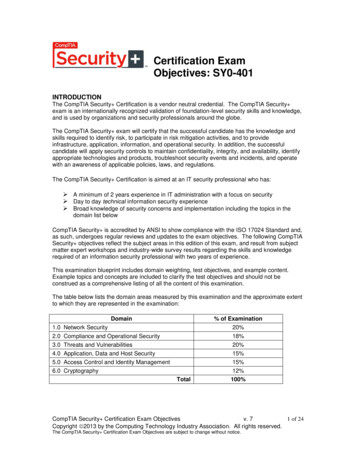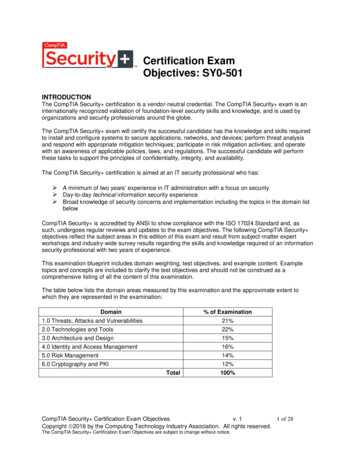
Transcription
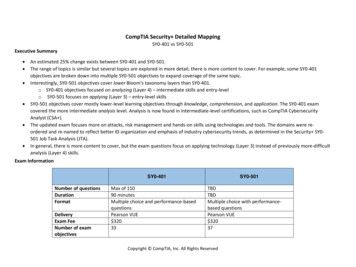
CompTIA Security Detailed MappingSY0-401 vs SY0-501Executive Summary An estimated 25% change exists between SY0-401 and SY0-501.The range of topics is similar but several topics are explored in more detail; there is more content to cover. For example, some SY0-401objectives are broken down into multiple SY0-501 objectives to expand coverage of the same topic.Interestingly, SY0-501 objectives cover lower Bloom’s taxonomy layers than SY0-401.o SY0-401 objectives focused on analyzing (Layer 4) – intermediate skills and entry-levelo SY0-501 focuses on applying (Layer 3) – entry-level skillsSY0-501 objectives cover mostly lower-level learning objectives through knowledge, comprehension, and application. The SY0-401 examcovered the more intermediate analysis level. Analysis is now found in intermediate-level certifications, such as CompTIA CybersecurityAnalyst (CSA ).The updated exam focuses more on attacks, risk management and hands-on skills using technologies and tools. The domains were reordered and re-named to reflect better ID organization and emphasis of industry cybersecurity trends, as determined in the Security SY0501 Job Task Analysis (JTA).In general, there is more content to cover, but the exam questions focus on applying technology (Layer 3) instead of previously more-difficultanalysis (Layer 4) skills.Exam InformationSY0-401Number of questionsDurationFormatDeliveryExam FeeNumber of examobjectivesMax of 11090 minutesMultiple choice and performance-basedquestionsPearson VUE 32033SY0-501TBDTBDMultiple choice with performancebased questionsPearson VUE 32037Copyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Exam Overview ComparisonSY0-401SY0-501The CompTIA Security certification is a vendor-neutral, internationallyrecognized credential used by organizations and security professionals aroundthe globe to validate foundation level security skills and knowledge.Candidates are encouraged to use this document to help prepare for CompTIASecurity SY0-401, which measures necessary skills for IT securityprofessionals.Successful candidates will have the knowledge required to: Identify risk Participate in risk mitigation activities Provide infrastructure, application, information and operational security Apply security controls to maintain confidentiality, integrity and availability Identify appropriate technologies and products Troubleshoot security events and incidents Operate with an awareness of applicable policies, laws and regulationsThe CompTIA Security certification is a vendor-neutral credential. TheCompTIA Security exam is an internationally recognized validation offoundation-level security skills and knowledge, and is used by organizationsand security professionals around the globe.The CompTIA Security exam will certify the successful candidate has theknowledge and skills required to install and configure systems to secureapplications, networks, and devices; perform threat analysis and respond withappropriate mitigation techniques; participate in risk mitigation activities; andoperate with an awareness of applicable policies, laws, and regulations. Thesuccessful candidate will perform these tasks to support the principles ofconfidentiality, integrity, and availability.Sample Job RolesSY0-401Security or Systems AdministratorNetwork AdministratorSecurity Specialist/AdministratorSecurity ConsultantSY0-501Systems AdministratorNetwork AdministratorSecurity AdministratorJunior IT Auditor/Penetration TesterCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Domain ComparisonSY0-401 DomainsSY0-501 Domain Equivalent1.0 Network Security20%2.0 Technologies and Tools22%2.0 Compliance and Operational Security18%5.0 Risk Management14%3.0 Threats and Vulnerabilities20%1.0 Threats, Attacks and Vulnerabilities21%4.0 Application, Data and Host Security15%3.0 Architecture and Design15%5.0 Access Control and Management15%4.0 Identity and Access Management16%6.0 Cryptography12%6.0 Cryptography and PKI12%SummaryCompTIA expects a smooth transition from SY0-401 to SY0-501. The purpose of the exam has not changed. Security continues to provide the universal baselinefor entry-level cybersecurity skills needed throughout the globe. SY0-501 provides the latest technology and industry job skills to mirror the changing world ofcybersecurity skills. It is anticipated that Security will continue to raise the standard for cybersecurity professionals worldwide.Objective by Objective Mapping (starts on next page)Copyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Objective ComparisonSY0-401SY0-5011.1 Implement security configuration parameters on network devicesand other technologies. Firewalls Routers Switches Load balancers Proxies Web security gateways VPN concentrators NIDS and NIPS- Behavior-based- Signature-based- Anomaly-based- Heuristic Protocol analyzers Spam filter UTM security appliances- URL filter- Content inspection- Malware inspection Web application firewallvs. network firewall Application aware devices- Firewalls- IPS- IDS- Proxies2.1 Install and configure network components, both hardware- andsoftware-based, to support organizational security. Firewallo ACLo Application-based vs. network-basedo Stateful vs. statelesso Implicit deny VPN concentratoro Remote access vs. site-to-siteo IPSec Tunnel modeo Dissolvable vs. permanento Host health checkso Agent vs. agentless Mail gatewayo Spam filtero DLPo Encryption Bridge SSL/TLS accelerators SSL decryptors Media gateway Hardware security module1.2 Given a scenario, use secure network administration principles.Copyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Rule-based management Firewall rules VLAN management Secure router configuration Access control lists Port security 802.1x Flood guards Loop protection Implicit deny Network separation Log analysis Unified threat management1.3 Explain network design elements and components. DMZ Subnetting VLAN NAT Remote access Telephony NAC Virtualization Cloud computing- PaaS- SaaS2.1 Install and configure network components, both hardware- andsoftware-based, to support organizational security. Firewallo ACLo Application-based vs. network-basedo Stateful vs. statelesso Implicit deny VPN concentratoro Remote access vs. site-to-siteo IPSec Tunnel modeo Dissolvable vs. permanento Host health checkso Agent vs. agentless Mail gatewayo Spam filtero DLPo Encryption Bridge SSL/TLS accelerators SSL decryptors Media gateway Hardware security module3.2 Given a scenario, implement secure network architecture concepts. Zones/topologieso DMZo Extraneto Intraneto Wirelesso Guesto Honeynetso NATo Ad hoc Segregation/segmentation/isolationo PhysicalCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
- IaaS- Private- Public- Hybrid- Community Layered security/defense in deptho Logical (VLAN)o Virtualizationo Air gaps Tunneling/VPNo Site-to-siteo Remote access Security device/technology placemento Sensorso Collectorso Correlation engineso Filterso Proxieso Firewallso VPN concentratorso SSL acceleratorso Load balancerso DDoS mitigatoro Aggregation switcheso Taps and port mirror SDN1.4 Given a scenario, implement common protocols and services.2.6 Given a scenario, implement secure protocols. Protocols Protocols- IPSeco DNSSEC- SNMPo SSH- SSHo S/MIME- DNSo SRTP- TLSo LDAPS- SSLo FTPS- TCP/IPo SFTP- FTPSo SNMPv3- HTTPSo SSL/TLS- SCPo HTTPS- ICMPo Secure POP/IMAP- IPv4 Use casesCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
- IPv6- iSCSI- Fibre Channel- FCoE- FTP- SFTP- TFTP- TELNET- HTTP- NetBIOS Ports- 21- 22- 25- 53- 80- 110- 139- 143- 443- 3389 OSI relevanceo Voice and videoo Time synchronizationo Email and webo File transfero Directory serviceso Remote accesso Domain name resolutiono Routing and switchingo Network address allocationo Subscription services1.5 Given a scenario, troubleshoot security issues related to wireless6.3 Given a scenario, install and configure wireless security settings.networking. Cryptographic protocols WPAo WPA WPA2o WPA2 WEPo CCMP EAPo TKIP PEAP Authentication protocols LEAPo EAP MAC filtero PEAP Disable SSID broadcasto EAP-FAST TKIPo EAP-TLS CCMPo EAP-TTLSCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Antenna placement Power level controls Captive portals Antenna types Site surveys VPN (over open wireless)2.1 Explain the importance of risk related concepts. Control types- Technical- Management- Operational False positives False negatives Importance of policies in reducing risk- Privacy policy- Acceptable use- Security policy- Mandatory vacations- Job rotation- Separation of duties- Least privilege Risk calculation- Likelihood- ALE- Impact- SLE- ARO- MTTR- MTTF- MTBF Quantitative vs. qualitative Vulnerabilities Threat vectors Probability/threat likelihoodo IEEE 802.1xo RADIUS Federation Methodso PSK vs. Enterprise vs. Openo WPSo Captive portals5.1 Explain the importance of policies, plans and procedures related toorganizational security. Standard operating procedure Agreement typeso BPAo SLAo ISAo MOU/MOA Personnel managemento Mandatory vacationso Job rotationo Separation of dutieso Clean desko Background checkso Exit interviewso Role-based awareness training Data owner System administrator System owner User Privileged user Executive usero NDAo Onboardingo Continuing educationo Acceptable use policy/rules of behavioro Adverse actions General security policiesCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Risk avoidance, transference,acceptance, mitigation, deterrence Risks associated with cloudcomputing and virtualization Recovery time objective andrecovery point objectiveo Social media networks/applicationso Personal email5.2 Summarize business impact analysis concepts. RTO/RPO MTBF MTTR Mission-essential functions Identification of critical systems Single point of failure Impacto Lifeo Propertyo Safetyo Financeo Reputation Privacy impact assessment Privacy threshold assessment2.2 Summarize the security implications of integrating systems and data 3.1 Explain use cases and purpose for frameworks, best practices andwith third parties.secure configuration guides. On-boarding/off-boarding Industry-standard frameworks and reference architecturesbusiness partnerso Regulatory Social media networks and/or applicationso Non-regulatory Interoperability agreementso National vs. international- SLAo Industry-specific frameworks- BPA Benchmarks/secure configuration guides- MOUo Platform/vendor-specific guides- ISA Web server Privacy considerations Operating system Risk awareness Application server Unauthorized data sharing Network infrastructure devices Data ownershipo General purpose guides Data backups Defense-in-depth/layered security Follow security policy and procedureso Vendor diversityCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Review agreement requirements to verifycompliance and performance standardso Control diversity Administrative Technicalo User training5.1 Explain the importance of policies, plans and procedures related toorganizational security. Standard operating procedure Agreement typeso BPAo SLAo ISAo MOU/MOA Personnel managemento Mandatory vacationso Job rotationo Separation of dutieso Clean desko Background checkso Exit interviewso Role-based awareness training Data owner System administrator System owner User Privileged user Executive usero NDAo Onboardingo Continuing educationo Acceptable use policy/rules of behavioro Adverse actions General security policieso Social media networks/applicationso Personal emailCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
2.3 Given a scenario, implement appropriate risk mitigation strategies. Change management Incident management User rights and permissions reviews Perform routine audits Enforce policies and proceduresto prevent data loss or theft Enforce technology controls- Data Loss Prevention (DLP)5.3 Explain risk management processes and concepts. Threat assessmento Environmentalo Manmadeo Internal vs. external Risk assessmento SLEo ALEo AROo Asset valueo Risk registero Likelihood of occurrenceo Supply chain assessmento Impacto Quantitativeo Qualitativeo Testing Penetration testing authorization Vulnerability testing authorizationo Risk response techniques Accept Transfer Avoid Mitigate Change management2.4 Given a scenario, implement basic forensic procedures.5.5 Summarize basic concepts of forensics. Order of volatility Order of volatility Capture system image Chain of custody Network traffic and logs Legal hold Capture video Data acquisition Record time offseto Capture system image Take hasheso Network traffic and logs Screenshotso Capture videoCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Witnesses Track man hours and expense Chain of custody Big Data analysis2.5 Summarize common incident response procedures. Preparation Incident identification Escalation and notification Mitigation steps Lessons learned Reporting Recovery/reconstitution procedures First responder Incident isolation- Quarantine- Device removal Data breach Damage and loss controlo Record time offseto Take hasheso Screenshotso Witness interviews Preservation Recovery Strategic intelligence/counterintelligence gatheringo Active logging Track man-hours5.4 Given a scenario, follow incident response procedures. Incident response plano Documented incident types/category definitionso Roles and responsibilitieso Reporting requirements/escalationo Cyber-incident response teamso Exercise Incident response processo Preparationo Identificationo Containmento Eradicationo Recoveryo Lessons learned2.6 Explain the importance of security related awareness and training.5.1 Explain the importance of policies, plans and procedures related to Security policy training and proceduresorganizational security. Role-based training Standard operating procedure Personally identifiable information Agreement types Information classificationo BPA- Higho SLA- Mediumo ISA- Lowo MOU/MOA- Confidential Personnel management- Privateo Mandatory vacationsCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
- Public Data labeling, handling and disposal Compliance with laws, bestpractices and standards User habits- Password behaviors- Data handling- Clean desk policies- Prevent tailgating- Personally owned devices New threats and newsecurity trends/alerts- New viruses- Phishing attacks- Zero-day exploits Use of social networking and P2P Follow up and gather training metrics to validate complianceand security postureo Job rotationo Separation of dutieso Clean desko Background checkso Exit interviewso Role-based awareness training Data owner System administrator System owner User Privileged user Executive usero NDAo Onboardingo Continuing educationo Acceptable use policy/rules of behavioro Adverse actions General security policieso Social media networks/applicationso Personal email5.8 Given a scenario, carry out data security and privacy practices. Data destruction and media sanitizationo Burningo Shreddingo Pulpingo Pulverizingo Degaussingo Purgingo Wiping Data sensitivity labeling and handlingo Confidentialo Privateo Publico Proprietaryo PIICopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
o PHI Data roleso Ownero Steward/custodiano Privacy officer Data retention Legal and compliance2.7 Compare and contrast physical security and environmental controls. 3.5 Explain the security implications of embedded systems. Environmental controls SCADA/ICS- HVAC Smart devices/IoT- Fire suppressiono Wearable technology- EMI shieldingo Home automation- Hot and cold aisles HVAC- Environmental monitoring SoC- Temperature and humidity controls RTOS Physical security Printers/MFDs- Hardware locks Camera systems- Mantraps Special purpose- Video surveillanceo Medical devices- Fencingo Vehicles- Proximity readerso Aircraft/UAV- Access list- Proper lighting3.9 Explain the importance of physical security controls.- Signs Lighting- Guards Signs- Barricades Fencing/gate/cage- Biometrics Security guards- Protected distribution (cabling) Alarms- Alarms Safe- Motion detection Secure cabinets/enclosures Control types Protected distribution/Protected cabling- Deterrent Airgap- Preventive Mantrap- Detective Faraday cageCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
- Compensating- Technical- Administrative Lock types Biometrics Barricades/bollards Tokens/cards Environmental controlso HVACo Hot and cold aisleso Fire suppression Cable locks Screen filters Cameras Motion detection Logs Infrared detection Key management5.7 Compare and contrast various types of controls. Deterrent Preventive Detective Corrective Compensating Technical Administrative Physical2.8 Summarize risk management best practices. Business continuity concepts- Business impact analysis- Identification of criticalsystems and components- Removing single points of failure- Business continuityplanning and testing- Risk assessment3.8 Explain how resiliency and automation strategies reduce risk. Automation/scriptingo Automated courses of actiono Continuous monitoringo Configuration validation Templates Master image Non-persistenceo SnapshotsCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
- Continuity of operations- Disaster recovery- IT contingency planning- Succession planning- High availability- Redundancy- Tabletop exercises Fault tolerance- Hardware- RAID- Clustering- Load balancing- Servers Disaster recovery concepts- Backup plans/policies- Backup execution/frequency- Cold site- Hot site- Warm siteo Revert to known stateo Rollback to known configurationo Live boot media Elasticity Scalability Distributive allocation Redundancy Fault tolerance High availability RAID5.6 Explain disaster recovery and continuity of operation concepts. Recovery siteso Hot siteo Warm siteo Cold site Order of restoration Backup conceptso Differentialo Incrementalo Snapshotso Full Geographic considerationso Off-site backupso Distanceo Location selectiono Legal implicationso Data sovereignty Continuity of operation planningo Exercises/tabletopo After-action reportso Failovero Alternate processing siteso Alternate business practicesCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
2.9 Given a scenario, select the appropriate control to meet the goals ofsecurity. Confidentiality- Encryption- Access controls- Steganography Integrity- Hashing- Digital signatures- Certificates- Non-repudiation Availability- Redundancy- Fault tolerance- Patching Safety- Fencing- Lighting- Locks- CCTV- Escape plans- Drills- Escape routes- Testing controls3.1 Explain types of malware. Adware Virus Spyware Trojan Rootkits Backdoors3.9 Explain the importance of physical security controls. Lighting Signs Fencing/gate/cage Security guards Alarms Safe Secure cabinets/enclosures Protected distribution/Protected cabling Airgap Mantrap Faraday cage Lock types Biometrics Barricades/bollards Tokens/cards Environmental controlso HVACo Hot and cold aisleso Fire suppression Cable locks Screen filters Cameras Motion detection Logs Infrared detection Key management1.1 Given a scenario, analyze indicators of compromise and determinethe type of malware. Viruses Crypto-malware Ransomware Worm TrojanCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Logic bomb Botnets Ransomware Polymorphic malware Armored virus3.2 Summarize various types of attacks. Man-in-the-middle DDoS DoS Replay Smurf attack Spoofing Spam Phishing Spim Vishing Spear phishing Xmas attack Pharming Privilege escalation Malicious insider threat DNS poisoning and ARP poisoning Transitive access Client-side attacks Password attacks- Brute force- Dictionary attacks- Hybrid- Birthday attacks- Rainbow tables Typo squatting/URL hijacking Rootkit Keylogger Adware Spyware Bots RAT Logic bomb Backdoor1.2 Compare and contrast types of attacks. Application/service attackso DoSo DDoSo Man-in-the-middleo Buffer overflowo Injectiono Cross-site scriptingo Cross-site request forgeryo Privilege escalationo ARP poisoningo Amplificationo DNS poisoningo Domain hijackingo Man-in-the-browsero Zero dayo Replayo Pass the hasho Hijacking and related attacks Clickjacking Session hijacking URL hijacking Typo squattingo Driver manipulation Shimming RefactoringCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Watering hole attacko MAC spoofingo IP spoofing Cryptographic attackso Birthdayo Known plain text/cipher texto Rainbow tableso Dictionaryo Brute force Online vs. offlineo Collisiono Downgradeo Replayo Weak implementations3.3 Summarize social engineering attacks and the associatedeffectiveness with each attack. Shoulder surfing Dumpster diving Tailgating Impersonation Hoaxes Whaling Vishing Principles (reasons for effectiveness)- Authority- Intimidation- Consensus/social proof- Scarcity- Urgency- Familiarity/liking- Trust1.2 Compare and contrast types of attacks. Social engineeringo Phishingo Spear phishingo Whalingo Vishingo Tailgatingo Impersonationo Dumpster divingo Shoulder surfingo Hoaxo Watering hole attacko Principles (reasons for effectiveness) Authority Intimidation Consensus Scarcity Familiarity Trust UrgencyCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
3.4 Explain types of wireless attacks. Rogue access points Jamming/interference Evil twin War driving Bluejacking Bluesnarfing War chalking IV attack Packet sniffing Near field communication Replay attacks WEP/WPA attacks WPS attacks3.5 Explain types of application attacks. Cross-site scripting SQL injection LDAP injection XML injection Directory traversal/command injection Buffer overflow Integer overflow Zero-day Cookies and attachments Locally Shared Objects (LSOs) Flash cookies Malicious add-ons Session hijacking Header manipulation Arbitrary code execution/1.2 Compare and contrast types of attacks. Wireless attackso Replayo IVo Evil twino Rogue APo Jammingo WPSo Bluejackingo Bluesnarfingo RFIDo NFCo Disassociation1.2 Compare and contrast types of attacks. Application/service attackso DoSo DDoSo Man-in-the-middleo Buffer overflowo Injectiono Cross-site scriptingo Cross-site request forgeryo Privilege escalationo ARP poisoningo Amplificationo DNS poisoningo Domain hijackingo Man-in-the-browsero Zero dayo Replayo Pass the hasho Hijacking and related attacksCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
3.6 Analyze a scenario and select the appropriate type of mitigation anddeterrent techniques. Monitoring system logs- Event logs- Audit logs- Security logs- Access logs Hardening- Disabling unnecessary services- Protecting managementinterfaces and applications- Password protection- Disabling unnecessary accounts Network security- MAC limiting and filtering- 802.1x- Disabling unused interfacesand unused application service ports- Rogue machine detection Security posture- Initial baseline configuration- Continuous security monitoring- Remediation Reporting- Alarms- Alerts- Trends Detection controls vs. prevention controls- IDS vs. IPS- Camera vs. guard2.3 Given a scenario, troubleshoot common security issues. Unencrypted credentials/clear text Logs and events anomalies Permission issues Access violations Certificate issues Data exfiltration Misconfigured deviceso Firewallo Content filtero Access points Weak security configurations Personnel issueso Policy violationo Insider threato Social engineeringo Social mediao Personal email Unauthorized software Baseline deviation License compliance violation (availability/integrity) Asset management Authentication issuesCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
3.7 Given a scenario, use appropriate tools and techniques to discoversecurity threats and vulnerabilities. Interpret results of security assessment tools Tools- Protocol analyzer- Vulnerability scanner- Honeypots- Honeynets- Port scanner- Passive vs. active tools- Banner grabbing Risk calculations- Threat vs. likelihood Assessment types- Risk- Threat- Vulnerability Assessment technique- Baseline reporting- Code review- Determine attack surface- Review architecture- Review designs2.2 Given a scenario, use appropriate software tools to assess thesecurity posture of an organization. Protocol analyzer Network scannerso Rogue system detectiono Network mapping Wireless scanners/cracker Password cracker Vulnerability scanner Configuration compliance scanner Exploitation frameworks Data sanitization tools Steganography tools Honeypot Backup utilities Banner grabbing Passive vs. active Command line toolso pingo netstato tracerto nslookup/digo arpo ipconfig/ip/ifconfigo tcpdumpo nmapo netcat3.8 Explain the proper use of penetration testing versus vulnerability1.4 Explain penetration testing concepts.scanning. Active reconnaissance Penetration testing Passive reconnaissance- Verify a threat exists Pivot- Bypass security controls Initial exploitation- Actively test security controls Persistence- Exploiting vulnerabilities Escalation of privilegeCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Vulnerability scanning- Passively testing security controls- Identify vulnerability- Identify lack of security controls- Identify common misconfigurations- Intrusive vs. non-intrusive- Credentialed vs. non-credentialed- False positive Black box White box Gray box Black box White box Gray box Pen testing vs. vulnerability scanning1.5 Explain vulnerability scanning concepts. Passively test security controls Identify vulnerability Identify lack of security controls Identify common misconfigurations Intrusive vs. non-intrusive Credentialed vs. non-credentialed False positive5.3 Explain risk management processes and concepts. Threat assessmento Environmentalo Manmadeo Internal vs. external Risk assessmento SLEo ALEo AROo Asset valueo Risk registero Likelihood of occurrenceo Supply chain assessmento Impacto Quantitativeo Qualitativeo Testing Penetration testing authorization Vulnerability testing authorizationo Risk response techniques Accept TransferCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Avoid Mitigate Change management4.1 Explain the importance of application security controls andtechniques.Fuzzing Secure coding concepts- Error and exception handling- Input validation Cross-site scripting prevention Cross-site Request Forgery(XSRF) prevention Application configurationbaseline (proper settings) Application hardening Application patch management NoSQL databases vs. SQL databases Server-side vs. client-side validation3.6 Summarize secure application development and deploymentconcepts. Development life-cycle modelso Waterfall vs. Agile Secure DevOpso Security automationo Continuous integrationo Baseliningo Immutable systemso Infrastructure as code Version control and change management Provisioning and deprovisioning Secure coding techniqueso Proper error handlingo Proper input validationo Normalizationo Stored procedureso Code signingo Encryptiono Obfuscation/camouflageo Code reuse/dead codeo Server-side vs. client-side execution and validationo Memory managemento Use of third-party libraries and SDKso Data exposure Code quality and testingo Static code analyzerso Dynamic analysis (e.g., fuzzing)o Stress testingo Sandboxingo Model verificationCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Compiled vs. runtime code4.2 Summarize mobile security concepts and technologies.2.5 Given a scenario, deploy mobile devices securely. Device security Connection methods- Full device encryptiono Cellular- Remote wipingo WiFi- Lockouto SATCOM- Screen lockso Bluetooth- GPSo NFC- Application controlo ANT- Storage segmentationo Infrared- Asset trackingo USB- Inventory control Mobile device management concepts- Mobile device managemento Application management- Device access controlo Content management- Removable storageo Remote wipe- Disabling unused featureso Geofencing Application securityo Geolocation- Key managemento Screen locks- Credential managemento Push notification services- Authenticationo Passwords and pins- Geo-taggingo Biometrics- Encryptiono Context-aware authentication- Application whitelistingo Containerization- Transitive trust/authenticationo Storage segmentation BYOD concernso Full device encryption- Data ownership Enforcement and monitoring for:- Support ownershipo Third-party app stores- Patch managemento Rooting/jailbreaking- Antivirus managemento Sideloading- Forensicso Custom firmware- Privacyo Carrier unlocking- On-boarding/off-boardingo Firmware OTA updates- Adherence to corporate policieso Camera use- User acceptanceo SMS/MMSCopyright CompTIA, Inc. All Rights Reserved
- Architecture/infrastructureconsiderations- Legal concerns- Acceptable use policy- On-board camera/videoo External mediao USB OTGo Recording microphoneo GPS taggingo WiFi direct/ad hoco Tetheringo Payment methods Deployment modelso BYODo COPEo CYODo Corporate-ownedo VDI4.3 Given a scenario, select the appropriate solution to establish host2.3 Given a scenario, troubleshoot common security issues.security. Unencrypted credentials/clear text Operating system security and settings Logs and events anomalies OS hardening Permission issues Anti-malware Access violations- Antivirus Certificate issues- Anti-spam Data exfiltration- Anti-spyware Misconfigured devices- Pop-up blockerso Firewall Patch managemento Content filter Whitelisting vs. blacklisting applicationso Access points Trusted OS Weak security configurations Host-based firewalls Personnel issues Host-based intrusion detectiono Policy violation Hardware securityo Insider threat- Cable lockso Social engineering- Safeo Social media- Locking cabinetso Personal email Host software baselining Unauthorized software Virtualization Baseline deviation- Snapshots License compliance violation (availability
CompTIA Security Detailed Mapping SY0-401 vs SY0-501 Executive Summary . CompTIA Security exam is an internationally recognized validation of foundation-level security skills and knowledge, and is used by o