Transcription
SNF PPS: Patient Driven Payment Model
Acronyms in this Presentation AIDS: Acquired Immune Deficiency SyndromeARD: Assessment Reference DateBIMS: Brief Interview for Mental StatusCMI: Case-mix IndexCMS: Centers for Medicare and Medicaid ServicesCOT: Change of TherapyCFS: Cognitive Function ScaleCPS: Cognitive Performance ScaleHIPPS: Health Insurance Prospective Payment SystemHIV: Human Immunodeficiency VirusICD-10-CM: International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical ModificationIPA: Interim Payment AssessmentMDS 3.0: Minimum Data Set, Version 3NF: Nursing FacilityNTA: Non-Therapy Ancillary2
Acronyms in this Presentation OBRA: Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1987OMRA: Other Medicare-Required AssessmentOSA: Optional State AssessmentOT: Occupational TherapyPDPM: Patient Driven Payment ModelPPS: Prospective Payment SystemPT: Physical TherapyRUG-IV: Resource Utilization Group, Version IVSLP: Speech Language PathologySNF: Skilled Nursing FacilityUPL: Upper Payment LimitVPD: Variable Per Diem3
Agenda PDPM OverviewPatient Classification Under PDPMPatient Classification ExampleMDS Related ChangesConcurrent & Group Therapy LimitInterrupted Stay PolicyAdministrative PresumptionPayment for Patients with AIDSRevised HIPPS CodingRUG-IV – PDPM TransitionMedicaid Related IssuesResources4
PDPM Overview5
Project Overview Issues with the current case-mix model, the Resource Utilization Groups, Version IV (RUG-IV)have been identified by CMS, the Office of Inspector General, the Medicare Payment AdvisoryCommission, the media, and others: Therapy payments under the Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF) Prospective Payment System (PPS) are basedprimarily on the amount of therapy provided to a patient, regardless of the patient’s unique characteristics,needs, or goals The Patient Driven Payment Model (PDPM), effective October 1, 2019, will improve paymentsmade under the SNF PPS in the following ways: Improves payment accuracy and appropriateness by focusing on the patient, rather than the volume ofservices provided Significantly reduces administrative burden on providers Improves SNF payments to currently underserved beneficiaries without increasing total Medicarepayments6
RUG-IV Components RUG-IV consists of two case-mix adjusted components: Therapy: Based on volume of services provided Nursing: The nursing Case-Mix Index (CMI) does not currently reflect specific variations in non-therapyancillary (NTA) utilization7
PDPM Components PDPM consists of five case-mix adjusted components, all based on data-driven, stakeholder-vettedpatient characteristics: Physical Therapy (PT) Occupational Therapy (OT) Speech Language Pathology (SLP) Nursing NTA PDPM also includes a “Variable Per Diem (VPD) adjustment” that adjusts the per diem rate over thecourse of the stay8
PDPM Snapshot9
RUG-IV vs. PDPM While RUG-IV (left) reduces everything about a patient to a single, typically volume-driven, case-mixgroup, PDPM (right) focuses on the unique, individualized needs, characteristics, and goals of eachpatient:10
Effect of PDPM By addressing each individual patient’s unique needs independently, PDPM improves paymentaccuracy and encourages a more patient-driven care model:11
Patient Classification Under PDPM12
PDPM Patient Classification Under PDPM, each patient is classified into a group for each of the five case-mix adjustedcomponents: PT, OT, SLP, Nursing and NTA Each component utilizes different criteria as the basis for patient classification: PT: Clinical Category, Functional Score OT: Clinical Category, Functional Score SLP: Presence of Acute Neurologic Condition, SLP-related Comorbidity or Cognitive Impairment,Mechanically-altered Diet, Swallowing Disorder Nursing: Same characteristics as under RUG-IV NTA: NTA Comorbidity Score13
PT & OT Components: RUG-IV & PDPM Under RUG-IV, the number of PT, OT, and SLP therapy treatment minutes are combined for a totalnumber of treatment minutes that is used to classify a given patient into a given therapy RUG Under PDPM, patient characteristics will be used to predict the therapy costs associated with a givenpatient, rather than rely on service use For the PT & OT components, two classifications are used: Clinical Category Functional Status14
PDPM Clinical Categories SNF patients are first classified into a clinical category based on the primary diagnosis for the SNFstay International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) codes,coded on the Minimum Data Set (MDS) in Item I0020B, are mapped to a PDPM clinical category: Clinical classification may be adjusted by a surgical procedure that occurred during the prior inpatient stay,as coded in Section J ICD-10 mapping available on the PDPM webpagePDPM Clinical CategoriesMajor Joint Replacement or Spinal SurgeryCancerNon-Surgical Orthopedic/MusculoskeletalPulmonaryOrthopedic - Surgical Extremities not Major JointCardiovascular and CoagulationsAcute InfectionsAcute NeurologicMedical ManagementNon-Orthopedic Surgery15
PT & OT Clinical Categories Based on data showing similar costs among certain clinical categories, the PT & OT components usefour collapsed clinical categories for patient classification:PDPM Clinical CategoriesPT & OT Clinical CategoriesMajor Joint Replacement or Spinal SurgeryMajor Joint Replacement or Spinal SurgeryAcute NeurologicNon-Orthopedic SurgeryNon-Surgical Orthopedic/MusculoskeletalOrthopedic - Surgical Extremities Not Major JointNon-Orthopedic Surgery & Acute NeurologicOther OrthopedicMedical ManagementCancerPulmonaryMedical ManagementCardiovascular & CoagulationsAcute Infections16
PT & OT Functional Score PDPM advances CMS’ goal of using standardized assessment items across payment settings byusing items in Section GG of the MDS as the basis for patient functional assessments The functional score for the PT & OT components is calculated as the sum of the scores on tenSection GG items: Two bed mobility items Three transfer items One eating item One toileting item One oral hygiene item Two walking items17
PT & OT Functional Score: GG Items Section GG items included in the PT & OT Functional Score:Section GG ItemFunctional ScoreRangeGG0130A1 – Self-care: Eating0–4GG0130B1 – Self-care: Oral Hygiene0–4GG0130C1 – Self-care: Toileting Hygiene0–4GG0170B1 – Mobility: Sit to LyingGG0170C1 – Mobility: Lying to Sitting on side of bed0–4(average of 2 items)GG0170D1 – Mobility: Sit to StandGG0170E1 – Mobility: Chair/bed-to-chair transfer0–4(average of 3 items)GG0170F1 – Mobility: Toilet TransferGG0170J1 – Mobility: Walk 50 feet with 2 turnsGG0170K1 – Mobility: Walk 150 feet0–4(average of 2 items)18
Nursing Functional Score: GG Items Section GG items included in the Nursing Functional Score:Section GG ItemFunctional ScoreRangeGG0130A1 – Self-care: Eating0–4GG0130C1 – Self-care: Toileting Hygiene0–4GG0170B1 – Mobility: Sit to LyingGG0170C1 – Mobility: Lying to Sitting on side of bed0–4(average of 2 items)GG0170D1 – Mobility: Sit to StandGG0170E1 – Mobility: Chair/bed-to-chair transfer0–4(average of 3 items)GG0170F1 – Mobility: Toilet Transfer19
Functional Score: Item Response Crosswalk (1) PT & OT and Nursing Functional Score Construction (Non-walking Items)Item ResponseScore05, 06 – Set-up Assistance, Independent404 – Supervision or touching assistance303 – Partial/Moderate assistance202 – Substantial/Maximal assistance101, 07, 09, 10, 88, missing – Dependent, Refused, Not applicable, Not attempted due toenvironmental limitations, Not Attempted due to medical condition or safety concerns020
Functional Score: Item Response Crosswalk (2) PT & OT Functional Score Construction (Walking Items)Item ResponseScore05, 06 – Set-up Assistance, Independent404 – Supervision or touching assistance303 – Partial/Moderate assistance202 – Substantial/Maximal assistance101, 07, 09, 10, 88, missing – Dependent, Refused, Not applicable, Not attempted due toenvironmental limitations, Not Attempted due to medical condition or safety concerns,Resident Cannot Walk (Coded based on response to GG0170I1)021
RUG-IV & PDPM Functional Score Differences Notable differences between G and GG scoring methodologies: Reverse scoring methodology: Under Section G, increasing score means increasing dependence Under Section GG, increasing score means increasing independence Non-linear relationship to payment: Under RUG-IV, increasing dependence, within a given RUG category, translates to higher payment Under PDPM, there is not a direct relationship between increasing dependence and increasingpayment Example: For the PT & OT component, payment for three clinical categories is lower for the mostand least dependent patients (who are less likely to require high therapy amounts of therapy),compared to those in between (who are more likely to require high amounts of therapy)22
PT & OT Components: Payment GroupsClinical CategoryMajor Joint Replacement or Spinal SurgeryMajor Joint Replacement or Spinal SurgeryMajor Joint Replacement or Spinal SurgeryMajor Joint Replacement or Spinal SurgeryOther OrthopedicOther OrthopedicOther OrthopedicOther OrthopedicMedical ManagementMedical ManagementMedical ManagementMedical ManagementNon-Orthopedic Surgery and Acute NeurologicNon-Orthopedic Surgery and Acute NeurologicNon-Orthopedic Surgery and Acute NeurologicNon-Orthopedic Surgery and Acute NeurologicPT & OTFunction 10-2324PT & OTCase Mix GroupTATBTCTDTETFTGTHTITJTKTLTMTNTOTPPT CMIOT .171.441.541.111.301.491.551.0923
SLP Component For the SLP component, PDPM uses a number of different patient characteristics that werepredictive of increased SLP costs: Acute Neurologic clinical classification Certain SLP-related comorbidities Presence of cognitive impairment Use of a mechanically-altered diet Presence of swallowing disorder24
SLP-Related Comorbidities Twelve SLP comorbidities were identified as predictive of higher SLP costs: Conditions and services combined into a single SLP-related comorbidity flag Patient qualifies if any of the conditions/services is present A mapping between ICD-10 codes and the SLP comorbidities is available on the PDPM webpageSLP ComorbiditiesAphasiaLaryngeal CancerCVA,TIA, or StrokeApraxiaHemiplegia or HemiparesisDysphagiaTraumatic Brain InjuryALSTracheostomy (while Resident)Oral CancersVentilator (while Resident)Speech & Language Deficits25
PDPM Cognitive Scoring Under RUG-IV, a patient’s cognitive status is assessed using the Brief Interview for Mental Status(BIMS): In cases where the BIMS cannot be completed, providers are required to perform a staff assessment formental status The Cognitive Performance Scale (CPS) is then used to score the patient’s cognitive status based on theresults of the staff assessment Under PDPM, a patient’s cognitive status is assessed in exactly the same way as under RUG-IV(i.e., via the BIMS or staff assessment): Scoring the patient’s cognitive status, for purposes of classification, is based on the Cognitive FunctionScale (CFS), which is able to provide consistent scoring across the BIMS and staff assessment26
PDPM Cognitive Score: Methodology PDPM Cognitive Measure Classification Methodology:Cognitive LevelBIMS ScoreCPS ScoreCognitively Intact13 – 150Mildly Impaired8 – 121–2Moderately Impaired0–73–4-5–6Severely Impaired27
SLP Component: Payment GroupsPresence of Acute Neurologic Condition,SLP Related Comorbidity, or CognitiveImpairmentMechanically AlteredDiet or SwallowingDisorderSLP Case MixGroupSLP Case MixIndexNoneNoneNoneAny oneAny oneAny oneAny twoAny twoAny twoAll threeAll threeAll 81.822.661.462.332.972.042.853.512.983.694.1928
Nursing Component RUG-IV classifies patients into a therapy RUG, based on how much therapy the patient receives,and a non-therapy RUG, based on certain patient characteristics: Only one of these RUGs is used for payment purposes Therapy RUGs are used to bill for over 90% of Part A days Therapy RUGs use a consistent nursing case-mix adjustment, which obscures clinically meaningfuldifferences in nursing characteristics between patients in the same therapy RUG PDPM utilizes the same basic nursing classification structure as RUG-IV, with certain modifications: Function score based on Section GG of the MDS 3.0 Collapsed functional groups, reducing the number of nursing groups from 43 to 2529
Nursing Component: Payment Groups C1/HB1Extensive ServicesClinical 2.23No6-14HBC11.85DepressionTracheostomy &VentilatorTracheostomy orVentilatorInfection IsolationSerious medical conditions e.g.comatose, septicemia, respiratorytherapySerious medical conditions e.g.comatose, septicemia, respiratorytherapySerious medical conditions e.g.comatose, septicemia, respiratorytherapySerious medical conditions e.g.comatose, septicemia, respiratorytherapyRestorativeNursingServices30
Nursing Component: Payment Groups ensiveServicesClinical ConditionsSerious medical conditions e.g. radiation therapyor dialysisSerious medical conditions e.g. radiation therapyor dialysisSerious medical conditions e.g. radiation therapyor dialysisSerious medical conditions e.g. radiation therapyor 4LBC11.43DepressionCE2/CD2Conditions requiring complex medical care e.g.pneumonia, surgical wounds, burnsYes0-5CDE21.86CE1/CD1Conditions requiring complex medical care e.g.pneumonia, surgical wounds, burnsNo0-5CDE11.62CC2/CB2Conditions requiring complex medical care e.g.pneumonia, surgical wounds, burnsYes6-14CBC21.54CA2Conditions requiring complex medical care e.g.pneumonia, surgical wounds, burnsYes15-16CA21.0831
Nursing Component: Payment Groups MGCMINo6-14CBC11.34No15-16CA10.942 or more0-111-1611-16BAB2BAB11.040.992 or more0-5PDE21.570-10-5PDE11.472 or more6-14PBC21.212 or cal ConditionsDepressionCC1/CB1Conditions requiring complex medical care e.g.pneumonia, surgical wounds, burnsCA1Conditions requiring complex medical care e.g.pneumonia, surgical wounds, PA1Behavioral or cognitive symptomsBehavioral or cognitive symptomsAssistance with daily living and generalsupervisionAssistance with daily living and generalsupervisionAssistance with daily living and generalsupervisionAssistance with daily living and generalsupervisionAssistance with daily living and generalsupervisionAssistance with daily living and generalsupervisionRestorativeNursingServices32
NTA Component NTA classification is based on the presence of certain comorbidities or use of certain extensiveservices We considered various options to incorporate comorbidities into payment: Total number of comorbidities is linked to NTA costs, but a simple count of conditions overlooks differencesin relative costliness A tier system accounts for differences in relative costliness but does not account for the number ofcomorbidities Comorbidity score is a weighted count of comorbidities: Comorbidities associated with high increases in NTA costs grouped into various point tiers Points assigned for each additional comorbidity present, with more points awarded for higher-cost tiers33
NTA Component: Comorbidity Coding Comorbidities and extensive services for NTA classification are derived from a variety of MDSsources, with some comorbidities identified by ICD-10-CM codes reported in Item I8000 A mapping between ICD-10-CM codes and NTA comorbidities used for NTA classification is availableon the PDPM webpage One comorbidity Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome(HIV/AIDS) is reported on the SNF claim, in the same manner as under RUG-IV: The patient’s NTA classification will be adjusted by the appropriate number of points for this condition by theCMS PRICER for patients with HIV/AIDS34
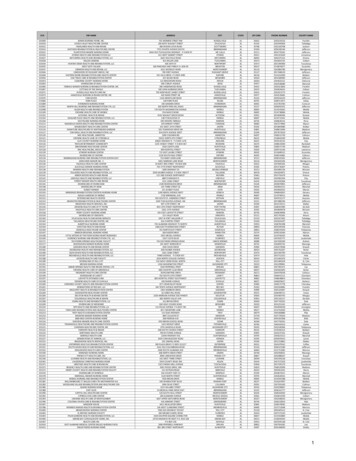
NTA Component: Condition Listing (1)Condition/Extensive ServiceHIV/AIDSParenteral Intravenous (IV) Feeding: Level HighSpecial Treatments/Programs: Intravenous Medication Post-admit CodeSpecial Treatments/Programs: Ventilator or Respirator Post-admit CodeParenteral IV feeding: Level LowLung Transplant StatusSpecial Treatments/Programs: Transfusion Post-admit CodeMajor Organ Transplant Status, Except LungMultiple Sclerosis CodeOpportunistic InfectionsAsthma Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Chronic Lung DiseaseCodeBone/Joint/Muscle Infections/Necrosis - Except Aseptic Necrosis of BoneChronic Myeloid LeukemiaWound Infection CodeDiabetes Mellitus (DM) CodeSourceSNF ClaimMDS Item K0510A2,K0710A2MDS Item O0100H2Points8MDS Item O0100F2MDS Item K0510A2,K0710A2, K0710B2MDS Item I8000MDS Item O0100I2MDS Item I8000MDS Item I5200MDS Item I80004MDS Item I62002MDS Item I8000MDS Item I8000MDS Item I2500MDS Item I290022227533222235
NTA Component: Condition Listing (2)Condition/Extensive ServiceSourcePointsEndocarditisImmune DisordersEnd-Stage Liver DiseaseOther Foot Skin Problems: Diabetic Foot Ulcer CodeNarcolepsy and CataplexyCystic FibrosisMDS Item I8000MDS Item I8000MDS Item I8000MDS Item M1040BMDS Item I8000MDS Item I8000111111Special Treatments/Programs: Tracheostomy Care Post-admit CodeMDS Item O0100E21Multi-Drug Resistant Organism (MDRO) CodeSpecial Treatments/Programs: Isolation Post-admit CodeSpecified Hereditary Metabolic/Immune DisordersMorbid ObesitySpecial Treatments/Programs: Radiation Post-admit CodeHighest Stage of Unhealed Pressure Ulcer - Stage 4Psoriatic Arthropathy and Systemic SclerosisChronic PancreatitisProliferative Diabetic Retinopathy and Vitreous HemorrhageMDS Item I1700MDS Item O0100M2MDS Item I8000MDS Item I8000MDS Item O0100B2MDS Item M0300D1MDS Item I8000MDS Item I8000MDS Item I800011111111136
NTA Component: Condition Listing (3)Condition/Extensive ServiceOther Foot Skin Problems: Foot Infection Code, Other Open Lesion on Foot Code,Except Diabetic Foot Ulcer CodeComplications of Specified Implanted Device or GraftBladder and Bowel Appliances: Intermittent CatheterizationInflammatory Bowel DiseaseAseptic Necrosis of BoneSpecial Treatments/Programs: Suctioning Post-admit CodeCardio-Respiratory Failure and ShockMyelodysplastic Syndromes and MyelofibrosisSystemic Lupus Erythematosus, Other Connective Tissue Disorders, andInflammatory SpondylopathiesDiabetic Retinopathy - Except Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy and VitreousHemorrhageNutritional Approaches While a Resident: Feeding TubeSevere Skin Burn or ConditionIntractable EpilepsyMalnutrition CodeSourceMDS Item M1040A,M1040B, M1040CMDS Item I8000MDS Item H0100DMDS Item I1300MDS Item I8000MDS Item O0100D2MDS Item I8000MDS Item I8000Points11111111MDS Item I80001MDS Item I80001MDS Item K0510B2MDS Item I8000MDS Item I8000MDS Item I5600111137
NTA Component: Condition Listing (4)Condition/Extensive ServiceSourcePointsDisorders of Immunity - Except : RxCC97: Immune DisordersMDS Item I80001Cirrhosis of LiverBladder and Bowel Appliances: OstomyRespiratory ArrestPulmonary Fibrosis and Other Chronic Lung DisordersMDS Item I8000MDS Item H0100CMDS Item I8000MDS Item I8000111138
NTA Component: Payment GroupsNTA Score Range12 9 – 116–83–51–20NTA Case Mix GroupNANBNCNDNENFNTA Case Mix Index3.252.531.851.340.960.7239
Variable Per Diem Adjustment The Social Security Act requires the SNF PPS to pay on a per-diem basis Const
Issues with the current case- mix model, the Resource Utilization Groups, Version IV (RUG- IV) have been identified by CMS, the Office of Inspector General, the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission, the media, and others: Therapy payments under the Skilled Nursing