Transcription
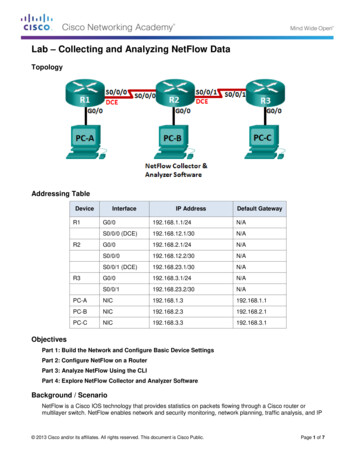
Lab – Collecting and Analyzing NetFlow DataTopologyAddressing TableDeviceR1InterfaceIP AddressDefault GatewayG0/0192.168.1.1/24N/AS0/0/0 192.168.12.2/30N/AS0/0/1 8.3.1R2R3ObjectivesPart 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device SettingsPart 2: Configure NetFlow on a RouterPart 3: Analyze NetFlow Using the CLIPart 4: Explore NetFlow Collector and Analyzer SoftwareBackground / ScenarioNetFlow is a Cisco IOS technology that provides statistics on packets flowing through a Cisco router ormultilayer switch. NetFlow enables network and security monitoring, network planning, traffic analysis, and IP 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.Page 1 of 7
Lab – Collecting and Analyzing NetFlow Dataaccounting. It is important not to confuse NetFlow’s purpose and results with that of packet capture hardwareand software. Packet capturing records all possible information exiting or entering a network device for lateranalysis, NetFlow targets specific statistical information.Flexible NetFlow is the latest NetFlow technology, improving on the original NetFlow by adding the capabilityto customize the traffic analysis parameters. Flexible NetFlow uses the Version 9 export format. Starting withCisco IOS Release 15.1, many useful Flexible NetFlow commands are supported.In this lab, you will configure NetFlow to capture both ingress (incoming) and egress (outgoing) packets. Youwill use show commands to verify that NetFlow is operational and gathering statistical information. You willalso explore available options for NetFlow collection and analysis software.Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 1941 Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) withCisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 (universalk9 image). Other routers and Cisco IOS versions can be used.Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and output produced might varyfrom what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of this lab for thecorrect interface identifiers.Note: Make sure that the routers have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure,contact your instructor.Required Resources 3 Routers (Cisco 1941 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 universal image or comparable) 3 PCs (Windows 7, Vista, or XP with terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term) Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports Ethernet and serial cables as shown in the topologyPart 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device SettingsIn Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings on the PC hosts and routers.Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.Step 2: Initialize and reload the routers as necessary.Step 3: Configure basic settings for each router.a. Disable DNS lookup.b. Configure device names as shown in the topology.c.Assign class as the encrypted privileged EXEC mode password.d. Assign cisco as the console and vty passwords and enable login.e. Encrypt the plain text passwords.f.Configure a MOTD banner to warn users that unauthorized access is prohibited.g. Configure logging synchronous for the console line.h. Set the clock rate for all DCE serial interfaces at 128000.i.Configure the IP addresses as listed in the Addressing Table.j.Configure OSPF using Process ID 1 and advertise all networks. Ethernet interfaces should be passive.k.Create a local database on R3 with the username admin and password cisco with the privilege level at15. 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.Page 2 of 7
Lab – Collecting and Analyzing NetFlow Datal.On R3, enable the HTTP service and authenticate HTTP users by using the local database.m. Copy the running configuration to the startup configuration.Step 4: Configure PC hosts.Step 5: Verify end-to-end connectivity.All devices should be able to ping other deices in the topology. Troubleshoot as necessary until end-to-endconnectivity is established.Note: It may be necessary to disable the PC firewall for pings between PCs to be successful.Part 2: Configure NetFlow on a RouterIn Part 2, you will configure NetFlow on router R2. NetFlow will capture all ingress and egress traffic on theR2 serial interfaces and export the data to the NetFlow collector, PC-B. Flexible NetFlow Version 9 will beused to export to the NetFlow collector.Step 1: Configure NetFlow capture.Configure NetFlow data capture on both serial interfaces. Capture data from ingress and egress packets.R2(config)# interface s0/0/0R2(config-if)# ip flow ingressR2(config-if)# ip flow egressR2(config-if)# interface s0/0/1R2(config-if)# ip flow ingressR2(config-if)# ip flow egressStep 2: Configure NetFlow data export.Use the ip flow-export destination command to identify the IP address and the UDP port of the NetFlowcollector to which the router should export NetFlow data. UDP Port number 9996 will be used for thisconfiguration.R2(config)# ip flow-export destination 192.168.2.3 9996Step 3: Configure the NetFlow export version.Cisco routers running IOS 15.1 support NetFlow versions 1, 5, and 9. Version 9 is the most versatile exportdata format, but is not backward-compatible with earlier versions. Use the ip flow-export version commandto set the NetFlow version.R2(config)# ip flow-export version 9Step 4: Verify the NetFlow configuration.a. Issue the show ip flow interface command to review the NetFlow capture interface information.R2# show ip flow interfaceSerial0/0/0ip flow ingressip flow egressSerial0/0/1ip flow ingressip flow egress 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.Page 3 of 7
Lab – Collecting and Analyzing NetFlow Datab. Issue the show ip flow export command to review the NetFlow data export information.R2# show ip flow exportFlow export v9 is enabled for main cacheExport source and destination details :VRF ID : DefaultDestination(1) 192.168.2.3 (9996)Version 9 flow records388 flows exported in 63 udp datagrams0 flows failed due to lack of export packet0 export packets were sent up to process level0 export packets were dropped due to no fib0 export packets were dropped due to adjacency issues0 export packets were dropped due to fragmentation failures0 export packets were dropped due to encapsulation fixup failuresPart 3: Analyze NetFlow Using the CLIIn Part 3, you will generate data traffic between R1 and R3 to observe NetFlow technology.Step 1: Generate data traffic between R1 and R3.a. Telnet from R1 to R3 using the IP address 192.168.3.1. Enter the password cisco to enter the userEXEC mode. Enter the password class to enable global EXEC mode. Issue the show run command togenerate some Telnet traffic. Keep your Telnet session active for now.b. From R3, issue the ping 192.168.1.1 repeat 1000 command to ping the R1 G0/0 interface. This willgenerate ICMP traffic through R2.c.From PC-A, browse to R3 using the 192.168.3.1 IP address. Login as admin with the password cisco.Keep the browser open after you have logged into R3.Note: Make sure the pop-up blocker is disabled on your browser.Step 2: Display a summary of the NetFlow accounting statistics.On R2, issue the show ip cache flow command to display changes to the summary of NetFlow data,including packet size distribution, IP flow information, captured protocols, and interface activity. Notice theprotocols now display in the summary data.R2# show ip cache flowIP packet size distribution (5727 total packets):1-326496 128 160 192 224 256 288 320 352 384 416 448 480.000 .147 .018 .700 .000 .001 .001 .001 .001 .011 .009 .001 .002 .000 .001512 544 576 1024 1536 2048 2560 3072 3584 4096 4608.001 .001 .097 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000IP Flow Switching Cache, 278544 bytes2 active, 4094 inactive, 114 added1546 ager polls, 0 flow alloc failuresActive flows timeout in 30 minutesInactive flows timeout in 15 secondsIP Sub Flow Cache, 34056 bytes0 active, 1024 inactive, 112 added, 112 added to flow 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.Page 4 of 7
Lab – Collecting and Analyzing NetFlow Data0 alloc failures, 0 force free1 chunk, 1 chunk addedlast clearing of statistics 00:07:35ProtocolTotalFlowsPackets Bytes-------Flows/Sec/Flow ullNull50Packets Active(Sec) 5.4DstIPaddress14612.5Pr SrcP DstP Pkts3.12.5DstIPaddress224.0.0.5224.0.0.5Pr SrcP DstP59 0000 000059 0000 0000Pkts4340Step 3: End the Telnet and browser sessions.a. Issue the exit command on R1 to disconnect from the Telnet session to R3.b. Close the browser session on PC-A.Step 4: Clear NetFlow accounting statistics.a. On R2, issue the clear ip flow stats command to clear NetFlow accounting statistics.R2# clear ip flow statsb. Re-issue the show ip cache flow command to verify that the NetFlow accounting statistics have beenreset. Notice that, even though you are no longer generating data through R2, data is being picked up byNetFlow. In the example below, the destination address for this traffic is multicast address 224.0.0.5, orOSPF LSA data.R2# show ip cache flowIP packet size distribution (124 total packets):1-326496 128 160 192 224 256 288 320 352 384 416 448 480.000 .000 1.00 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000512 544 576 1024 1536 2048 2560 3072 3584 4096 4608.000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000IP Flow Switching Cache, 278544 bytes2 active, 4094 inactive, 2 added1172 ager polls, 0 flow alloc failuresActive flows timeout in 30 minutesInactive flows timeout in 15 secondsIP Sub Flow Cache, 34056 bytes2 active, 1022 inactive, 2 added, 2 added to flow0 alloc failures, 0 force free1 chunk, 0 chunks addedlast clearing of statistics 00:09:48 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.Page 5 of 7
Lab – Collecting and Analyzing NetFlow /Sec0.00.0Packets Bytes/Flow /Pkt1937919379Packets Active(Sec) ress224.0.0.5Pr SrcP DstP59 0000 fNullDstIPaddress224.0.0.5Pr SrcP DstP59 0000 0000Pkts33Part 4: Explore NetFlow Collector and Analyzer SoftwareNetFlow Collector and Analyzer Software is available from many vendors. Some software is provided asfreeware, others are not. The following URL provides a summary web page of some of the Freeware NetFlowsoftware /ps6537/ps6555/ps6601/networking solutions products genericcontent0900aecd805ff72b.htmlReview this web page to acquaint yourself with some of the available NetFlow Collector and Analyzersoftware products.Reflection1. What is the purpose of NetFlow collector software?2. What is the purpose of NetFlow analyzer software?3. What are the seven critical fields used by the original NetFlow to distinguish flows? 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.Page 6 of 7
Lab – Collecting and Analyzing NetFlow DataRouter Interface Summary TableRouter Interface SummaryRouter ModelEthernet Interface #1Ethernet Interface #2Serial Interface #1Serial Interface #21800Fast Ethernet 0/0(F0/0)Fast Ethernet 0/1(F0/1)Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0)Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1)1900Gigabit Ethernet 0/0(G0/0)Gigabit Ethernet 0/1(G0/1)Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0)Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1)2801Fast Ethernet 0/0(F0/0)Fast Ethernet 0/1(F0/1)Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0)Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1)2811Fast Ethernet 0/0(F0/0)Fast Ethernet 0/1(F0/1)Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0)Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1)2900Gigabit Ethernet 0/0(G0/0)Gigabit Ethernet 0/1(G0/1)Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0)Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1)Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how manyinterfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each routerclass. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device.The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. Anexample of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can beused in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface. 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.Page 7 of 7
NetFlow is a Cisco IOS technology that provides statistics on packets flowing through a Cisco router or multilayer switch. NetFlow enables network and security











