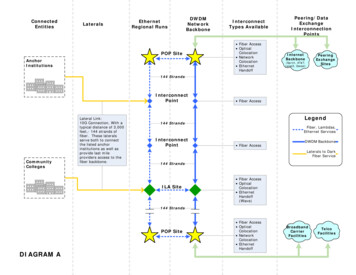
Transcription
Evaluation of National Healthcare SafetyNetwork (NHSN) Data Available through theArizona Department of Health Services DataUse Agreement (DUA)Geoff Granseth, MPHCDC/CSTE Applied Epidemiology FellowArizona Department of Health ServicesHealthcare-Associated Infections Program
Outline xt Steps
Learning Objectives Describe the National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN)and its components Identify the completeness and representativeness ofNHSN data available to ADHS Describe differences in MRSA surveillance data betweenMEDSIS and NHSN Understand how the sensitivity of NHSN for capturingMRSA events reported to MEDSIS was calculated Describe positive outcomes as a result of this surveillancesystem evaluation
Background The National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) is the most widelyused healthcare-associated infection (HAI) tracking system in theU.S.– Used by over 17,000 healthcare facilities– Standardized definitions, protocols Acute care hospitals and dialysis facilities represent the majority ofreporting facilities– Other participants include: Critical access hospitalsLong-term acute care hospitalsRehabilitation hospitals Psychiatric hospitalsAmbulatory surgery centersNursing homes
NHSN: Growth in Facility Participation, 2006-2015Pollock, Daniel A. National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) Antimicrobial Use and Resistance (AUR) Reporting and the Standardized Antimicrobial AdministrationRatio (SAAR) http://www.houstontx.gov/health/Epidemiology/7 Pollock-NHSN AUR and SAAR.pdf
Background In Arizona, reporting HAIs through NHSN is notmandatoryo 33 states and the District of Columbia have mandatoryreporting requirementso Most acute care hospitals report data to NHSN as arequirement for reimbursement by the Centers forMedicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Through a data use agreement (DUA) with CDC, the HAIprogram gained direct access to NHSN data in the fall of2015– 6 other states currently have a DUA with CDC
CDC Reports Hospital-Specific HAI Event Data to theCenters for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS)Pollock, Daniel A. National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) Antimicrobial Use and Resistance (AUR) Reporting and the Standardized Antimicrobial AdministrationRatio (SAAR) http://www.houstontx.gov/health/Epidemiology/7 Pollock-NHSN AUR and SAAR.pdf
Background Main infection types tracked include: Central Line-Associated Bloodstream Infection(CLABSI) Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) Surgical Site Infections (SSIs) Lab-identified methicillin-resistant Staphylococcusaureus (MRSA) bacteremia Lab-identified Clostridium difficile (C. difficile)infections
NHSN Components
Surveillance Objectives Estimate the burden of selected HAIs in the state ofArizona Monitor changes in the number of HAIs over time Target prevention efforts Evaluate the impact of prevention strategies Detect HAI-related outbreaks
National Healthcare Safety Network(NHSN) Evaluation Using the CDC’s Updated Guidelines forEvaluating Public Health Surveillance Systemsevaluated on: Data Quality(Completeness) Representativeness Sensitivity Stability SimplicityTimelinessPredicted Value PositiveAcceptabilityFlexibility
Methods Representativeness was assessed by identifying all Arizona acute carehospitals (ACH) and critical access hospitals (CAH) and comparing dataavailable through NHSN; facilities without available data were identifiedand characterized Completeness was assessed by comparing hospitals with NHSN dataavailable to ADHS, by infection type, to those available to CDC Sensitivity of NHSN for capturing invasive MRSA events reported toArizona’s communicable disease surveillance system (MEDSIS) wascompleted by matching all 2014 NHSN LabID MRSA data to 2014 MEDSISMRSA cases Additional surveillance system attributes were also considered in theevaluation
Representativeness We identified 74 acute care hospitals (ACH) in the state ofArizona through the American Hospital Directory by using thelast four digits of each facility’s CMS Certification Number(CCN)– 53 of the 54 hospitals in our Super Group are classified as acute carehospitals The Center for Rural Health at the University of Arizonarecognizes 14 critical access hospitals (CAH) in the state– 1 of the 54 hospitals in our Super Group, one is designated a criticalaccess hospital
Hospitals RepresentedVeteran Affairs (VA) and Indian Health Services (IHS)/638 facilities were identified asgroup not available to ADHSAll 54 of our Hospitals were classified as “General Hospital” in NHSN
Hospitals in Arizona
Hospital Reporting Plans, January 2015Reporting Plan Total # of Hospitals# of Hospitals Reporting,in ADHS Super Group per facility’s reporting plan% ReportingCLABSI5454100%CAUTI5454100%VAE542648%SSI COLO545398%SSI HYST545398%MRSA LabID(Blood)544074%MRSA LabID5415**28%MRSA (Any)5454**100%CDI LabID5454100%*Not all hospitals are required to report all infections; for example some hospitals do not have ventilatedpatients or do not perform surgeries**One Hospital reported MRSA as both LabID Blood and LabID
Hospitals Reporting to NHSN
Completeness 54 hospitals in our DUA Super Group ADHS has access to the data for 90% of the acutecare hospitals in the state reporting CLABSI andCAUTI ADHS only has data available for 79% of thereporting hospitals in state for MRSA and CDILabID reporting.
Sensitivity Due to a lack of patient identifiers, a fairlystrict matching protocol was used Variables used to match include date of birth(DOB), gender, and date of specimencollection– Only cases that matched within seven days ofspecimen collection between the two surveillancesystems were included– Age was used for MEDSIS cases missing DOB
MRSA Sensitivity Matching Process2014 MEDSIS Cases 1178
MRSA Matching and Sensitivity Nearly two-thirds matched the exact date of specimen collection 54% Sensitivity of NHSN for capturing invasive MRSA events reported to MEDSISrepresents a conservative estimate of sensitivity
Limitations to comparing MEDSIS and LabID dataMEDSISNHSNMEDSIS case combines all reports for asingle patientEach unique report is a separate eventrecorded in NHSNOnly sterile body sites included“Blood Only” or “All Specimen”depending on reporting planPatient names availablePatient names not availableDOB not a required fieldDOB a required fieldNo onset classificationCommunity-Onset (CO) or HospitalOnset (HO) based on admission and testdateDate of specimen collection not required Date of specimen collection required andused in CO or HO classificationPopulation-level surveillance systemHospital-based surveillance system
ConclusionsAs a result of identifying gaps in facility data completeness: ADHS was granted access to 18 additional facilities in December2015 10 long-term acute care hospitals (LTACHs) and 8 inpatientrehabilitation facilities (IRFs)ADHS was granted access to 11 additional facilities in February2016 representing six additional facility types: Children’s HospitalOncology HospitalCritical Access Hospital Orthopedic HospitalPsychiatric HospitalSurgical Hospital ADHS was granted access to 115 dialysis facilities in April 2016
ConclusionsNHSN Facility Type# Facilities (August 2015)# Facilities (February PSYCH02Total5483* 54% increase in Facilities
Potential Reasons for Low Sensitivity Hospital not reporting to NHSN or not in our supergroup Invasive MRSA cases that were not hospitalized MEDSIS cases that did not meet the criteria for reporting to NHSN– MRSA in non-blood normally sterile sites in facilities only reportingblood isolates to NHSN Persons present in both sets of data but whose records did not match basedon our matching criteria Under-reporting to NHSN of MRSA events by the reporting facilities47/54 (87%) hospitals reported at least 1 MRSA LabID event in 2014– 42/47 (89%) matched at least 1 event with MEDSISData validation with Arizona hospitals will help distinguish some of these factors
Next StepsThis surveillance evaluation has provided the HAI Programwith the groundwork necessary to conduct more specificanalyses, and be better equipped to accurately interpret thefindings from Arizona’s NHSN dataFuture Activities: Use NHSN data to create annual reports for HAIs Use data to drive collaborative interventions to reduceHAIs in the state Begin conducting data validation
Acknowledgement This study/report was supported in part by anappointment to the Applied Epidemiology FellowshipProgram administered by the Council of State andTerritorial Epidemiologists (CSTE) and funded by theCenters for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)Cooperative Agreement Number 1U38OT000143-03.
THANK YOUGeoff Granseth CDC/CSTE Applied Epidemiology FellowGeoffrey.granseth@azdhs.gov 602-364-3753azhealth.gov@azdhsfacebook.com/azdhs
The National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) is the most widely used healthcare-associated infection (HAI) tracking system in the U.S. -Used by over 17,000 healthcare facilities -Standardized definitions, protocols Acute care hospitals and dialysis facilities represent the majority of reporting facilities