revetment andfoot protection.GravelA non-cohesive, coarse granular material, resulting from natural disintegration of rock with or without finermaterial. In general the particles are irregular or flaky. It is used as material of surface course and to correct lossof shape, ruts, potholes and erosion gullies.GuardrailA safety barrier on embankment or river crossingGutterA shallow waterway provided at the edge of the road to carry surface water longitudinally.HeadwallsThe walls located on the top of outlet/inlet of culvert. The walls of inlet direct the flow into the culvert, whilethe walls of outlet provide a transition from the culvert to the outlet channel. Headwalls also protect theembankment from erosion by flood waters.InletThe point at which surface water enters a pipe culvert or box culvert.InvertThe lowest point of the internal cross section of a ditch or culvert.LaneThe width of carriageway required to accommodate one line of traffic.ManholeAccessible chamber with a cover forming part of the drainage system and permitting inspection andmaintenance of underground drainage pipes.Mitre DrainShort, open, skew ditches used to remove water from the roadside ditches or gutters. Use of this reduces thenecessary size of the side ditches and minimizes the velocity of water and thereby the risk of erosion.10 P a g e
Cost Estimation Manual for Road Maintenance Works 2011Original Ground LevelLine of natural ground.OutfallThe point at which water discharges from a pipe or box culvert.Paved RoadFor the purpose of this manual a paved road is a road with a concrete surface, concrete block,bituminous surface or surface dressing.PavementThe road structure above the formation, designed to spread the loading over the base and subbase.Pipe CulvertA culvert of circular cross-section, usually constructed in pre-cast concrete.PremixPremix is a paving material manufactured by mixing aggregates, filler and bitumen. Most premix is mixed andplaced hot. Premix is used in the construction of wearing course, binder courses and base courses.Prime CoatA coating of low viscosity binder applied to a surface of stabilised or naturally compacted soil before sealing orpaving.Road Reserve (Right-of-way)The area within the road limits over which members of the public have the right to pass and re-pass.Road FurnitureRoad or street furniture e.g. traffic sign, traffic board, traffic signal, lane marking, guardrail, street light, etc.RoadwayThe portion of a road including shoulders for vehicular use.Scour ChecksThe structures to prevent scouring of drains. Simple scour checks may be constructed of wood pegs or stones.All scour checks should have an apron downstream built of stones or grass turves pinned to the ditch invert withwooden pegs.ShoulderPaved or unpaved part of the road next to the outer edge of the pavement. The shoulder provides side support forthe pavement and allows vehicles to stop or pass in an emergency.Side DrainDrain beyond the shoulders, parallel to the centerline, to take the run-off from the road surface.SlopeA natural or artificially constructed soil plane at an angle to the horizontal.Sub-baseThe layer of material between the base course and the subgrade.SubgradeUpper layer of the soil that supports the pavementSuperelevationThe raising of the outside level of the road on curves to reduce the effect of centrifugal forces and improve roadholding qualities.11 P a g e
Cost Estimation Manual for Road Maintenance Works 2011SurfacingTop layer of the pavement. Consists of wearing course, and sometimes a base course or binder course.Surface DressingA sprayed or hand applied film of bitumen followed by the application of a layer of stone chippings, which isthen rolled.Tack CoatAsphalt material to bond lower layer (asphalt material or cement) and upper layer (asphalt mixture). It issprayed on surface of lower layer.Traffic LaneThe portion of the carriageway defined by road marking for the movement of a single line of vehicles.Transverse JointJoint at right angles to the road centreline.Transverse Joint TaperSlope or ramp of asphalt mix at the end of a freshly laid asphalt course.Unpaved RoadFor the purpose of this manual an unpaved road is a road with a gravel or earth surfaceWearing CourseThe part of the road surface in contact with traffic wheels.Wing-wallRetaining wall at a bridge abutment to retain and protect the embankment fill behind the abutment.12 P a g e
Cost Estimation Manual for Road Maintenance Works 20113. Contents of the Manual3.1 Work items and codingWork items covered in this manual are shown in Table 1. These are thecommon types of works which are widely implemented in roadmaintenance works in Kenya.The coding for each work item is derived from the Road MaintenanceManagement System (RMMS), and categorized in accordance with theStandard Specifications for Road and Bridge Construction (1986).Table 1 Work Items4. Site Clearance and Topsoil StrippingNo12Work Category34Bush ClearingCode04.50.00104.50.002Mechanical mowingGrass cutting (manual)Work Item Name04.50.003Heavy bush clearing04.50.004Light bush clearing567891011 Site Clearing 4.50.08504.50.09004.50.0951304.50.115Pruning of tree branchesTree cutting and stump removal (200 -450 mm)Tree cutting and stump removal ( 450 mm)Clearing obstructions (mechanical)Clearing obstructions (manual)Stripping and grubbing (mechanical)Stripping and grubbing (manual)Clearing trees, hedges, bushes, vegetation and deleteriousmaterials (mechanical)Clearing trees, hedges, bushes, vegetation and deleteriousmaterials (manual)04.50.110UnitDescriptionm2 Cut grass by machine along the side of the road or on slopes.m2 Cut grass manually along the side of the road or on slopes.Cut, remove and dispose bushes along the side of the road, slopes orm2alongside ditches.Cut grass by hand from shoulders, slopes, inlet ditches, and side ditchesm2including back slopes, turnouts and culvert outlet.m2 Cut, remove and dispose branches of trees along the side of the road,No Cut, remove and dispose whole trees of 200 - 450mm in girth includingNo Cut, remove and dispose whole trees of above 450mm in girth includingm2 Mechanically clear any obstruction including boulders and debris out ofm3 Manually clear any obstruction including boulders and debris out of roadm2 Clear site on road reserve mechanically by stripping and grubbing roots.m2 Clear site on road reserve manually by stripping and grubbing roots.Clear site on road reserve mechanically by removal of trees, hedges,m2bushes, vegetation and other deleterious materials.Clear site on road reserve manually by removal of trees, hedges, bushes,m2vegetation and other deleterious materials.Demolish reinforced or mass concrete structures and cart to spoil orm3stockpile for re-use.14 Concrete Demolition04.50.010Excavate remove & disposal of concrete structures15 Top Soil Stripping10.80.002Removal of overburdenm31604.50.120Removal of cracked small pipe culverts below 600mmm04.50.125Removal of cracked large pipe culverts above 600mmmPipe Culvert Removal175. Earth WorksNoWork Category18CodeWork Item NameUnit05.50.006Fill in soft material and compactm305.50.006aFill in soft material and compact (soil purchased)m32005.50.007Fill in hard material and compactm32105.50.007aFill in hard material and compact (soil purchased)m32223Material Cutting242526 Rock 50.12005.50.125Cut to spoil in softCut to spoil in soft (mechanical)Cut to spoil in hardCut to spoil in hard (mechanical)Rock fill to swampRock fill to embankment constructionm3m3m3m3m3m319Material Filling28 ompaction of subgrade in cutCompaction of subgrade in fillm2m305.60.016Compaction of original ground levelm231CompactionRemove topsoil to a maximum depth of 200mm.Excavate, remove and dispose cracked pipe culverts below 600mm indiameter.Excavate, remove and dispose cracked pipe culverts above 600mm indiameter.DescriptionProvide, place and compact soft patching material to surface defects orgravel road. It is assumed that soil to be filled is on the site or providedfrom cut area.Provide, place and compact soft purchased patching material to surfacedefects or gravel road.Provide, place and compact hard patching material to surface defects orgravel road. It is assumed that soil to be filled is on the site or providedfrom cut area.Provide, place and compact hard purchased patching material to surfacedefects or gravel road.Cut manually soft material to spoilCut mechanically soft material to spoilCut manually hard material to spoilCut mechanically hard material to spoilManually provide and place rock fill to swampManually provide and place rock fill to construct embankment.Plant grass on the slope and inverts of ditches to reduce scour effects, oron slopes to reduce soil erosion and to improve stability.Grading and compaction of subgrade in cutGrading and compaction of subgrade in fillCompact the top 150 mm layer of existing ground below fills and cuts to95% MDD (AASHTO T99)13 P a g e
Cost Estimation Manual for Road Maintenance Works 20117. Excavation and Filling for StructureNoWork CategoryCode3207.50.00133 Material Excavation07.50.001a34 for Structures07.50.0023507.50.002aWork Item NameExcavate for structure in soft material (manual)Excavate for structure in soft material (mechanical)Excavate for structure in hard material (manual)Excavate for structure in hard material (mechanical)36Gabion3738 Stone Pitching08.70.004Gabion Installationm208.70.00508.70.001Rock fill to GabionsStone pitchingm3m28. Culverts and Drainage WorksNoWork CategoryCodeUnitDescriptionExcavate manually soft material for structures.Excavate mechanically soft material for structures.Excavate manually in hard material for structures.Excavate mechanically in hard material for structures.Provide and place Macaferri or equivalent gabion boxes (2m * 1m *1m).Provide and place rock fill to gabions.Provide stone pitching including grouting of ratio 1:4 cement to mortar.08.50.001Ditch cleaning - mechanical4008.50.002Ditch cleaning - manualm41424308.60.001a08.60.001b08.60.003cSmall culvert cleaning-partially blocked-below 450mmMedium culvert cleaning-partially blocked-600mmLarge culvert cleaning-partially blocked-900 mm and abovemmmDescriptionMechanically excavate/desilt, grade to shape inlets outfalls, side drains tofree flow conditionsManually excavate/desilt, grade to shape inlets outfalls, side drains to freeflow conditions.Clean culverts of below 450mm in diameter to free flow conditionsClean culverts of below 600mm in diameter to free flow conditionsClean culverts of below 900mm in diameter to free flow conditions4408.50.025Manhole cleaningNoRemove all silt and debris and wash out manhole to free flow conditions.4508.50.016Gulley pot cleaningNo08.50.009Covered (slotted) lined drain cleaningm4708.50.050Ditch/mitre drain excavation in soft (mechanical)m34808.50.052Ditch/mitre drain excavation in soft (manual)m34908.50.054Ditch/mitre drain excavation in hard (mechanical)m35008.50.056Ditch/mitre drain excavation in hard (manual)m35108.60.020Culvert installation-300mm with surroundmProvide, lay and joint pipe culvert of 300mm in diameter with surroundProvide, lay and joint unhounched pipe culvert of 300mm in diameterwithout surround39Work Item NameUnitm3m3m3m3mDitch Cleaning46Culvert CleaningClean siltation and debris from gulley pot to good impoundmentconditions.Remove all silt and debris and wash out covered lined drain to free flowconditionsExcavate mechanically for inlet, outfall, mitre and catchwater drains in softmaterialExcavate manualy for inlet, outfall, mitre and catchwater drains in softmaterialExcavate mechanically in hard material for inlet, outfall, mitre andcatchwater drains.Excavate manually in hard material for inlet, outfall, mitre and catchwaterdrains5208.60.021Culvert installation-300mm without surroundm5308.60.022Culvert installation-450mm with surroundmProvide, lay and joint pipe culvert of 450mm in diameter with surround.5408.60.023Culvert installation-450mm without surroundmProvide, lay and joint pipe culvert of 450mm in diameter withoutsurround.5508.60.024Culvert installation-600mm with surroundmProvide, lay and joint pipe culvert of 600mm in diameter with surroundPipe Culvert56 Installation08.60.025Culvert installation-600mm without surroundmProvide, lay and joint pipe culvert of 600mm in diameter without surround5708.60.026Culvert installation-900mm with surroundmProvide, lay and joint pipe culvert of 900mm in diameter with surround.5808.60.027Culvert installation-900mm without surroundmProvide, lay and joint pipe culvert of 900mm in diameter without surround5908.60.028Culvert installation-1200mm with surroundmProvide, lay and joint pipe culvert of 1200mm in diameter with surround60616208.60.02908.60.03008.60.031Culvert installation-1200mm without surroundExcavate in soft material for culvertsExcavate in hard material for culvertsmm3m36308.60.190Headwall construction for 450mm pipe culvertNo08.60.192Headwall construction for 600mm pipe culvertNo6508.60.194Headwall construction for 900mm pipe culvertNo6608.60.196Headwall construction for 1200mm pipe culvertNo08.50.240Manhole construction less than 1mNo6808.50.245Manhole construction more than 1mNo69 Gulley Pot installation08.50.015Gulley pot constructionNo7008.50.140Lay drain lining with concretem208.50.220Laying of dressed stonesm2m2Provide, lay and joint culvert of 1200mm in diameter without surroundExcavation manually in soft material for culvert in any size.Excavation manually in hard material for culvert in any size.Reconstruct or repair damaged headwall (wingwall and apron) for450mm pipe culvert to prevent the collapse and the potential slippage ofthe material and pavement above the culvert.Reconstruct or repair damaged headwall (wingwall and apron) for600mm pipe culvert to prevent the collapse and the potential slip of thematerial and pavement above the culvert.Reconstruct or repair damaged headwall (wingwall and apron) for900mm pipe culvert to prevent the collapse and the potential slip of thematerial and pavement above the culvert.Reconstruct or repair damaged headwall (wingwall and apron) for1200mm pipe culvert to prevent the collapse and the potential slip of thematerial and pavement above the culvert.Install new small manhole of less than 1m in depth (900-1200mm in innerdiameter)Install new large manhole of more than 1m in depth (900-1200mm ininner diameter)Provide and place gulley pots including grating (H 900mm) for inletstructures as directed by the Engineer.Place concrete lining to the slopes and invert of the ditch to prevent thescour.Place dressed stone lining to the slopes and invert of the ditch to preventthe scour.Place side slab lining to the slopes and invert of the ditch to prevent thescour.Provide, lay and joint invert block drain of 300mm in diameterProvide, lay and joint invert block drain of 750mm in width64HeadwallConstruction67Manhole installation71Drain Lining7208.50.225Laying of side slabs737408.60.05008.60.051Laying of 300mm invert block drainLaying of 750mm invert block drainmm14 P a g e
Cost Estimation Manual for Road Maintenance Works 20119. Passage of TrafficNoWork CategoryCodeWork Item NameTraffic ControlUnit7509.50.00476 Traffic Control09.50.005WatchmanNo7709.50.006Wateringm210. Grading and Gravelling WorksNoWork CategoryCode78DayWork Item NameUnit10.50.001Heavy grading without watering or compactionm210.50.002Heavy grading with watering and compactionm28010.50.003Light m210.60.001Regravellingm310.60.001aRegravelling without wateringm379Grading83Gravelling8411. Paved Roads - Shoulder Maintenance and RepairsNoWork CategoryCode85Work Item NameUnit11.50.001Shoulder gradingm211.50.002Shoulder repairingm211.50.030Shoulder gravelling with natural gravelm311.50.035Shoulder gravelling with quarry wastem3Shoulder Rebuilding8687Shoulder Gravelling8812. Natural Material Base and SubbaseNoWork CategoryCodeWork Item NameUnit89 Pavement Removal12.70.001Scarify existing pavement to form subbasem39012.50.001Handpacked stone pavingm39112.50.020Provide, place and compact quarry wastem392 Base Rebuilding12.50.002Provide, place, spread and compact natural gravelm3Subbase Rebuilding13. Graded Crushed Stone Base and SubbaseNoWork CategoryCodeWork Item NameGraded Crushed9313.50.002 Graded Crushed Stone for subbaseStone9413.50.003 Graded Crushed Stone for baseUnitDescriptionPlace warning signs, barriers and cones around the working lane on thecarriageway and guide the passage of traffic through the worksProvide watchman for all round surveillance.Sprinkle water to control dust for passage of traffic through the works orcompaction at earth worksDescriptionTrim with Motor Grader or heavy towed grader existing carriagewaysurface to camber, including slopes and ditches without providingwatering and compactionTrim with Motor Grader or heavy towed grader existing carriagewaysurface to camber, including slopes and di
to standardise the cost estimation of road maintenance countrywide. The introduction of this manual is noble since it will contain instructions for estimating price of maintenance works for bidding price in any part of the country. This manual will also guide the respective Authoritie