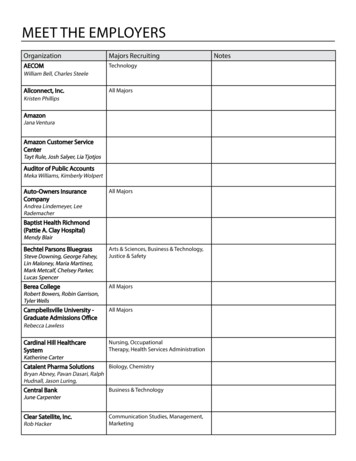
Transcription
MEETYOURDIGITALMASTERA guide totransformingmasterdata in thedigital age.
As we journey througha digital era, traditionalMaster Data Management(MDM) is increasinglyunable to serve emergingbusiness and applicationrequirements. There isa need to expand therealm of master datato create value asbusiness applicationsget a digital makeover.Traditionally, master data has focused onestablishing a few attributes of a criticalbusiness entity extracted from transactionalsystems to create a high-quality versionof the truth. A lot of time and money hasbeen invested into this, primarily for drivingconsistency of business reporting.This traditional approach has an increasinglylimited impact in the digital age. The characteristicsof data are evolving rapidly and today’s businessneeds have become more granular and requirenear real-time responses. Data is not simplyconfined to structured, internally-generatedtransactional data but now spans heterogeneous,machine-generated, unstructured and alsoexternally-sourced datasets.The changing needs and evolving data,combined with the advent of analytics, machinelearning and cognitive technologies haveopened up new possibilities. Traditionally slowand selective master data can now be mademore comprehensive, varied and insightspowered to provide a near real-time view ofcritical business entities. This expanded viewnot only supports quality business reportingbut can actually start supporting transactionaldigital applications, making real-time decisionsby leveraging the “new” master data attributes.Master data now, more than ever before,needs to be highly business outcome focused,adaptable and scalable across the enterprise.In this article, we look at how to evolve beyond atraditional MDM to a “Digital Master”, an enterprisethat is near real-time, analytically-powered anddirectly influences business transactions in adigital world. The end result is business processesthat consistently deliver tangible outcomes andimpacts, powered by these master entities.Meet Your Digital Master2
Contents4 Then and Now10 Shift from Golden Recordto Golden Profile15 The Contextual and AnalyticalElements of a Digital Master18 Laying the Foundation fora Digital Master21 Architecting the Digital Master24 Exploring the ArchitecturalComponents28 Digital MasterPowered Business32 Deploying the Digital Master36 Transitioning to the New39 ConclusionMeet Your Digital Master3
Then and NowMDM has traditionally been the framework ofprocesses and technologies aimed at creating andmaintaining an authoritative, reliable, sustainable,accurate, timely and secure data environment.Meet Your Digital Master4
Master DataMaster data is the consistent and uniformcore dataset within an enterprise that describesentities around which business is conducted.Master data includes hierarchical or dimensionaldata that categorizes core objects of businessfor analytical or reporting purposes.Increasingly a business requires masterentities to support analytical applications andnot just serve as a reference. This dynamic viewof master data requires probabilistic inferenceof data characteristics, which leads to profilesrather than records.This definition, accurate as it is in the contextof traditional MDM, is limiting in the digital age.The “consistent and uniform” designation impliesthat the data represents the single version of thetruth, i.e. a golden record. However, it does notcover external data sources that provide contextin a dynamic manner. Secondly, it also impliesthat the data is infrequently changed. Is thatreally a positive feature in the digital age?Thirdly, this definition does not refer tothe interactions and relationships that existwithin the data entities across an enterprise.The focus is on logical and integrated modelsof structured datasets. In the digital age,datasets now increasingly include unstructureddata in batch, real-time and interactive modesrequiring contextual analytical models.Meet Your Digital Master5
ChallengesOrganizations should reconcile investment in traditional MDMto help meet their business needs with digital transformationthat makes use of evolving MDM capabilities. Many recent MDMprojects have fallen short of delivering on their full potential.There could be several factors behind this, such as: Implementations can take too longand cost too much. Project scope is often much too large. Business and IT teams are sometimes poorlycoordinated for achieving the desired end state. Traditional approaches can lag inkeeping up with new technologies. Creating a data governance frameworkand measuring and resolving data qualityissues can be difficult. Scaling MDM solutions to deal with thevolume and complexity of data (especiallywith increased use of unstructured,digital data) can be a challenge. Solutions can delay inclusion of newdata sources.Meet Your Digital Master6
New Digital DemandsFrom our point of view, the back office-drivenapproach runs contrary to the way the businessand its employees need to function if they areto achieve their goals and objectives.In Case Study 2 on the following page, theorganization wanted to recognize consumersas individuals wherever they interacted withthe company and connect this identificationwith intelligence which could enhance thecustomer experience and increase earnings.The approach needed to be transformational andevolutionary. Transformational in the sense that wesee more overtly business-defined approachesthat enable the technologies underlying MDM.Evolutionary because we see the expansionof the meaning of MDM in the digital age.These business-defined approaches usually reflect thecomplex, sophisticated needs of many organizations: Working from the desired end state and/or from therequirements of complex business problems. Choosing contextual and analytic solutions over traditionalMDM tools that can handle new approaches for multi-dimensionaland complex hierarchical data, including social and commercialgraphs that underlie digital business use cases. Utilizing new technologies that simplify the developmentof industry-focused business applications that take advantageof master data to help solve business problems. Transforming model-driven approaches to be more flexibleand agile so they can work with existing business processes(instead of creating new processes) and help deliver businessvalue. IT and business teams can then transition to optimizingvarious processes for additional value.Meet Your Digital Master7
Case Study 1:Case Study 2:A life sciences company was severely held back frompromoting drugs to individual healthcare organizations.An organization in the travel industry found it very difficultto combine consumer data with visit and hotel informationusing their traditional solution. They could not recognizecustomers without authentication nor anonymous visitorsto their websites. Call centers did not have visibility intoconsumer profiles or prior consumer touchpoints andhad limited ability to update customer preferences.They were limited to a few offers and did not havethe ability to customize based on recent activity.The traditional solution made it difficult to pull togethercritical master data such as: Which insurance companies or payers accepted bythe healthcare organization actually cover the drugs. And for those payers, which insurance plans provide coverage. What other sales teams in the same company were alreadypromoting to the healthcare organization. Attributes that derive from complex hierarchies andnetworks of relationships. What contracts for the pharmaceuticals companywere already in place.Only after incorporating changes to enable the Digital Mastercould the sales team determine if any business opportunitiesexisted before actually having to approach a healthcare target.Meet Your Digital Master8
The Changing Face of DataIn addition to the evolving requirements, the data has changedsignificantly and with it the resulting disruption from digitaldata on traditional MDM capabilities. If we take a few of thesecapabilities and drill down, it quickly becomes clear thattraditional methods are not sufficient.For example, match and merge for digital data is too complex,with a wide variety of digital datasets that run too slowly withtoday’s data volumes. Hierarchical management is too complex,especially considering the nature of digital data with itsinterrelated complex data relationships and formats.Furthermore, most enterprise data is either unstructured orsemi-structured. New techniques are required to adequatelycapture, curate and store these types of data. These data typesalso require different strategies for metadata capture andmanagement. Matching and merging these types of data usuallyrequire not only deterministic, but probabilistic and fuzzy matchingalgorithms. These probabilistic matching and merging methods enablethe contextual and analytical models necessary for dynamic profiles.Case Study 3:In a recent project, a hospitality company embarked ona digital data platform project with Accenture to ensurethat digital master data consumption use cases weremet. The digital data platform provided the foundationto capture, curate, process and store emerging datatypes. The objective was to drastically improve customerexperience, retain loyal customers, prevent churn andincrease market share through personalization andtruly understanding customers.Only after incorporating these digital changes was theorganization able to recognize individuals at any touchpointacross channels and enrich their view with intelligentinsights. By using a Digital Master that provides a 360-degreeview, they have begun the journey to a smarter experiencefor their customers, generating increased earnings andsignificant business uplift.Meet Your Digital Master9
Shift fromGolden Recordto Golden ProfileExamining the MDM landscape reveals a shift fromgolden records to golden profiles powered by online,transactional and dynamic data characteristics.We could say that there are two fundamental drivers.The first is the new onus placed on master data, andthe second is the changing nature of digital data.Meet Your Digital Master10
ResetTraditional MDM focused on establishing a sanitized single version of the truth. The process usually involvedidentifying missing or erroneous entries in highly structured datasets, eliminating duplicate records whileintegrating multiple data sources. While this is still vital, its value alone has diminished in the digital era.The new Digital Master needs to accommodate the evolving requirements and emerging digital data.RethinkThe general consensus is that these evolving requirementsare becoming more granular and real-time in nature, inaddition to being much more context and insight driven.There is a shift from traditional golden records to dynamicgolden profiles. This also stems from the need to empowerbusiness users to be able to consume more data andenable patterns that allow for self-service.golden records by validating and eliminating duplicatesand integrating multiple MDM solutions. Changes in databecome rather obvious.This evolution from back office IT-centric golden recordsto business user-centric golden profiles has resulted inthe need for complementary models. Integration andlogical models (associated with traditional MDM) produceThese two drivers have given rise to aspirations to modifyor augment traditional MDM to achieve a more completeand dynamic view of data entities. The requirements ofMDM have evolved in the era of digital data and data lakes.We are now producing an unprecedented amount ofdata, including digital data sources, machine-generated,unstructured, semi-structured and streaming data.Meet Your Digital Master11
Figure 1: Contrast Between Golden Record and Golden ProfileGolden RecordTraditional MDMGolden ProfileNew Digital MasterThe asks (requirements)The asks (requirements)Identify missing or erroneous entriesValidate addresses or phone numbersEliminate duplicate recordsCleanse names and addressesIntegrate multiple-point MDM solutionsExpand to context and insightsProvide data insights directly to end usersSupport real-time solutions with capabilitiesAccommodate big data sourcesCreate a 360-degree view from dataThe solution modelsThe solution modelsIntegration Logical ModelsContextual Analytical ModelsCopyright 2019 Accenture. All rights reserved.Meet Your Digital Master12
Re-ImagineContextual and Analytical Models are nowemployed to help accommodate these newdrivers and to help evolve and transform theDigital Master. These models associated withthe new Digital Master produce a goldenprofile by providing data insights directlyto end users, supporting real-time decisionmaking and leveraging digital data sourcesto create a 360-degree view. So, the questionthen is, what is this golden profile, and howis it different from a golden record?Figure 2 represents a customer dataentry used in a recent digital master dataimplementation that Accenture conductedfor an insurance firm. The key objective wasfraud prevention. The company alreadyhad the traditional golden record.Figure 2: Customer Data EntityThird-partyInformationCredit scoreProfessional affiliationsMembershipsLiensPublic recordsTraditionalGolden RecordNameAddressPhoneAgeJane Doe1 Accenture RoadDallas, TX 00000777-777-777736UnstructuredInternal DataUnstructuredExternal DataCall center conversationsPoint of sale dataClick streamNetwork dataConversationsReviewsTweets/BlogsImages and picturesVideosCopyright 2019 Accenture. All rights reserved.Meet Your Digital Master13
This customer data entity goes further than traditional dataattributes to provide a meaningful context and a panoramicview of critical data entities beyond just attributes (or what youget from the golden records). It provides dynamic actionableinsights in real-time from other sources like unstructuredinternal and external data and third-party sources.These additional data s
not just serve as a reference. This dynamic view of master data requires probabilistic inference of data characteristics, which leads to profiles rather than records. Thirdly, this definition does not refer to the interactions and relationships that exist within the data entities across an enterprise.