
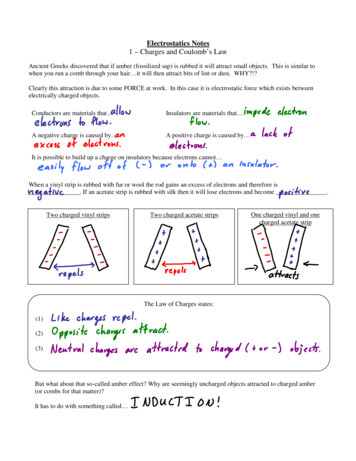
Transcription
Physics 102: Lecture 02Coulomb’s Lawand Electric FieldsToday we will get some practice using Coulomb’s Law learn the concept of an Electric FieldPhysics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 1
Recall Coulomb’s LawForce between charges q1 and q2 separateddistance r:1 22“Coulomb constant”9Opposite charges attract, like charges repelPhysics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 21092/2
Coulomb Law practice:Three Charges Calculate force on 2μC charge due to other two chargesDraw forcesCalculate force from 7μC chargeCalculate force from –7μC7μC chargeAdd (VECTORS!)F 7Q 2.0μC4m––––Q 7.0μCPhysics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 36mF-7Q -7.0 μC
Three Charges – Calculate forces Calculate force on 2μC charge due to other two charges––––Draw forcesCalculate force from 7μC chargeCalculate force from –7μC7μC chargeAdd (VECTORS!)F 7Q 2.0μC4m Calculate magnitudesQ 7 0μCQ 7.0μCPhysics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 46mF-7Q 7 0 μCQ -7.0
Three charges – Adding Vectors F 7 FF-77 Calculate components of vectors F 7 and F-7:F 74mQ 2.0μCQ 7.0μCPhysics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 56mF-7Q -7.0 μC
Three charges – Adding Vectors F 7 FF-77 Add like components of vectors F 7 and F-7:F 7Q 2.0μC4m Final vector F has magnitudeandd directiondi tiQ 7.0μC Double-check with drawingPhysics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 66mFF-7Q -7.0 μC
Electric Field Charged particles create electric fields.– Direction is the same as for the force that a chargewould feel at that location.– Magnitude given by:E F/q kq/r2Qp 1.6x10-19 C r 1x10-10 mEE (9 109)(1.6 10-19)/(10-10)2 N 1.4 1011 N/C (to the right)Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 7
CheckPoint 2.1What is the direction of the electric field at point A?7%1) Up7%2) Down2%3)) Left53% 4) Right32% 5) ZeroPhysics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 8yABx
ACT: E FieldWhat is the direction of the electric field at point C?A. LefteB. RightC ZeroC.Away from positive charge (right)Towards negative charge (right)Net E field is to right.rightAyCBxPhysics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 9
E Field from 2 Charges Calculate electric field at point A due to two unequal charges––––Draw electric fieldsCalculate E from 7μC chargeCalculate E from –3.5μCμ chargegAdd (VECTORS!)A4mNote: this is similar to ((but a bitharder than) my earlier example.We ll do some of thisWe’llhere you try the rest athome!Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 10Q 7.0μC6mQ –3.5 μC
E Field from 2 Charges Calculate electric field at ppoint A due to chargesg– Calculate E from 7μC charge– Calculate E from –3.5μC charge– Add*E7E k q/r2A4mE3Q 7.0μCPhysics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 116mQ -3.5 μC
Adding Vectors E7 E3 Decompose into x and y components.componentsE74mE7y E7 (4/5)( / )A θE7x E7 (3/5)θQ 7.0μCPhysics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 126mQ -3.5 μC
Adding Vectors E7 E3 Decompose into x and y components. Add components.E7Etotal4mAEx 2.25 10 3 N/CEy 1.0 101 0 10 3 N/CPhysics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 13Q 7.0μC6mE3Q -3.5 μC
Comparison:Electricl i Force vs. Electricl i Fieldld Electric Force (F) – the force felt by a charge atsome location Electric Field (E) – found for a location only (anylocation) – tells what the electric force would be ifa charge were located there:F Eq Both are vectors,vectors with magnitude and direction.directionOk, what is E actually good for?Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 14
Electric Field Map Electric field defined at any locationyACBxPhysics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 15
Electric fields:A useful record-keeping tool!Calculate once for fixed charges,use to find force on other charges(like ions/electrons in neurons,heart tissue,tiss e and cell membranes)Eisenberg, BUPhysics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 16
Electric Field Lines Closeness of lines shows field strength (lines never cross)Number of lines at surface QArrow gives direction of E (Start on , end on –)Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 17This is becoming a mess!!!
CheckPoint 3.1XACharge A isYBField lines start on positive charge, end on negative.1) positive93%Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 182) negative4%3) unknown3%
CheckPoint 3.2 / ACTXXAAYYBBCompare the ratio of charges QA/ QB # lines proportional to QA) QA 0.5QB15%Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 19B) QA QB17%C) QA 2 QB53%
CheckPoint 3.4XAYBThe electric field is stronger when thelines are located closer to one another.The magnitude of the electric field at point X is greater than at point Y1) True18%Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 202) False82%Density of field lines gives E
E inside of conductor Conductor electrons free to move– ElElectrons feelsf l electricl i forcef- willill move untililthey feel no more force (F 0)– F Eq:F E if FF 00 ththen EE 00 E 0 inside a conductor (Always!)Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 21
Demo: E-fieldE field from dipoleyACBxPhysics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 22
Recap E Field has magnitude and direction:– E F/q– Calculate jjust like Coulomb’s law– Careful when adding vectors Electric Field Lines– Density gives strength (# proportional to charge.)– Arrow gives direction (Start end on –) Conductors– Electrons free to move E 0Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 23
To Do Campus closed on Monday; no office hours. Homework 1 due Wednesday, Jan 23 @ 8 AM! Do your Checkpoint by 8:00 AM Wednesday.Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 24
Electric Force (F) - the force felt by a charge at some location Electric Field (E) - found for a location only (any location) - tells what the electric force would be if a charge were located there:a charge were located there: F Eq Both are vectors with magnitude and directionBoth are vectors, with magnitude and direction.




![2 CHAPTER 1 [Topic 1] Coulomb's law, electrostatic field and electric .](/img/52/physics.jpg)




