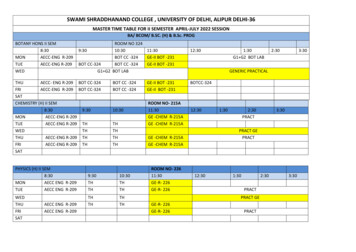
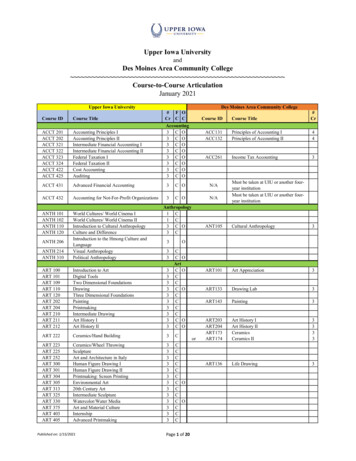
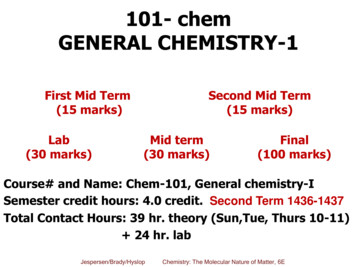
Transcription
Crystal StructuresChapter 7Wednesday, October 21, 2015
Interstitial sites in CP StructuresA large number of ionic structures can be regarded as built of CP layers of anionswith the cations placed in interstitial sitesfor every anion, there is 1 Octahedral site and 2 Tetrahedral sites
Octahedral Holes in CCPcoordinates:of O holes½,0,00,½,00,0,½½,½,½ O site
Tetrahedral Holes in CCPT sites:¾,¼,¼¼,¾,¼¼,¼,¾¾,¾,¾T- sites:¼,¼,¼¾,¾,¼¼,¾,¾¾,¼,¾
Octahedral Holes in CCP and HCP
Tetrahedral Holes in CCP and HCP
Ionic Crystal StructuresMany ionic crystals consist of a close-packed lattice of the largeranions with the smaller cations occupying interstitial sites.let’s lookat thesestructures
NaCl StructureCCP with all octahedral holes filledCoordination 6, 6Cation Coord. OctahedronAnion Coord. OctahedronConnectivity Edge sharing octahedra4 NaCl in unit cell
Zinc Blende (ZnS) StructureCCP with all T holes filledCoordination 4, 4Cation Coord. TetrahedronAnion Coord. TetrahedronConnectivity Corner sharing Tetrahedra4 ZnS in unit cell
Fluorite (CaF2) and Antifluorite (Li2O)Fluorite: CCP of Ca2 with all T and T- holes filled with FAntifluorite: CCP of O2- with all T and T- holes filled with Li Ca2 Coordination 8, 4 (fluorite)Cation Coord. CubicAnion Coord. TetrahedralConnectivity Edge sharing FCa4tetrahedra or edge sharing CaF8 cubes4 CaF2 in unit cell
Alternative Representations of FluoriteCa2 Displacing the unit cell by ¼ of a body diagonal emphasizes the cubic cation coordination:F-
Fluorite (CaF2) and Antifluorite (Li2O)Ca2 origin of the term “fluorescence”(George Stokes, 1852) fluorite common for fluorides of large,divalent cations and oxides of largetetravalent cations (M2 F2 and M4 O2) antifluorite common foroxides/chalcogenides of alkali earths (M2O)CaF2with Eu2 impurities
Wurtzite (ZnS) StructureHCP with all T holes filledZnO50 nmCoordination 4, 4Cation Coord. TetrahedronAnion Coord. TetrahedronConnectivity Corner sharing Tetra.2 ZnS per unit cell
Diamond Structuresame as zinc blende, but with only one elementdiamondzinc blendeCoordination 4Connectivity Corner sharing Tetrahedra8 C atoms per unit cell
CsCl Structuresimple cubic lattice with Cs at cube center (not CP, not BCC!)Coordination 8, 8Cation Coord. CubicAnion Coord. CubicConnectivity face sharing cubes1 CsCl per unit cellAdoption by chlorides, bromides andiodides of larger cations
Self TestIdentify the following crystal structures:Fluorite, AntifluoriteNaClDiamondCCPZincblendeLi3Bi
Fluorite (CaF2) and Antifluorite (Li2O) Fluorite: CCP of Ca2 with all T and T-holes filled with F-Antifluorite: CCP of O2-with all T and T-holes filled with Li Coordination 8, 4 (fluorite) Cation Coord. Cubic Anion Coord. Tetrahedral Connectivity Edge sharing FCa 4 tetrahedra or edge sharing CaF 8 cubes 4 CaF 2 in unit cell Ca2