Transcription
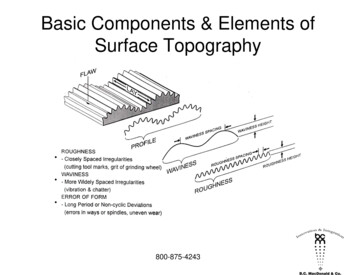
Basic Components & Elements ofSurface Topography 800-875-4243
Skid and SkidlessMeasuring Equipment800-875-4243
Surface Profile Measurement Lengths Sampling Length (l) Assessment (Evaluation) Length (L) Traversing Length800-875-4243
Cutoff Selection Effect onSurface Finish Measurement800-875-4243
Recommended Cutoffs for DifferentSurface Finishes800-875-4243
Traditional Surface TextureParameters and Functions Some of these parameters can also be calculated from unfiltered and wavinessprofiles. (P and W families of parameters)800-875-4243
Ra AA CLARq RMSOn majority of prints only Ra is specified.800-875-4243
Roughness Average Ra800-875-4243
Ra – Roughness AverageAdvantages The most commonly used parameter to monitor a production process. Default parameter on a drawing if not otherwise specified. Available even in the least sophisticated instruments. Statistically a very stable, repeatable parameter. Good for random type surfaces, such as grinding. A good parameter where a process is under control and where theconditions are always the same, e.g. cutting tips, speeds, feeds, cutting fluid(lubricant).Disadvantages Not a good discriminator for different types of surfaces (no distinction ismade between peaks and valleys). Not very informative on surfaces with Rsk outside 2. Not a good measure of sealed surfaces.800-875-4243
Ra, Rq Parameters Roughness average Ra is the arithmetic average of theabsolute values of the roughness profile ordinates. Root mean square (RMS) roughness Rq is the root meansquare average of the roughness profile ordinates.800-875-4243
Rq – Root Mean RoughnessRq is more sensitive to peaks and valleys thenRa, because the amplitudes are squared.Applications Very similar to Ra, which practically replaced itfor general use. Used to control very fine surfaces in scientificmeasurements and statistical evaluations.800-875-4243
Rz, Rmax Parameter800-875-4243
Rz – Mean Peak-to-Valley HeightRmax – Maximum Peak-to-Valley HeightApplications Rz is more sensitive than Ra to changes in surface finish asmaximum profile heights and not averages are being examined. Rmax is useful for surfaces where a single defect is notpermissible, e.g. a seal with a single scratch. Rz and Rmax are used together to monitor the variations of surfacefinish in a production process. Similar values of Rz and Rmaxindicate a consistent surface finish, while a significant differenceindicates a surface defect in an otherwise consistent surface.800-875-4243
Rp, Rpm Parameter The Mean Leveling Depth Rpm is the mean of five leveling depths of fivesuccessive sample lengths l.Rpm 1/5 (Rp1 Rp2 Rp3 Rp4 Rp5) The Leveling Depth Rp is also the largest of the five leveling depths. TheMaximum Roughness Depth Rt (peak to valley height) is the vertical distancebetween the highest peak and the lowest valley of the roughness profile Rwithin the evaluation length L.800-875-4243
Rp and Rpm Rp, per ISO 4287, is the max height of any peak to the mean line within onesampling length. Rpm, the mean leveling depth - per rules of ISO 4288, is an averaging of Rp over5 cutoffs; according to ASME B46.1-2002, Rp calculated over the evaluationlength is Rpm. Many instruments, e.g., M2 Series, measure Rpm but report the result as Rp. ApplicationsRpm is useful in predicting bearing characteristics of a surface.A low value of Rpm and large value of Rz indicates a plateau surfaceThe ratio Rpm/Rz quantifies the asymmetry of profile.Rpm is recommended for bearing and sliding surfaces and surface substratesprior to coating.Rv is a good parameter where stress is a major factor.Rp is a good parameter to control coating quality.800-875-4243
R3Z, R3zmax ParametersPer Daimler Benz Corporate StandardN31007:1983 R – mean third highest peak-to-valley height over 5 sampling length.3z R3zmax – maximum third highest peak-to-valley height of the 5 third highestpeak-to-valley height.R3z disregards the 2 highest peaks and deepest valleys that have little effect on thesurface performance, with the intent to reduce the instability of peak parameters(such as Rz), by ignoring profile extremes.ApplicationsSealing SurfacesPorous Surfaces800-875-4243
Bearing Length Ratio tp (Rmr)800-875-4243
Bearing Area Curve (BAC)800-875-4243
Different Methods of tp (Rmr)BAC EvaluationApplications Probable run-in behavior and wear resistanceof surfaces such as sliding and rolling faces(e.g., cylinder liners). Seals, bearings, electrical and thermalcontrols, adhesives, coatings, etc.800-875-4243
Pc (RPc) – Peak CountNr – Normalized Peak CountThe peak count is the number of local roughness peaks whichproject through a selectable band centered about the meanline. The count is determined over the evaluation length andis reported in peaks per cm or inch.HSC (RHSC) – High Spot CountThe number of roughness peaks, reported in peaks per cm,projecting through the mean line, or a line parallel to it, at aselected distance above or below the mean line.800-875-4243
Pc (RPc), NrHSC (RHSC)Applications Sheet metal industry to measure quality ofsurfaces subjected to bending, forming andpainting and where appearance is critical. General adhesion and coating applications.800-875-4243
Rk Family of ParametersA1A2RkRpkRvkMr1Mr2Rpkx (Rpk*)Rvkx (Rvk*)Material filled profile peak areaLubricant filled profile valley areaCore roughness depthReduced peak heightReduced valley depthMaterial component relative to peaksMaterial component relative to valleysTotal Peak HeightTotal Valley DepthApplications– Multiprocessed, multipurpose surfaces, such asplateau honed– Sintered, porous surfaces800-875-4243
Waviness Height - WtSum of the largest peak height and the largest valley depth ofwaviness profile within evaluation length LApplications– To monitor processes where in addition to roughness, waviness, possiblycaused by vibrations (both within the machine and external), is also critical.– e.g. – cylinder head waviness of the sealing surface produced on a verticalmill largely depends on the alignment of the cutting tips in the milling head.800-875-4243
Parameters Defined in ASME B46.1-2002Ra Arithmetic Average Deviation of the Assessed ProfileRq Root Mean Square Deviation of the Assessed ProfileRp Maximum Profile Peak HeightRv Maximum Profile Valley DepthRt Maximum Height of the ProfileRpm Average Maximum Profile Peak HeightRz Average Maximum Height of the ProfileRmax Maximum Roughness DepthSm Mean Spacing of Profile IrregularitiesPc Peak Density800-875-4243CorrespondingParameters inISO 4287-1997RaRqRpRvRt---Ry---Rsm----
Parameters Defined in ASME B46.1-2002tpHtpRskWtRku a qProfile Bearing RatioDifference in the Heights for Two tp RatiosSkewnessWaviness HeightKurtosisAverage Absolute SlopeRoot Mean Square Slope800-875-4243CorrespondingParameters inISO 4287-1997Rmr(c)RδcRskWtRku---Rdq
ISO Standards on Surface FinishISO 1302 - 2001ISO 3274 - 1996ISO 4287 - 1997ISO 4288 - 1996ISO 5436-1 - 2000ISO 5436-2 - 2000ISO 8785 - 1999ISO 11562 - 1996ISO 12085 - 1996ISO 12179 - 2000ISO 13565 - 1996Part 1Part 2Part 3Indication of Surface TextureNominal Characteristics of Contact (Stylus) InstrumentsTerms, Definition and Surface Texture ParametersRules and Procedures for Assessment of Surface TextureCalibration, Measurement StandardsCalibration, Soft GagesSurface Imperfections - Terms, Definitions and ParametersMetrological Characteristics of Phase Correct FiltersMotif ParametersCalibration of Contact (Stylus) InstrumentsCharacterization of Surfaces Having Stratified FunctionalPropertiesFiltering and General Measurement ConditionsHeight Characterization using the Linear Ratio Curve ConditionsHeight Characterization using the Material Probability Curve ofSurfaces Consisting of Two Vertical Random Components800-875-4243
Rz to Ra Conversion BS 1134/1-1972Rz x4 - x7 Ra Siemens RecommendationsRz x4 - x10 Ra– Actual ratio depends upon the shape of the profile.800-875-4243
Surface Texture SymbolsASME Y14.36M-1996 ISO 1302-1992ISO 1302-2000bcaxcefabdea roughness value Rab production method, treatment,coating, other text, or note calloutc roughness cutoff or sampling lengthd direction of laye minimum material removal requirementf roughness value other than Ra precededby its parameter symbol (e.g. Rz 0.4) material removal symbolda one single parameter and samplinglength or cutoffb other parametersc production method, treatment,coatingd direction of laye material removal allowancex not to be used material removal symbol800-875-4243
Different Methods of Designating Ra 32Symbol32 AA32 CLA32 AARHRNR 0.80.8aStandardANSI B46.1-1962BS 1134-1961Rare US DesignationOld US MIL SpecificationsJIS B0601-1976JIS B0601-1976DIN3141-19600.8JIS B0601-1976N6CH 180.8Charmilles – VDI 3400ASME Y14.36M-1996Ra 0.832ISO 1302-1978ISO 1302-2002Common US Designation800-875-4243ISO 1302-1978
WHERE DO WE GO WRONG INSURFACE FINISH GAGING? Including Flaws and Defects into the MeasurementsInattention to LevelingNot Taking Into Consideration Environmental ConditionsNot Understanding Calibration Procedures and LimitationsIgnoring Advanced Gage Functions800-875-4243
ASME Y14.36M-1996 ISO 1302-1978 ISO 1302-2002 Common US Designation 0.8 0.8 32 Ra 0.8 Symbol Standard CH 18 32 AA 32 CLA 32 AARH RNR 0.8 0.8a N6. 800-875-4243 WHERE DO WE GO WRONG IN SURFACE FINISH GAGING? Including Flaws and Defects into the Measurements Inattention to Leveling Not Taking Into Consideration Environmental Conditions Not Understanding Calibration