Transcription
STEAM TABLENur Istianah,ST.,MT.,M.EngTHP UB 2017
STEAM Water in gas phase Contain higher energy (heat) Has wide uses in food industry: Preheating Boiling Sterilisation Pasutisation Cleaning etc
EnergyPotentialEnergySourcesCoal, oil, urbin)Electricity(Generator)Saved ight
Fire Tube boiler
Water Tube boiler
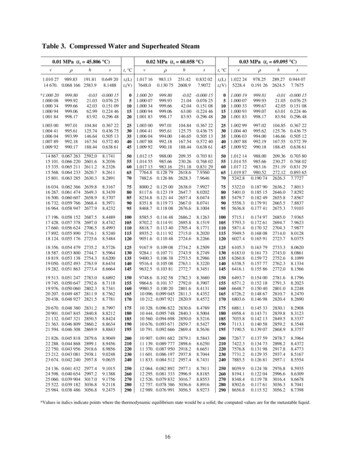
STEAM TABLE The steam tables are tabulated values for theproperties of saturated and superheated steam. Specific volume is the volume in cubic feetoccupied by 1 lb of water or steam under theconditions given. Enthalpy is the heat content of a unit mass ofsteam or water at the indicated temperature andpressure.
Boiling pointBoilingpoint
Saturated Vs Superheated steamSuperheatedSat.LiquidSat.Vapor
Saturated steam
Superheated steam
STEAM TABLEExample:At what vacuum would water boil at 80 F?Answer:0.50683 psia
HEAT Heat is a kind of energy that is related to thetemperature or phase change. It involved inthermodynamic transformations Sensible heat is defined as the energy transferredbetween two bodies at different temperatures Latent heat is the energy associated withphasetransitions
ENDOTERMEnvironmentEnergy(steam)SystemQ 0
Steam in endothermic processSensible heat:mCp(T2-T1)Susu(60 C)Steam(sat.vapor)Latent heat:mhfgSteam(sat.liquid)Susu(30 C)Ilustasi pasterisasi susu dengan HE
Sensibel and latent heat H H2 – H1 Q m𝑇2𝐶𝑑𝑇𝑝𝑇1 𝑚𝐶𝑝 𝑇2 𝑇1 𝑄Q mhf atau Q mhv
Energy BalanceThe first law of thermodynamic states that energy can be neithercreated nor destroyed.Total energy enteringthe systemTotal energy leavingthe system Change in the totalenergy of system
ConservationLawE in Eout AccFor steady state process:E in Eout
Steam in energy balanceQ 𝑚𝐶𝑝 𝑇2 𝑇1 ms(hg – hf)For T2 T1
Laten heat
Laten heat140Heat ofVaporization ( )120100Temperatur80Heat ofCondensation (-)604020Heat ofFusion ( )0-20-40Heat ofSolidification (-)Entalpi
Heat term Units of heat: joule (J), Calorie (Cal), or Britishthermal unit (Btu) 1 Calorie: amount of heat needed to raise thetemperature of 1 gram of water by 1 C0 (from14.50C to 15.50C) 1 Btu: amount of heat needed to raise thetemperature of 1 lb of water by 1 F0 (from 630Fto 640F) 1 cal 10-3 kcal 3.969 x 10-3 Btu 4.186 J
Example– 150 kg of apple was heated at 30oC until thetemperature raise up to 50oC. Calculate the heattransfered if the apple has composistion; water84,4%, Protein 0,2%, carbohydrate 14,5%, fat 0,6%,dan Ash 0,3% ?– How much steam (saturated at 105oC) need for thatprocess ?
– Defined:– Q ?m 150 kgT1 0oCT2 20oCXw 0,844, Xp 0,002,Xh 0,145, Xf 0,006, Xa 0,003
– Solusi: H Q m 𝑇2CpdT𝑇1For unknown Cp, Cp can be calculated from Siebel Eq. Cp 1,424Xh 1,549Xp 1,675Xf 0,837Xa 4,187Xw 1,424 (0,145) 1,549 (0,002) 1,675 (0,006) 0,837(0,003) 4,187 (0,844) 3,76 kJ/kg.K H Q m𝑇2CpdT𝑇1 150 kg x 3,76 kJ/kg.oC x (20-0) oC 11280 kJ
Steam Table
Q 𝑚𝐶𝑝 𝑇2 𝑇1 ms(hg – hf)ms Q/ (hg – hf)ms Q/hfg
ms 11280 kJ2243.54 kJ/kgms 5.03 kg
THANKS FOR YOUR ATTENTIONThe best person is one give something useful always28/04/2017Nur Istianah-KP1-neraca energi-2015
MATERI KULIAH BISA DIUNDUH DI:nuristianah.lecture.ub.ac.id lecture semester genap
STEAM TABLE The steam tables are tabulated values for the properties of saturated and superheated steam. Specific volume is the volume in cubic feet occupied by 1 lb of water or steam under the conditions given. Enthalpy is the heat content of a unit mass of