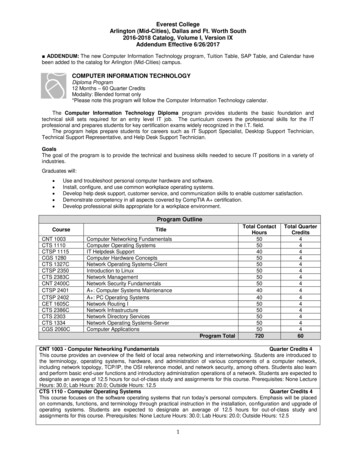
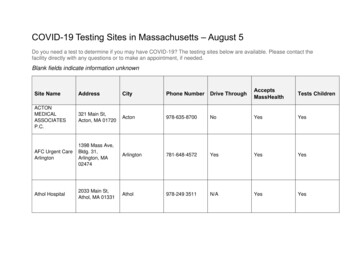
Transcription
UT Arlington Authorized Safety and HealthTrainer Program ProceduresRevised January 2018The University of Texas at ArlingtonBox 19197, 140 W. Mitchell Street,Arlington, TX 76019866-906-9190outreach@uta.eduwww.uta.edu/ded1
2
Table of ContentsI.UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Program Requirements.4A.UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Program Requirements. 4B.UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Program Procedures . 4II.UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Program Summary.4A.Program Purpose . 4B.Voluntary Program . 4C.UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Program Procedures . 4III. UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Designation .4A.Becoming an UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer. . 4B.Update Requirement . 4IV. UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Program Procedures .5A.Designated Training Topics . 51.Bloodborne Pathogens . 52.Confined Space . 53.Cranes . 6Rigging. 6B.4.Electrical. 65.Excavation . 76.Fall Protection . 77.Hazard Communication/Global Harmonization System (GHS). 78.Healthcare. 89.Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S). 810.Material Handling . 811.Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). 912.Respiratory Protection. 913.Scaffolding . 914.Silica . 10Reporting Training Classes . 103
I.UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Program Requirements. Requirements fortrainers authorized through the UT Arlington Authorized Trainer Program are contained in thefollowing two documents:A. UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Program Requirements. This coversthe requirements for UT Arlington Authorized Trainers in all UT Arlington AuthorizedTrainer Programs.B. UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Program Procedures. Theseprocedures contain requirements for the specific designations under the UT ArlingtonAuthorized Safety and Health Trainer Program, including Bloodborne Pathogens,Confined Space, Cranes and Rigging, Electrical, Excavation, Fall Protection, HazardCommunication/Global Harmonization System (GHS), Healthcare, Hydrogen Sulfide(H2S), Material Handling, Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), Respiratory Protection,Scaffolding, and Silica.II. UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Program Summary.A. Program Purpose. The UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Program isdesigned for personnel interested in teaching a range of safety topics. Individuals whomeet the requirements of this program may be approved to teach four (4) to eight (8)hours of a designated training topic and issue participant completion cards to those thatqualify. This training does not satisfy the training requirements found in any OSHAStandards and does not create competent persons.B. Voluntary Program. The UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Program is avoluntary program through which authorized trainers teach occupational safety andhealth, hazard recognition, and prevention in an effort to promote workplace safety andhealth.C. UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Program Procedures. Theseprocedures provide instructions for UT Arlington Authorized Trainers. The proceduresare designed to ensure consistency of classes and that the participants receive the bestpossible training.III. UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Designation.A. Becoming an UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer. To attend the ATP191 Safety and Health Authorized Trainer and become a UT Arlington Authorized Safetyand Health Trainer, a person must meet the following training and experienceprerequisites:1. Three (3) years of safety and health experience, including experience trainingothers, or2. Be a current authorized Outreach TrainerB. Update Requirement. Trainers are required to attend and complete the ATP 190 UTAAuthorized Safety and Health Trainer Update, the ATP 190O Online UTA AuthorizedSafety and Health Trainer Update, or retake the ATP 191 Safety and Health AuthorizedTrainer course every three (3) years. If a trainer’s authorization has expired, the trainerhas a 90-day grace period after their expiration date to attend an Update. The 90-day4
grace period is designed to allow for unexpected circumstances like coursecancellations, illness, and other unavoidable obligations such as jury duty. After thegrace period, a trainer’s authorization may only be reinstated by retaking the ATP 191.During the grace period the trainer will be unable to conduct training and receivestudent completion cards.IV. UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Program Procedures.This section contains information on the procedures for conducting UT Arlington AuthorizedSafety and Health Trainer Program training classes. Trainers are responsible for understandingthese procedures when planning and conducting their classes. Student completion cards in theUT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Program do not expire.A. Designated Training Topics.1. Bloodborne Pathogens Minimum: 4 hoursa) Intro to Bloodborne Pathogensb) OSHA’s Bloodborne Pathogens Standardc) Key Provisions of the Standardd) Types of Bloodborne Pathogense) Risks and Good Work Practicesf)Exposure Controlg) Written Exposure Control Planh) Trainingi)Summary/Review2. Confined Space Minimum: 8 hoursa) Definitionsb) Hazardsc) Key Provisions of the Standardd) Risks and Good Work Practicese) Written Control Planf)Atmospheric Monitoring and Making Safe Entryg) Entry Permitsh) Trainingi)Summary/Review5
3. Cranes and Rigging Minimum: 8 hoursCranesa) Hazard Identification and Common Causes of Crane Accidentsb) Types and Components of Cranesc) OSHA Standards and Directivesd) Roles and Responsibilities of Lifting Personnele) Maintenance, Inspection, and Certification Requirementsf)Load Capacities, Limits, and Lifting Principlesg) Assembly/Disassembly Activitiesh) Hand Signalsi)Preventative Measuresj)Summary/ReviewRigginga) Hazard Identification and Common Causes of rigging accidentsb) OSHA Standards and Directivesc) Types of Rigging Equipmentd) Loads, Limits, and Lifting Principlese) Safety Operating Practices (1910.184)f)Understanding Hand Signalsg) Summary/Review4. Electrical Minimum: 8 hoursa) Hazard Identification and Common Causes of Shock and Electrocutionb) Overhead Power Linesc) GFCI Protectiond) Safety Requirementse) Roles and Responsibilities of the Qualified Personf)Summary/Review6
5. Excavation Minimum: 8 hoursa) Overview – Scope, Application, and Definitionsb) Soil Mechanicsc) General Requirements of the Standardd) Soil Classificatione) Protective Systemsf)Engineered Systemsg) Summary/Review6. Fall Protection Minimum: 8 hoursa) Intro to Fall Protection and Standardsb) Fall Prevention and Fall Protectionc) Fall Distanced) Types Of Fall Protection Equipmente) Fall Arrest Systemsf)Positioning Systemsg) Suspension Systemsh) Other Fall Prevention Typesi)Risks and Good Work Practicesj)Inspecting Equipmentk) Trainingl)Summary/Review7. Hazard Communication/Global Harmonization System (GHS) Minimum: 4 hoursa) What is GHS?b) GHS Guiding Principlesc) Hazard Communications Standardd) Health Hazardse) Physical Hazardsf)HAZCOM Toolsg) Safety Data Sheetsh) Summary/Review7
8. Healthcare Minimum: 4 hoursa) Intro to Safety and Health Issues for Healthcareb) Safety and Health Hazardsc) Infectious Diseasesd) Safe Patient Handlinge) Workplace Violencef)Other Hazardsg) Standards of Enforcementh) Summary/Review9. Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Minimum: 4 hoursNote: H2S trainers are required to conduct a minimum of two (2) H2S training classeseach year.a) What is H2S?b) Common Industrial Sitesc) Physical and Chemical Properties of H2Sd) Concentrations/Toxic Levelse) H2S Effects on Individualsf)Detection and Monitoringg) Contingency and Emergency Action Plansh) Personal Protective Equipmenti)Rescue, First Aid Techniques, and Post Exposure Evaluationj)Summary/Review/Exam10. Material Handling Minimum: 4 hoursa) Hazard Identification and Common Causes of Incidentsb) Use of Mechanical Equipmentc) Manual Handlingd) Hazards and Hazard Controlse) Summary/Review8
11. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Minimum: 4 hoursa) Introduction and Objectivesb) PPE Programc) Eye Hazardsd) Head Protectione) Hearing Protectionf)Foot Protectiong) Hand Protectionh) Body Protectioni)Summary/Review12. Respiratory Protection Minimum: 8 hoursa) Introduction to Respiratory Protection and Objectivesb) Respiratory Hazards and Diseases Caused by those Hazardsc) General Requirements of the Standardd) Respiratory Protection Selectione) Summary/Review13. Scaffolding Minimum: 8 hoursa) Hazard Identification and Common Causes of Scaffold Collapseb) Types and Components of Scaffoldsc) OSHA Standards and Directivesd) Roles and Responsibilities of “Competent Person”e) Assembly/Disassembly Activitiesf)Ladders, Stairs, and Other Structuresg) Fall Protection Equipmenth) Summary/Review9
14. Silica Minimum: 4 hoursa) What is Silica?b) Health Hazards of Silicac) Human Exposure Limitsd) OSHA Requirementse) Monitoringf)Control Measuresg) Respiratory Protectionh) Summary/ReviewB. Reporting Training Classes.1. All classes must be reported within 30 days of completion of the training session.2. When planning and reporting the class, ensure coverage of the required topics.3. Participants should print their name legibly and provide a signature.4. Trainers are responsible for collecting their participants’ mailing addresses for thepurpose of contacting participants and forwarding their participant cards.5. Classes must be entered through the UT Arlington Authorized Trainer OutreachPortal.6. Cards will be mailed to the trainer once the report is approved and payment isconfirmed.7. See the UT Arlington Authorized Trainer Requirements for further information onobtaining participant completion cards.10
UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health Trainer Program Procedures . Revised January 2018 . The University of Texas at Arlington . . This training does not satisfy the training requirements found in any OSHA Standards and does not create competent persons. B. Voluntary Program. The UT Arlington Authorized Safety and Health TrainerProgram is a