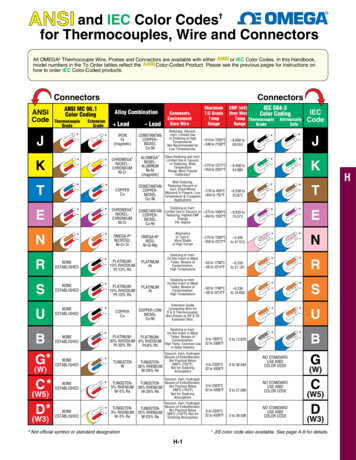
Transcription
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyCOLOR PSYCHOLOGYNature is not only all that is visible to the eye --italso includes the inner pictures of the soul.-Edvard Munch
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyIn the early 1800's Johann WolfgangGoethe challenged Newton's ideasand created his own color system.Newton's studies in color had beenscientifically based, while Goethe'sinterest was more in thepsychological effects of color. Hewished to investigate whether rulescould govern the artistic use of color.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvGoethe Color TriangleOriginally planning oncreating an improved colorwheel, he later found that hisideas were best expressedwithin an equilateral triangle.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvGoethe divided all thecolors into two groups.Colors that produceexcitement andcheerfulness. Colors thatassociated with weaknessand unsettled feelings.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvColors can stimulate, excite,depress, tranquilize, increaseappetite and create a feeling ofwarmth or coolness. This is knownas chromodynamics.Color is light energy: actualphysiological changes take placewhen people are exposed to certaincolors. Red results in the highestblood pressure, respiration, heartrate, and eye-blink frequency, bluelowest.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvAn executive for a paint companyreceived complaints from workers ina blue office that the office was toocold.When the offices were painted awarm peach, the complaints endedeven though the temperature hadnot changed.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvCoordinated color schemes canhelp motion pictures create a moodthat underscores the theme.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvColor has an effect on our emotions and behavior.In terms of exactly what kind of effect and how it effects, findings aresomewhat inconclusive. Our reactions to colors are led by acombination of biological, physiological, psychological, social andcultural factors.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvPeople will actually gamble moreand make riskier bets when seatedunder a red light as opposed to ablue light. That's why Las Vegas isthe city of red neon.Green, brown, and red are the mostpopular food colors. Red is oftenused in restaurant decoratingschemes because it is an appetitestimulant
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvIn fashion, advertising, andpresentations, color is one of themost effective tools.Psychologists have suggested thatcolor impression can account for60% of the acceptance or rejectionof that product or service.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvColors can stand in as symbols forlarger ideas, concepts and beliefs.Colors often have different symbolicmeanings in different cultures. Forexample, white is the color forweddings in western societies but forfunerals in traditional Chineseculture; red is generally associatedwith rage in America but withhappiness in China.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvWhat do the colors of the US flagsymbolize?Why were those specific colorschosen as the best representation ofthe ideals they represent?
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvWarm colorsThey can produce feelings that arewarm, cozy, and inviting. Thesecolors are associated withexcitement, happiness and comfort.Yellow, orange and red areassociated with the heat of sun andfire.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvCool ColorsEmotions associated with thesecolors range from calm and peace tosadness, withdrawal and repression.Blue, Green and violet areassociated with the coolness ofleaves, sea and the sky.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvRedThe most emotionally intense color.Red clothing gets noticed but makesthe wearer appear heavier. Red carsare targets for thieves. Decoratorssay that red furniture will attractattention. Since it is an extremecolor, red clothing might not helppeople in negotiations orconfrontations.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvYellowCheerful sunny yellow is an attentiongetter. While it is considered anoptimistic color, people lose theirtempers more often in yellow rooms,and babies will cry more. It can beoverpowering if overused. Yellowenhances concentration, hence itsuse for legal pads. It also speedsmetabolism.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvGreenGreen symbolizes nature. It is acalming, refreshing color. Peoplewaiting to appear on televisionprograms sit in "green rooms" torelax. Hospitals often use greenbecause it relaxes patients.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvBlueThe color of the sky & ocean. Bluecauses the body to produce calmingchemicals; is often used inbedrooms. It can symbolizes loyalty.People are more productive in bluerooms. Weightlifters lift heavierweights in blue gyms. Blue is alsoone of the least appetizing. Bluefood is rare in nature; when fooddyed blue is served to studysubjects, they lose appetite.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvVioletThe color of royalty, purple connotesluxury, wealth, and sophistication.However, because it is rare innature, purple can appear artificial.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvBlackBlack is the color of authority andpower. It is popular in fashionbecause it makes people appearthinner. It is also stylish andtimeless. Black also impliessubmission. Priests and Nunswear black to signify submission toGod. Black outfits can also beoverpowering, or make the wearerseem aloof or evil.
COLOR THEORY – PsychologyPRIMARY yo Y yg LightHue SECONDARY O G ObjectValuetertiary roCOLOR bg ObserverVision/PerceptionIntensity- BTemperatureRrvV bvWhiteBrides wear white to symbolizeinnocence and purity. White reflectslight and is considered a summercolor. White is popular in decoratingand in fashion because it is light,neutral, and goes with everything.Doctors and nurses wear white toimply sterility.
COLOR THEORY – Psychology Y V R B OHue G COLOR yo yg ro bg rv bv Value Intensity Temperature PRIMARY SECONDARY tertiary Light Object Observer Vision/Perception -People will actually gamble more and make riskier bets when seated under a red light as opposed to a