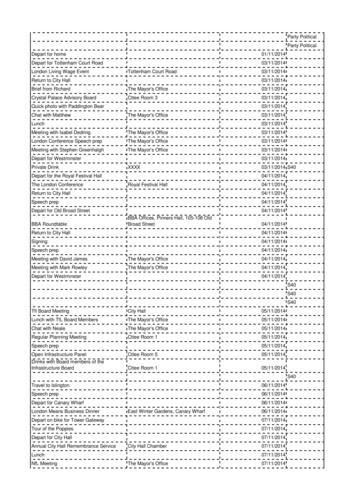
Transcription
2014 AFCIcode compliant safetyUnderstanding the2014 NEC forAFCI protectionEaton is a registered trademark.All other trademarks are propertyof their respective owners.Eaton1000 Eaton BoulevardCleveland, OH 44122United StatesEaton.comElectrical Sector203 Cooper CirclePeachtree City, GA 30276United StatesEaton.comArrowhart.com 2013 EatonAll Rights ReservedPrinted in USAPub Number : BR003005ENNovember 2013
Understanding the codefor code compliant safetyAn arc fault is an unintendedarc created by current flowingthrough an unplanned path.Arcing creates excessive heatthat can easily ignite surrounding material, such as woodframing or insulation, resultingin a hazardous fire.NEC 2014 AFCI requirements 210.12An AFCI breaker protects the entire circuitfrom its origin in the load center for bothparallel and series arcsAFCI Breakerinstalled in the ding the codePer section 201.12 of the 2014 NEC Arc FaultCircuit Interrupter Protection is expanded toinclude kitchens and laundry room areas inaddition to other areas specified in previousversions of the code for dwelling units.Additionally, the new code will now requireAFCI protection for dormitory units. The useof AFCI receptacles are permitted for use innew construction with some restrictions.Parallel arc protectionSeries arc protectionAn AFCI receptacle can protect all downstream wireand appliances from both parallel and series arcs, butonly protects from series arcs upstream in the home runHome Run wiring restrictionsto first AFCI receptacle50’ for #14 wire70’ for #12 wireAT A GLANCE· The 2014 NECallows 6 different installationmethods to provide AFCI protectionin new construction(see pages 8-9)· Each application has preferredinstallation methods based on levelof protection and rdreceptacleHome Runonly protectedfrom series arcsParallel arc protectionSeries arc protection2EATON 2014 AFCI code compliant safety EATON 2014 AFCI code compliant safety 3
Arc faults left unattendedcould potentially ignitesurrounding materialresulting in potentiallydeadly firesTight staple can pierce insulationTypical causes of arc faults1. Arcing in installed electrical wiring from physicaldamage such as: Wires accidentally punctured by nails or screwsCables that are stapled tightly against wall studAnimals and vermin chewing through wiring insulationHeat, humidity and voltage stressInadvertent nails can puncture wire behind wall2. Arcing at loose connections or joints in the circuitor at outlets3. Arcing in appliance or extension cords Bent or crimped cordsBrittle or aged cordsCords under or behind furnitureAnimals can chew through insulation4. Arcing internal to appliances or electrical devices Defective productsDamaged or products at end of lifeElectrical cords can be damaged under or behind furniture4EATON 2014 AFCI code compliant safety EATON 2014 AFCI code compliant safety 5
Code compliant installationsProtection Using AFCIsThe 2014 NEC allows for variousmethods to protect a circuit usingarc fault technology1. Combination AFCI Breaker5. Metal conduit to first AFCI ReceptacleA combination AFCI Breaker can be used at the panelRequires installation of armored cable (RMC, IMC,EMT, TYPE MC or TYPEAC) for the homerun portionof the branch circuitAdvantage:Protects the whole circuit from the sourceDisadvantage: LegacyAFCI breakersloadcenters may not accommodate2. Branch AFCI breaker with AFCI ReceptacleA listed branch feeder type AFCI breaker installed at theorigin of the branch circuit in combination with a listedAFCI receptacleProtects the whole circuit from the source,allows local reset in most casesAdvantage:Disadvantage:be costlyRequires two AFCI devices which canAdvantage: Allowsfor local reset in most casesDisadvantage: Installationof conduit can be costly, andmay be difficult to identify first receptacle in the circuitduring remodel or retrofit6. Conduit in concrete with AFCI ReceptacleMetal or nonmetallic conduit or tubing or Type MC cableis encased in not less than 2 in. of concrete for theportion of the branch circuit between the branch circuitovercurrent device and the first outletAdvantage:Allows for local reset in most casesLimited applications and installationof conduit can be costlyDisadvantage:3. “Supplemental Arc Protection” breakerwith AFCI Receptacle “recognized pair”A listed supplemental arc protection circuit breakerinstalled at the origin of the branch circuit in combinationwith a listed AFCI receptacleAdvantage:Allows for local reset in most casesA supplemental arc protection breakeris not currently available. There are also limitations inhomerun length and location of the first receptacle.Disadvantage:4. Listed breaker AFCI Receptacle “tested pair”A listed AFCI receptacle installed at the first outletin combination with a listed branch circuit overcurrentprotective deviceAdvantage:Allows for local reset in most casesLimited tested combinations ofAFCI receptacles and upstream branch breakers,limitations in homerun length and location of firstreceptacleDisadvantage:6EATON 2014 AFCI code compliant safety AFCI breaker and AFCI receptacleOBC AFCI breakers and/or AFCIreceptacles can be used toprotect a circuit under variousconditions per the 2014 NECEATON 2014 AFCI code compliant safety 7
Code compliant installationsEach application is allowable by code with preferred installation methods based on level ofprotection or practicalityNew ConstructionApplication1. Combination AFCI breakerA combination AFCI Breaker can be used at the panel2. Branch AFCI breaker with AFCI receptacleA listed branch feeder type AFCI breaker installed at theorigin of the branch circuit in combination with a listed arcfault receptacle3. “Supplemental Arc Protection” breaker with AFCIreceptacle (“recognized pair”)A listed supplemental arc protection circuit breaker installedat the origin of the branch circuit in combination with a listedarc fault receptacle4. Listed breaker AFCI receptacle (“tested pair”)A listed arc-fault receptacle installed at the first outletin combination with a listed branch circuit overcurrentprotective device5. Metal conduit to first AFCI receptacleRMC, IMC, EMT, Type MC, or steel armored Type AC cablesinstalled for the portion of the branch circuit homerun6. Conduit in concrete with AFCI receptacleMetal or nonmetallic conduit or tubing or Type MC Cable isencased in not less than 2 in. of concrete for the portion ofthe branch circuit between the branch circuit overcurrentdevice and the first outletPRemodelDorms/Hotels/AssistedLivingRemodel /RetrofitSingle FamilyMulti-FamilyPP NRNRNRNRNRNRNRNR NR PNRNRNRNRNR Preferred Code CompliantNR Not recommended due to cost or insufficient protectionTypes of arcingArcing can be classified into two types: High current “Parallel” arcs Low current “Series” arcsParallel arcing is typically found between two parallelconductors. Series arcs typically occur within oneconductor or at termination points.Both AFCI breakers and receptacles aredesigned to detect both types of arcingconditions. However, an AFCI receptacle will not miti-gate parallel arcing taking place upstream of the device asthe current path does not flow through the AFCI receptacle.Therefore, it is reliant on the upstream breaker to provideprotection against parallel arcing in the homerun section ofthe circuit.AFCIBreakerTypes of ArcingHigh Current “Parallel” ArcsUpstreamLow Current “Series” ArcsHigh Current “Parallel” ArcsDownstream8EATON 2014 AFCI code compliant safety Low Current “Series” Arcs AFCIReceptacleNO EATON 2014 AFCI code compliant safety 9
Arc faulttechnologysaves livesThings you should knowTechnological MaturityArc Fault technology saves lives and has been an industrystandard in new construction for over 15 years. Today’sarc fault technology has been proven through arc faultbreakers and has gone through several iterations toreduce unwanted tripping due to interference fromdevices or appliances. Arc fault circuit interrupters havebeen established as a stable technology which can beused in conjunction with various loads through the homein both AFCI breakers and AFCI receptacles.Other ConsiderationsDue to the restrictions of use per the 2014 NEC, there areseveral considerations to take into account when decidingwhether to use a Receptacle AFCI or Breaker AFCI: Length Restrictions – Due to length restrictions, AFCIreceptacles must be placed within the specified distances to the load centers per the 2014 NEC. Location of the First Receptacle – The AFCI receptaclemust be placed as the first outlet. Care must be takento ensure this location is easily accessible, it cannotbe blocked by any furniture or appliances and the location must make logical sense for the end user shouldthe device need to be reset. Wiring Practices – Because the AFCI receptacle mustbe placed in the first outlet, the contractor may needto change their wiring practices. Each circuit, including dedicated lighting circuits, would need to flowthrough an AFCI outlet before proceeding to the otheroutlets.The last wordRemember your local (AHJ) Authority Having Jurisdiction(inspector) has the ultimate say in the application and useof electrical equipment per the prevailing Electrical Code.10EATON 2014 AFCI code compliant safety It’s clear arc fault protection saveslives by mitigating arcing that couldbe an ignition source of a fire.The 2014 code mandates AFCIprotection in designated areas ofdwelling units and dormitories andallows several installation methods.It’s important to consider theapplication and then choose thebest installation method to providethe safest form of protection.Eaton is a diversified power management companyproviding energy-efficient solutions that help ourcustomers effectively manage electrical, hydraulicand mechanical power.The Residential and Wiring Device Divisionis a leader in electrical connectivity and loadmanagement providing a full line of innovativesolutions for residential, commercial and industrialapplications. From the load center to the receptacle,Eaton provides proven AFCI, GFCI, Surge Protectionand connectivity solutions required to keep poweraccessible, reliable and safe.EATON 2014 AFCI code compliant safety 11
2014 NEC for AFCI protection 2014 AFCI code compliant safety. 2 EATON 2014 AFCI code compliant safety 2014 AFCI code compliant safety 3 An arc fault is an unintended arc created by current flowing through an unplanned path. Arcing creates excessive heat that can easily ignite surround-ing material, such as wood framing or insulation, resulting in a hazardous fire. for code .