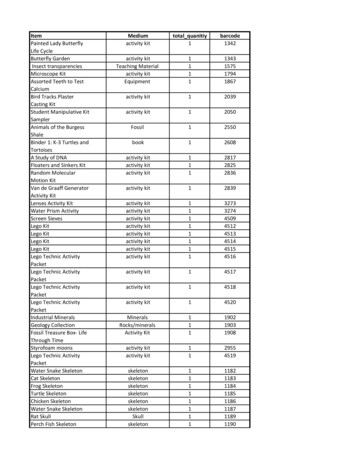
Transcription
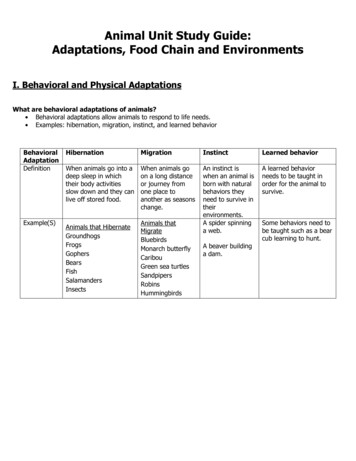
Animal Unit Study Guide:Adaptations, Food Chain and EnvironmentsI. Behavioral and Physical AdaptationsWhat are behavioral adaptations of animals?Behavioral adaptations allow animals to respond to life needs.Examples: hibernation, migration, instinct, and learned bernationMigrationInstinctLearned behaviorWhen animals go into adeep sleep in whichtheir body activitiesslow down and they canlive off stored food.When animals goon a long distanceor journey fromone place toanother as seasonschange.An instinct iswhen an animal isborn with naturalbehaviors theyneed to survive intheirenvironments.A spider spinninga web.A learned behaviorneeds to be taught inorder for the animal tosurvive.Animals that sInsectsAnimals thatMigrateBluebirdsMonarch butterflyCaribouGreen sea turtlesSandpipersRobinsHummingbirdsA beaver buildinga dam.Some behaviors need tobe taught such as a bearcub learning to hunt.
What are physical adaptations?Physical adaptations help animals survive in their environment.Examples: camouflage and ryCamouflage is when animals blendinto their environments to protectthem from enemies or predators.Mimicry is when animals look like otheranimals to avoid being eaten. Thisadaptation helps protect them from theirpredators.Example(s)The Scarlet King Snake mimics theCoral Snake. It looks just like it sopredators will leave it alone because theythink it is poisonous.(a frog blendinginto the leaves)(an octopus blending into theocean floor)Animals also use their physical adaptations as a defense. See the chart below for examples.DefenseVenomAnimalBee, some snakes, scorpion, spiders, puffer fish,Portuguese man-of-warSkinArmadillo, rhinocerosWeapons Antlers: deer, moose, elk, caribouHooves: deerClaws: cat, kangarooTeeth: raccoon, elephant, walrus, catSpines: hedgehog, porcupine, lion fish, caterpillarPlayOpossum, hognose snakedead
II. Food ChainsWhat does a food chain show?A food chain shows a food relationship among plants and animals in a specific area orenvironment?decomposers(decayed material)ProducerConsumerA producer is a plantthat creates its own foodfrom sunlight, air, andwater.PredatorA consumer is ananimal that eatslivingorganisms(plant oranimal)PreyHunts forotheranimalsHunted byotheranimalsDecomposerA decomposer is an organism that breaksdown decayed plants and animals into smallerpieces which again can be used again by livingthings.CarnivoreHerbivoreOmnivoreMeat EaterPlant EaterMeat and Plant Eater
III. esertcactuscamel, snakesgrasslandtall grasses,very littletreescheetahs,zebras, lions,giraffesrainforesttall trees that cover theforestforesttall grasses and treessnakes, toucan,birds, monkeyssnakes, bears,deer, wolves,rabbits, owls,beavers
WaterrelatedenvironmentsPlantsAnimalspondWater lilies, tallgrassesSmall fish, tadpoles, frogs, eelsmarshlandGrasses,shrubs, treesFrogs, beaver,turtles, muskratswampGrasses, shrubs,treesfrogs, snakes,beaver, turtlestreamgrassesfish,rivergrassesfish, snake,oceanSeaweed,coralLarge fish,dolphin, shark,crab,PopulationA population is a group of organisms of the same kind that lives in the same place.Examples of a population are a group of swans in a pond, a school of fish in a river, and a herd ofcattle in the grassland.CommunityA community is all of the populations that live together in the same place.An example of a dry-land community would be a forest made up of trees, squirrels, worms, rabbits,and hawks. An example of a water-related community would be an ocean made up of fish, crabs, andseaweed.
What are behavioral adaptations of animals? Behavioral adaptations allow animals to respond to life needs. Examples: hibernation, migration, instinct, and learned behavior . Frogs, beaver, turtles, muskrat swamp Grasses, shrubs, trees frogs, snakes, beaver, turtle stream grasses fish, river grasses fish, snake, ocean Seaweed,