Transcription
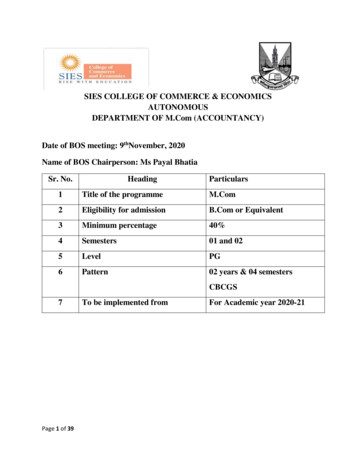
SIES COLLEGE OF COMMERCE & ECONOMICSAUTONOMOUSDEPARTMENT OF M.Com (ACCOUNTANCY)Date of BOS meeting: 9thNovember, 2020Name of BOS Chairperson: Ms Payal BhatiaSr. No.HeadingParticulars1Title of the programmeM.Com2Eligibility for admissionB.Com or Equivalent3Minimum percentage40%4Semesters01 and 025LevelPG6Pattern02 years & 04 semestersCBCGS7Page 1 of 39To be implemented fromFor Academic year 2020-21
SIES COLLEGE OF COMMERCE & ECONOMICS(AUTONOMOUS)(Affiliated to University of Mumbai)RE-ACCREDITED GRADE “A” BY NAACBOARD OF STUDIESDEPARTMENT OF MCOM ACCOUNTANCY(WITH EFFECT FOR THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2020-2021)Page 2 of 39
OBJECTIVES : To Provide the students with strong foundation, skills and expertise inthe field of Finance and Accountancy To enable the learners in understanding, developing, preparing andpresenting the financial report in the business scenario. To understand concepts relating to financing decisions. To develop ability to analyse and interpret various tools of financialanalysis and planning. To provide a sound platform for the students to exploit self employmentavenues. To enhance the career prospects of students and help them to becomemore competitive To develop research aptitude and analytical skills of students.Page 3 of 39
SCHEME OF MODULESSEMESTER ICreditsCourse NameCORE COURSES (CC)Serial No1Course code1.1MACCS10106Strategic conomics for Business DecisionsCost and Management AccountingBusiness Ethics and Corporate SocialResponsibilityTOTAL CREDITS2SEMESTER IICreditsCourse NameCORE COURSES (CC)Serial No1Course 040606TOTAL CREDITSPage 4 of 3924Research MethodologyMacro Economics Concepts andApplicationsCorporate FinanceE-Commerce
SEMESTER ISerial NoCourse codeCredits Course Name1CORE COURSES (CC)1.1MACCS10106STRATEGIC MANAGEMENTCOURSE OBJECTIVES and OUTCOMES:Course ObjectivesCourse Outcome1. To enable the learners to understandTo expose Students to variousperspectives & concepts of StrategicManagement & its applications.new forms of Strategic Managementconcepts and their use in business2. To understand recent developmentsand trends in the business corporateworld s3. To develop learning and analyticalskills to solve cases and to providestrategic solutions.SN1234Page 5 of 39Students to explore the principles ofstrategy formulation, implementationand control in organizations.To help students develop skills forapplying these concepts to the solutionof business problems.REVISED SYLLABUSMODULESMODULESIntroduction to Strategic ManagementStrategy Formulation Implementation andEvaluationBusiness, Corporate & Global StrategiesEmerging Strategic TrendsTOTALNO OFLECTURES1515151560
Sr.No.Modules1Module-1Introduction to Strategic Management Concept of Strategic Management, StrategicManagement Process, Vision, Mission and Goals,Benefits and Risks of Strategic Management Levels of Strategies: Corporate, Business &Operational Level Strategy Functional Strategies: Human Resource StrategyMarketing Strategy, Financial Strategy, OperationalStrategy Business Environment Components of Environment Micro & Macro Environmental Scanning2Module-2Strategy Formulation, Implementation & Evaluation Strategic Formulation: Stages and Importance.Formulation of Alternative Strategies: Mergers,Acquisitions, Takeovers, Joint Ventures Diversification,Divestment and liquidation Strategic Analysis and Choice Issues and Structures,Corporate Portfolio Analysis- SWOT Analysis BCGMatrix, GE Nine Cell Matrix, Hofer's Matrix ETOP- Environmental Threat and Opportunity Profile Strategic Implementation: Steps Importance andProblems, Resource Allocation - Importance &ChallengesStrategic Choice – Factors and Importance Strategic Evaluation and Control Importance.Limitations and Techniques Budgetary Control Advantages. LimitationsPorters Five Forces Model & VUCA EnvironmentPage 6 of 39No. oflectures1515
3Page 7 of 39Module-3Business ,Corporate & Global Strategies Corporate Restructuring Strategy: Concept, Need &Forms, Corporate Renewal Strategies: Concept, Internaland External factors and Causes. Strategic Alliance Concept, Types, Importance,Problems of Indian Strategic Alliances & InternationalBusinesses Public Private Participation: Importance, Problems &Governing Strategies of PPP model. Information Technology Driven Strategies: Importance,Limitations & contribution of IT sector in IndianBusiness.15Module-14Emerging Strategic Trends Business Process Outsourcing and Knowledge ProcessOutsourcing in India : Concept and Strategies. Reasonsfor growing BPO and KPO businesses in India. Reengineering Business Processes - BusinessReengineering, Process Reengineering and OperationalReengineering Disaster Management : Concept, Problems andConsequences of Disasters, Strategies for Managing andPreventing disasters and Cope up Strategies Start-up Business Strategies And Make in India Model:Process of business start ups and its Challenges, GrowthProspects and government initiatives in Make in IndiaModel with reference to National manufacturing ,Contribution of Make in India Policy in overcomingindustrial sickness.15Total Lectures60
Note:Particulars (Universitysyllabus)Remarks: Revised SyllabusModule-2Strategy Formulation,Implementation &EvaluationDeleted- Strategic Choice – Factors andImportanceAdded Inclusion Of Porters Five Forces Model &VUCA Environment , J. Barneys VRIOFrameworkReference Materials :1) Business Policy and Strategic Management – Sukul Lomash and P KMishra, Vikas Publication House Pvt Ltd, New Delhi2) Business Policy & Strategic Management by Dr. Azhar Kazmi (TataMcgraw Hill )3) Strategic Management, by Fred R. David (Prentice Hall International)Page 8 of 39
SEMESTER ISerial NoCourse codeCredits Course Name11.2CORE COURSES (CC)MACCS10206ECONOMICS FOR BUSINESSDECISIONSCourse Objectives: Economics for Business Decisions1To enable the students to understand the basic concepts in economicsand their applications in business decision making2To give them a comprehensive knowledge about market structures andtheir functioning3To help them to understand cost and revenue functions and theirapplications in business4To enable students to analyse consumer behavior with the help ofeconomic theoriesREVISED SYLLABUSNumberLecturesModule NoTopics1Basic principles in Business Economics 2Demand and Supply analysis: Page 9 of 39Meaning, Scope and Significance of BusinessEconomics; twin principles of scarcity andefficiency; profit maximisation principle; marketeconomy and invisible hand; production possibilityfrontier; opportunity cost; accounting profit andeconomic profit; market failure, externality, publicgoods and economic role of governmentDeterminants of demand- market demand functiontheory of attributes, snob appeal, band wagon andVeblen effect and demand function. Law of supplyelasticity of supply.15of
3 4Applications of elasticity of demand and supply toeconomic issues; Paradox of bumper harvest-tax onprice and quantity-minimum floor and maximumceilings; minimum wages controversy andadministered price control.The theory of consumer choice-Consumerpreference and budget constraint-equilibriumposition of tangency with the help of indifferencecurve analysis –effect of changes in price andincome on consumer equilibrium.Production decisions and Cost analysis:Production function-short run and long run-Law ofvariable proportion, returns to scale, scaleeconomies, scope economies – least cost factorcombination for a given output – Expansion path andMultiproduct firm-cost reduction through experience– learning curve.Economic analysis of Cost: Classification of costs,short run and long run cost functions.15Market Structure analysis: Difference between perfectly and imperfectlycompetitive markets – Perfect competition andMonopoly as limiting cases of market imperfectionssources of market power – profit maximization ofsimple and discriminating monopolist – methods ofmeasuring monopoly power – public policy towardsmonopoly power.Different forms of imperfect competition –Monopolistic competition and oligopoly – strategicdecision making in oligopoly markets – collusive andnon -collusive oligopoly – colliding oligopoly;rivalry among few, price war and kinked demandcurve – collusive oligopoly models of priceleadership and cartel – basic concepts of game theory– Using game theory to analyse strategic decisions –application of model of prisoner’s dilemma in marketdecisionsTotal LecturePage 10 of 39151560
Note:Particulars (Universitysyllabus)RemarksModule 1- BasicPrinciples in BusinessEconomicsSignificance of Business economics has beenincluded in Module 1.The sub topic “incremental and marginal principle”has been deleted.References:1) Samuelson and Nordhas Eonomics2) Gregory Mankiw Principles of Economics3) H.L. Ahuja Principles of Micro Economics4)Pal Sumitra Managerial economics Cases and ConceptsPage 11 of 39
SEMESTER ISerial NoCourse codeCredits Course Name1CORE COURSES (CC)1.3MACCS10306COST AND MANAGEMENTACCOUNTINGCOURSE OBJECTIVES:Learning ObjectivesLearning Outcomes1 To enable the learner to understand theStudents would be able toconcepts of cost and management accounting get a clear picture ofconcepts of costaccounting andmanagement accounting,its differences and itsimportance and relevancein business.2 To understand the various concepts ofstandard costingStudents would be able todetermine standard costand its types, determinetotal standard cost andvariances and itsapplicability3 To provide information regarding costaccounting as a tool of managerial decisionsStudents wouldunderstand about profitplanning, make or buydecisions, cost reductionand cost control.Page 12 of 39
4 To develop various skills among the studentsrelated with budget and budgetary controlStudents would analysethe motive behindpreparing the variousbudgets. Establishing abudgetary control systemand its administration.5 To understand the concept of operatingcosting in different areasStudents would be able tounderstand the concept ofoperating costing and itsapplicability in serviceindustry i.e hotel, hospital,transport, etc.REVISED SYLLABUSMODULESSNMODULES1Introduction to Cost and ManagementAccountingStandard CostingMarginal Costing, Absorption Costing andManagement DecisionsBudgetary ControlOperating CostingTOTAL2345Page 13 of 39NO OFLECTURES041416141260
Sr.No.Modules1Module 1Introduction to Cost and Management AccountingIntroduction to Cost accounting and its conceptsIntroduction to Management Accounting, DifferenceBetween Cost Accounting and ManagementAccountingImportance and Relevance of Cost and ManagementAccounting2Module 2 Standard Costing3Numberoflectures0414Standard Costing as an Instrument of Cost Control and CostReduction - Fixation ofStandards- Theory and Problems based on Analysis of Variancesof Materials, LabourOverheads and sales including Sub-variancesModule 3 - Marginal Costing, Absorption Costing and 16Management DecisionsMeaning of Absorption Costing - Distinction betweenAbsorption Costing andMarginal Costing - Problems on Breakeven Analysis - CostVolume Profit Analysis Breakeven Charts - Contribution Margin and Various DecisionMaking Problems Managerial Decisions through Cost Accounting such as PricingAccepting Special Offer- Profit Planning - Make or Buy Decisions - Determining KeyFactors - DeterminingSales Mix - Determining Optimum Activity Level - PerformanceEvaluation Alternative Methods of Production, Cost Reduction & CostControl4Page 14 of 39Module 4 Budgetary Control14Budget and Budgetary Control - Zero Based Budget Performance Budgets -
Functional Budgets Leading to the Preparation of MasterBudgets - CapitalExpenditure Budget - Fixed and Flexible Budgets - Preparationof Different Types ofBudgets (Excluding Cash Budget)Module 5 Operating Costing125Meaning of Operating Costing - Determination of Per Unit Cost- Collection of CostingData - Practical Problems based on Costing of Hospital, Hoteland Goods & Passenger TransportTotal Lectures60References Advanced Cost & Management Accounting book by Saxena V.Edition: 4th editionPublisher: Sultan Chand & Sons Advanced Cost Accounting book by Jain, S/ Narang, K.Edition: 9th editionPublisher: Kalyani Publication Cost & Management Accounting by Inamdar S MEdition: 14theditionPublisher: Everest Publishing House Cost & Management Accounting Kishore R. M.Edition: 4th editionPublisher: Taxman Allied Service Principles & Practice Of Cost Accounting by Bhattacharyya, A. K.Edition: 3rd edition Publisher: PHI Learning Pvt Ltd Management & Cost Accounting by DruryEdition: 6th editionPublisher: ThompsonBooks Cost Accounting: Managerial Emphasis by HorngrenEdition: 12th editionPublisher: Pearson Education Cost Accounting by Jawahar LalEdition: 3rd editionPublisher: Tata McGraw HilPage 15 of 39
Note on changes in syllabusParticularsRemarksNew ModuleAddedIntroduction to Cost and ManagementAccounting as Module 1 and hence Module 1,2,3,4 is now Modules 2,3,4,5ModuleControlPage 16 of 394Budgetary Deleted from syllabusCash Budget as it is there in MCOM part 2Financial Management
SEMESTER ISerial NoCourse codeCredits Course Name1CORE COURSES (CC)1.4MACCS10406BUSINESS ETHICS & CORPORATESOCIAL RESPONSIBILITYCOURSE OBJECTIVES and OUTCOMES:Course ObjectivesTo familiarize with the concept andrelevance of Business Ethics in themodern eraCourse Outcome.To help the students to recognizelegal and ethical issues whenmaking business decisionsTo understand the scope andcomplexity of Corporate Socialresponsibility.To gain an enhanced understandingof following ethical rules andethical constraints in Indian &global context.To describe the concept of corporate To help students Formulate ethicalsocial responsibility and the primary philosophy to explain how itcontributes to current practice.fundamentals.To enhance the career prospects &to be more competitive.SN1234Page 17 of 39To Explain students the relationshipbetween ethics, morals and valuesin the workplaceREVISED SYLLABUSMODULESMODULESNO OFLECTURESIntroduction to Business Ethics15Indian Ethical Practices and Corporate15GovernanceIntroduction To Corporate Social15ResponsibilityAreas Of CSR & CSR Policy15TOTAL60
Sr.No.Modules1Module-1Introduction to Business Ethics Business Ethics: Concept, Characteristics, Importanceand Need for business ethics. Indian Ethos, Ethics andValues, Work Ethos Sources of Ethics, Concept of Corporate Ethics, codeof Ethics-Guidelines for developing code of ethics,Ethics Management Programme, Ethics Committee Various approaches to Business Ethics - Theories ofEthics - Friedman's Economic theory, Kant'sDeontological theory, Mill & Bentham's Utilitarianismtheory Gandhian Approach in Management and Trusteeship,Importance and relevance of trusteeship principle inModem Business. Gandhi's Doctrine of Satya andAhimsa Emergence of new values in Indian Industries aftereconomic reforms of 19912Module-2Indian Ethical Practices and CorporateGovernance Ethics in Marketing and Advertising, HumanResources Management, Finance and Accounting,Production, Information Technology. Copyrights andPatents Corporate Governance Concept, Importance.Evolution of Corporate Governance, Principles ofCorporate Governance,Failure of CorporateGovernance and its consequences Regulatory Framework of Corporate Governance inIndia, SEBI Guidelines and clause 49, AuditPage 18 of 39Numberoflectures1515
Committee, Role of Independent Directors, Protectionof Stake Holders, Changing roles of corporate Boards Elements of Good Corporate Governance,Freedom Of Speech In the Workplacea)Whistle-Blowingb)Consequences of Whistle-Blowingc)Government’s Protection of Whistle-Blowersd)Management Responsiveness to Potential WhistleBlowing Situations3Module-3Introduction To Corporate Social Responsibility Corporate Social Responsibility: Concept, Scope,Relevance and Importance of CSR in Contemporarysociety15 Corporate Philanthropy, Models for implementationof CSR, Drivers of CSR, Prestigious awards for CSRin India CSR and Indian Corporations – Legal provisions andspecifications on CSR, A scorecard, Future of CSR inIndia Role of NGOs an international agencies in CSR,Integrating CSR into business4Module-415Areas Of CSR & CSR Policy CSR towards Stakeholders— Shareholders, Creditorsand Financial Institutions, Government, Consumers,Employees and Workers, Local Community andSociety CSR and environmental concerns Designing CSR Policy- Factors influencing CSRPolicy, Role of HR Professionals in CSRPage 19 of 39
Global Recognitions of CSR- ISO- 14000-SA 8000— AA 1000 — Codes formulated by UN GlobalCompact — UNDP, Global Reporting Initiative; majorcodes on CSR CSR and Sustainable Development CSR through Triple Bottom Line in BusinessTotal Lectures60Note:Particulars (Universitysyllabus)Remarks:Revised SyllabusModule-2Deleted: Failure of Corporate Governance and itsconsequencesStrategy Formulation,Implementation &EvaluationAdded: Freedom Of Speech In the Workplacea)Whistle-Blowingb)Consequences of Whistle-Blowingc)Government’s Protection of Whistle-Blowersd)Management Responsiveness to PotentialWhistle Blowing SituationsUday Kotak Committee Report On CorporateGovernanceReference Materials :1. Business Ethics & Corporate Governance S K Bhatia2. Business Ethics & Corporate Social responsibility by Narayan Kar(International Book House Pvt. Ltd.)3. Business Ethics & Corporate Social responsibility Corp. Governance bySaroj Kumar & Veera KaroliPage 20 of 39
SEMESTER IISerial NoCourse codeCredits Course Name1CORE COURSES (CC)1.1MACCS20106RESEARCH METHODOLOGYCOURSE OBJECTIVES and OUTCOMES:Course ObjectiveCourse OutcomeTo understand some basic concepts ofResearch and its MethodologiesTo help students to understand keyresearch concepts & issues.To know primary characteristics ofquantitative research and qualitativeresearchStudents to have adequate knowledgeon measurement & scaling techniquesas well as the quantitative data analysisTo be able to write a good introduction To identify various sources of datato an educational research study and its collection and collecting informationcomponentsfrom various sources.To enhance the career prospects ofstudents and help them to developanalytical approachTo develop students to understandvarious research designs andtechniques & its applications incomplex and decision making becompetitive.REVISED SYLLABUSMODULESSNMODULES123Introduction to ResearchResearch ProcessData Processing & Statistical AnalysisPage 21 of 39NO OFLECTURES151515
4Sr.No.Research Reporting & Modern Practices e-1Introduction to Research Features and Importance of research id businessObjectives and Types of research- Basic, Applied',Descriptive, Analytical and Empirical Research. Formulation of research problem, Research Design,significance of Review of Literature Hypothesis: Formulation, Sources, Importance andTypes Sampling Significance, Methods, Factorsdetermining sample size2Module-2Research Process Stages in Research Process Data Collection : Primary data: Observation,Experimentation, Interview, Schedules, Survey Limitations of Primary data Secondary data : Sources and Limitations Factors affecting the choice of method of datacollection Questionnaire: Types, Steps in QuestionnaireDesigning, Essentials of a good questionnaire3Module-315Data Processing & Statistical Analysis Data Processing : Significance in Research, Stages inPage 22 of 3915
Data Processing: Editing, Coding, Classification,Tabulation Graphic Presentation Statistical Analysis : Tools and Techniques,Measures of Central Tendency, Measures ofDispersion, Correlation Analysis and RegressionAnalysis. Testing of Hypotheses - Parametric Test - t test, f test, z test- Non-Parametric Test - Chi square test, ANOVA,FactorAnalysis Interpretation of Data : Significance and Precautionsin data Interpretation4.Module-4Research Reporting & Modern Practices InResearch Research Report Writing: Importance, Essentials,Structure/ layout, Types References and Citation Methods :APA (American Psychological Association)CMS (Chicago Manual Style)MLA (Modern Language Association) Footnotes and Bibliography Modern Practices : Ethical Norms in Research,Plagiarism, Role of Computers in Research15Use of online mediums for researchTotal LecturesPage 23 of 3960
Note on changes in syllabusParticularsRemarks:Revised SyllabusModule -4Deleted- Role of computers inResearch Reporting & Modern Practices In researchResearchAdded – Use of online mediumsfor research.Introduction Of tools in ResearchMS Excel & SPSS Reference Materials :1. Research Methodology Tests and Cases with SPSS Applications, by Dr SL Gupta and Hitesh Gupta, International Book House Pvt Ltd2. Research Methodology –Guide For Beginner’s by Kumar Ranjit (Pearson)3. Research Methodology –by C.R.Kothari (New Age International)Page 24 of 39
SEMESTER IISerial NoCourse codeCredits Course Name1CORE COURSES (CC)1.2MACCS20206MACRO ECONOMIC CONCEPTSAND APPLICATIONSCourse Objectives:1To enable students to understand various concepts related to nationalincome2To help students understand Macro economic theories3To help learners to understand General Equilibrium4To help learners to understand issues related to balance of paymentsREVISED SYLLABUSModuleNo.1TopicsAggregate Income and its Dimensions 2Page 25 of 39No. oflectures15Aggregate Income and its dimensions: Nationalincome aggregates- GNP, GDP, NDP, Real andnominal income concepts, Green NationalIncome, measures of inflation and price indices GDP deflator, - Nominal and real interest ratesPPP income and HDIKeynesian concepts of Aggregate Demand (ADF), 15Aggregate Supply (ASF) Keynesian concepts of Aggregate Demand (ADF),Aggregate Supply (ASF), Interaction of ADF andASF and determination of real income; Inflationarygap
Policy trade- off between Inflation andunemployment – Phillips’ curve – short run andlong runEconomic Policy Implications in the IS-LM framework 153 4The IS-LM model: Equilibrium in goods and moneymarket; Monetary and real influences on IS-LMcurves, Economic fluctuations and Stabilisationpolicies in ISLM framework - Transmissionmechanism and the crowding out effect;composition of output and policy mix, IS-LM in IndiaInternational Aspects of Macroeconomic Policy 15International aspects of Macroeconomic policy:Balance of payments disequilibrium of an openeconomy - corrective policy measures -Expenditurechanging policies and expenditure switchingpolicies BOP adjustments through monetary andfiscal policies -The Mundell-Fleming model Devaluation, revaluation as expenditure switchingpolicies - effectiveness of devaluation and J - curveeffectTotal Lectures60Note: Changes in syllabusParticulars (Universitysyllabus)RemarksModule 1- AggregateIncome and itsDimensionsDeleted the topic on measurement ofNational Income and its difficultiesAdded a topic on Green National IncomeReferences:1)2)3)4)5)Ahuja H.L Modern EconomicsDwivedi D.N Macro Economics Theory and PolicyJhingan M.L. Principles of EconomicsGregory N Mankiw Macro EconomicsM.C Vaish Macro Economic TheoryPage 26 of 39
SEMESTER IISerial NoCourse codeCredits Course Name1CORE COURSES (CC)MACCS2031.306CORPORATE FINANCECOURSE OBJECTIVES and OUTCOMES:Learning ObjectivesLearning Outcomes1 To enhance the ability of learners to develop Students would be able toget a clear picture of itsthe objectives of Financial ManagementMeaning, scope, importance,Objectives of financialmanagement2 To enhance the ability of learners to analyse Students would understandfinancial statementsthe financial analysis andapplication of ratio analysisin financial decision making.This analysis would beapplied in understandingprofitability ratios, efficiencyratios, liquidity ratios,stabilitiy ratios, Investorsanalysis etc.3 To enable the learners to understand,develop and apply the techniques ofinvestment in financial decision makingStudents would be able tounderstand cost of capital,wacc, and marginal cost of ofcapitalStudents would be able tofocus on capital structurePage 27 of 39
decisions market price,capital structure theories,dividend policy etc4 To understand the concepts of businessrisk, financial risk and capital structuretheories.Students would be able tounderstand the concept ofleverage and its types.5 To enable the learners to understand,develop and apply the techniques of capitalstructure theoriesStudents gets a clear idea ofcapital structure theories,MM Theory, Pecking OrderTheory. Dividend Decisionsand its model withillustrationsREVISED SYLLABUSMODULESSNMODULES12345Introduction to Financial ManagementFinancial AnalysisCost of CapitalBusiness Risk and Financial RiskCapital Structure TheoriesTOTALPage 28 of 39NO OFLECTURES061814121060
Sr.No.12345Page 29 of 39ModulesNumberoflectures06Module 1Introduction, Meaning, scope, importance,objectives,Profit v/s Value MaximisationModule 2 Financial Analysis16Application of Ratio Analysis in Performance evaluation andFinancial Decision Making Profitability Ratios: Gross Profit Ratio, Operating Profit Ratio,Return onCapital Employed Efficiency Ratios: Sales to Capital Employed, Fixed AssetTurn overRatio, Profit to Fixed Assets, Stock Turnover Ratio, DebtorsTurnoverRatio, Creditors Turnover Ratio Liquidity Ratios: Current Ratio, Quick Ratio Stability Ratio: Capital Gearing Ratio, Interest Coverage Ratio Earnings per Share, P/E Ratio, Dividend Yield RatioModule 3 Cost of CapitalIntroduction, Definition, Measurement of Cost of Capital,WACC, Marginal Cost of CapitalModule 4 Business Risk and Financial RiskIntroduction, Debt v/s Equity Financing, Types of Leverage,Investment Objective, criteria for individuals/Non-businesspurpose14Module 5 Capital Structure TheoriesMeaning, Net Income Approach, Net Operating IncomeApproach, illustrations on capital structure theories, MMTheory, Pecking Order Theory. Dividend Decisions and itsmodel10Total Lectures6012
Reference Materials:1. Corporate Accounting - R. L . Gupta and V. K . Gupta - S. Chand andCompany (P) Ltd., New Delhi2. Corporate Finance - Stephen A. Ross, Randolph W. Westerfield, JeffreyJaffe, Bradford D. Jordan - Tata Mc Graw Hill and Co. Ltd., Mumbai3. Corporate Finance – 12th Edition – Richard A. Brealey, Stewart C. Myers,Franklin Allen, Pitabas MohantyNote on changes in syllabusParticularsRemarksModule 2 Time value of deleted from the syllabusMoneyModule 4 Financial Divided in to Module 3,4,5 and Change inDecisionsModule NamePage 30 of 39
SEMESTER IISerial NoCourse codeCredits Course Name1CORE COURSES (CC)1.4MACCS20406E-COMMERCECOURSE OBJECTIVES and OUTCOMES:Course ObjectivesCourse OutcomeTo Understand the E-Commerce and E- Students to understand e-commerce,web sites for quality, reliability andbusiness infrastructure and trendseffectiveness and Evaluate e-commercemarkets and transactions.To Analyze real business casesTo help students assess the effect ofregarding their e-business strategieschanging technology on traditionaland transformation processes andbusiness models and strategy &choicesunderstand e-commerce on business &how firms cope-up & are organize.To be very efficient at selling throughTo make students understand changingunderstanding complex consumerconsumer needs and resources requiredbehavior.to match to technology consideringhuman factors and budget constraints.Communicate effectively ,ethicallyusing electronic media.REVISED SYLLABUSMODULESSNMODULES1Introduction to Electronic CommerceEvolution & ModelsWorld Wide Web & E-enterpriseE-Marketing & Electronic Payment system23Page 31 of 39NO OFLECTURES151515
4Sr.No.Legal Regulatory Environment & Securityissues Of E-commerceTOTALModules1Module-1Introduction to Electronic Commerce-Evolution &Models Evolution of E-commerce-introduction,History/Evolution 01 Electronic Commerce, Roadmapof E-Commerce in India, Main activities. Functionsand Scope of E-Commerce. Benefits and Challenges of E-Commerce, ECommerce Business Strategies for Marketing, Salesand Promotions Business Models of E-Commerce- Characteristics ofBusiness to Business(B2B), Business to Consumers(B2C), Business to Government (B2G) Concepts of other models of E-commerce. Business to Consumer E-Commerce process,Business to Business E-Commerce- Need andImportance, alternative models of 8213 E-Commerce. E-Commerce Sales Product Life Cycle (ESLC)Model2Module-2World Wide Web & E-Enterprise World Wide Web-Reasons for building own website,Benefits of Website, Registering a Domain Name,Role of web site in B2C E-commerce; push and pullapproaches; Web site design principles. EDI and paperless trading; Pros & Cons of EDI;Page 32 of 391560Numberoflectures1515
Related new technologies use in E-commerce. Applications of E-commerce and E-enterprise Applications to Customer Relationship Management Types of E-CRM Functional Components of E-CRM. Managing the E-enterprise - Introduction, Managingthe E-enterprise, Comparison between Conventionaland E-organisation, Organisation of Business in an Eenterprise Benefits and Limitations of E- enterprise3Module-3E-Marketing & Electronic Payment System E Marketing- Scope and Techniques of E-Marketing.Traditional web promotion. Web counters. Webadvertisements. Role of Social media E-commerce Customer Strategies for Purchasing andsupport activities. Planning for Electronic Commerceand its initiatives, pros and cons of online shopping,Justify an Internet business Electronic Payment System-Characteristics of Epayment system SET Protocol for credit card payment.prepaid e-payment se post-paid E-payment system,Types of payment systems Operational, credit and legal risks of F -paymentsystem, Risk management options for E-paymentsystems, Set standards / principles for E-payment15Consumer-Oriented Business: Consumer Market,One-to-One Marketing, Consumer Demographics,Maintaining Loyalty, Gaining Acceptance, Onl
SIES COLLEGE OF COMMERCE & ECONOMICS AUTONOMOUS DEPARTMENT OF M.Com (ACCOUNTANCY) Date of BOS meeting: 9thNovember, 2020 Name of BOS Chairperson: Ms Payal Bhatia Sr. No. Heading Particulars 1 Title of the programme M.Com 2 Eligibility for admission B.Com or Equivalent 3 Minimum percentage 40% 4 Semesters 01 and 02










