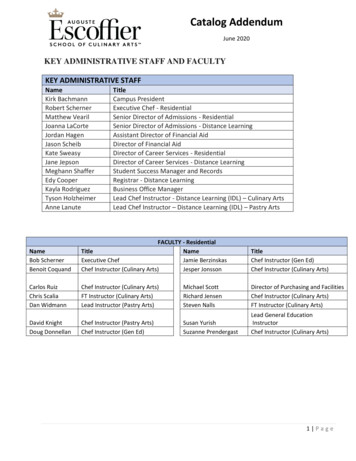
Transcription
BCS LEVEL 5 DIPLOMA IN ITSMART SYSTEMSSYLLABUSSeptember 2021 v3.0This qualification is regulated by one or more of the following:Ofqual, Qualifications Wales, CCEA Regulation or SQA.
CONTENTS3. Introduction4. Qualification Suitability and Overview5. SFIA Levels6. Learning Outcomes7. Syllabus18. Examination Format18. Question Weighting19. Recommended Reading21. Document Change History
IntroductionLevel 5 Diploma in ITThe second stage within the BCS three-stage Higher Education Qualification programme, the Level 5Diploma enables candidates who have already achieved the Level 4 Certificate in IT to progress to higherlevels of knowledge and competency.This internationally-recognised qualification introduces you to the business-related aspects of the ITindustry, developing your technological expertise while also considering the potential challenges of the dayto-day running of an organisation, such as legal obligations and intellectual property.Our modules have been created in-line with the latest developments in the industry, giving you acompetitive edge in the IT job market. You will have the opportunity to learn about object-orientedprogramming, user experience, systems analysis and design, as well as to build upon knowledge and skillsdeveloped during the Level 4 Certificate.To successfully achieve the qualification, candidates need to complete: One core module Three optional modules One Professional Project in ITCandidates who wish to progress onto the next stage will need to complete the Project at end of the Level 6Professional Graduate Diploma in IT.3
Smart Systems Optional ModuleThe Smart Systems module is an optional module that forms part of the Level 5 Diploma in IT – the secondstage within the BCS three-stage Higher Education Qualification programme.Candidates will be introduced to core concepts such as the fundamentals of artificial intelligence andpervasive computing, enabling technologies such as mobile and cloud computing, the application of smartsystems, the impacts and challenges of using Smart Systems and Cyber Physical Systems security.Qualification Suitability andOverviewCandidates must have achieved the Certificate in IT or have an appropriate exemption to be entered forthe Diploma in IT. Candidates can study for this diploma by attending a training course provided by a BCSaccredited Training Provider or through self-study, although it is strongly recommended that all candidatesregister with an approved centre. Studying with an approved centre will deliver significant benefits.Candidates are required to become a member of BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT, to sit and be awardedthe qualifications. Candidates may apply for a four-year student membership that will support themthroughout their studies.The Level 5 Diploma is suitable for professionals wishing to gain a formal IT qualification, and this modulemay be particularly relevant for candidates interested in career opportunities such as systems and urbanengineering, industrial strategy, or consulting.Total Qualification Time Guided Learning HoursAssessment Time1086 hours2 hours225 hours4
SFIA LevelsThis module provides candidates with the level of knowledge highlighted within the table, enablingcandidates to develop the skills to operate successfully at the levels of responsibility indicated.LevelLevels of KnowledgeK7Levels of Skill and Responsibility (SFIA)Set strategy, inspire and mobiliseK6EvaluateInitiate and influenceK5SynthesiseEnsure and tK1RememberFollowSFIA PlusICPM3This syllabus has been linked to the SFIAknowledge skills and behaviours required at LevelCoordinates content management processes tomeet the needs of users, including those withdisabilities. Uses content publishing systemsto manage published content across differentchannels. Takes into account any legal issuesrelated to publishing, including that associatedcopyright concerns are adequately managed.5.INAN3Undertakes analytical activities and deliversanalysis outputs, in accordance with customerneeds and conforming to agreed standards.SCTY4Explains the purpose of and provides advice andguidance on the application and operation ofelementary physical, procedural and technicalsecurity controls. Performs security risk,vulnerability assessments, and business impactanalysis for medium complexity informationsystems. Investigates suspected attacks andmanages security incidents. Uses forensics whereappropriate.Further detail regarding the SFIA Levels can be found at www.bcs.org/levels.5
Learning OutcomesUpon completion of this module, candidates will be able to: Show an understanding of Smart Systems, their implementation and applications. Interpret and explain the impact of Smart Systems, ethical, legal, social, environmental implications. Explain concepts used in Smart Systems and associated architectures. Explain the major Smart Systems application areas and techniques used within them. Discuss examples of Smart Systems used in real life situations.6
Syllabus1. Core conceptsLearners will be able to:1.1 Define and explain the purpose of Smart Systems.Indicative contenta. The background andhistorical perspective of theSmart Systems domainb. Smart Servicesc. Smart Industryd. Smart Manufacturing, etc.GuidanceSmart Systems are the next generation of computing andinformation systems that use a number of enabling technologiesto provide real-time networked information. The term ‘Smart’has given rise to a number of areas of application and candidatesare expected to gain knowledge of these areas and to be able todefine Smart systems and demonstrate an understanding of theirpurpose, their background, and evolution.1.2 Describe and explain the principles and fundamentals of Artificial Intelligence (AI).Indicative contenta. Historical background,principles and fundamentalsof AIb. Knowledge of thecharacteristics of AIc. Different levels of AId. Aspects of humanintelligence used tocharacterise intelligentknowledge-based systemse. Potential of AIf. Advantages anddisadvantages of AIGuidanceAI is a wide ranging interdisciplinary field which has roots in, andintersects with many other domains and plays an essential rolein Smart Systems. Candidates should have the knowledge of AI,its background, current, future and potential use, and be able todiscuss its role, purpose and contribution to Smart Systems.7
1.3 Define and explain the role of Pervasive Computing.Indicative contenta. Key principles of PervasiveComputing and its purposeb. Advantages of pervasivecomputingc. Knowledge of its features,connectivity, productivity etc.d. Pervasive Computing and itsapplicationGuidancePervasive Computing is a software engineering concept that allowscomputerised technology to be used by any device and format inany place. Candidates should have the knowledge of its differentforms, how it is used and the key principles and be able to explainand discuss its role in Smart Systems.1.4 Describe and explain the purpose of Cyber Physical Systems (CPS).Indicative contenta. Definition and explanation ofthe nature of Cyber PhysicalSystemsb. Purpose of Cybersecuritywith respect to thesesystemsc. Security challengesd. Classification of the areas ofsecurity in CPSsGuidanceCPSs introduce many cybersecurity challenges in smart systemsand it is important to understand the purpose of cybersecurity withrespect to Cyber Physical Systems. CPSs are being increasinglyused and form the basis for Smart Systems development.Candidates should have the ability to define and explain thepurpose of CPSs as well as identify and discuss examples ofcybersecurity challenges instigated by their use in Smart Systems.8
1.5 Explain the Internet of Things (IoT).Indicative contenta. Definition and purpose of IoTb. Its role and applications inSmart Systemsc. Advantages anddisadvantages of IoTGuidanceThe IoT is an essential technology in Smart Systems; candidatesshould be able to define and discuss the purpose and role of theIoT using relevant examples. The IoT is an enabling technologyfor Smart Systems and candidates should be able to identify andevaluate any challenges with regard to this technology.1.6 Define and describe the purpose of Big Data (BD), Data Analytics (DA) and Data Mining (DM).Indicative contenta. Purpose of Big Data, DataAnalytics and Data Miningand their applicationb. How they are used in SmartSystemsc. Advantages anddisadvantages of their useGuidanceBig Data, Data Analytics and Data Mining are now widely used andcandidates should be able to define and explain the purpose of BD,DA and DM, and how they are used globally for a variety of businesspurposes. They should also be able to identify and discuss anychallenges of their use and role in Smart Systems.9
2. Enabling TechnologiesLearners will be able to:2.1 Explain distributed systems.Indicative contenta. Definition and examples ofdistributed systemsb. Purpose of distributedsystems and their applicationGuidanceCandidates should be able to define and give examples ofdistributed systems and demonstrate knowledge of their purposeand discuss advantages for their use.2.2 Describe mobile computing.Indicative contenta. Definition and role of mobilecomputingb. Applications of mobilecomputingc. Features of mobilecomputing and how it worksGuidanceCandidates should demonstrate an understanding of mobilecomputing and how it works, identify its features, types, andapplications for its use.2.3 Explain cloud computing.Indicative contenta. Definition of Cloud Computingb. Purpose of Cloud Computingc. Types of cloud, cloud servicesand its infrastructure as aserviced. Its role in Smart Systemse. Advantages, disadvantagesand challengesGuidanceCloud Computing facilitates shared computing resources viaservers over the internet and provides on-demand individualaccess to global computer system resources and services, anytime,anywhere. Candidates should have an understanding of CloudComputing and its application and use. They should be able toidentify its infrastructure as a service and evaluate the advantagesand disadvantages of the technology as well as be able to discussthe ethical considerations of cloud technology and the implicationsfor its use in Smart Systems.10
2.4 Describe development methods and tools.Indicative contenta. Sensors, sensor networksand actuators, e.g.:i.Movementii. Accelerationiii. Lightiv. Proximityv. Audiovi. Temperaturevii. Humidityviii. Mechanical forcesix. Wireless networksGuidanceCandidates should have an understanding of what sensorsand actuators are, and be able to identify their differences,differentiating between the two. They should gain knowledge ofhow actuators and sensors work together as well as be able toexplain the basic components of sensor networks and their rolein wireless communication. They should also be able to identifydifferent types of sensors.2.5 Explain Near-field communication (NFC), Radio-frequency identification (RFID) and their purpose.Indicative contenta. NFC and its purposeb. RFID, its purpose, how itworks and its usesc. Security concerns with thetechnologyd. Security measuresGuidanceCandidates should be able to define NFC and RFID technologiesand explain how they are used. They should be able to evaluate anyconcerns with the technologies.2.6 Explain AI and Machine Learning (ML).Indicative contenta. Role of AI in Smart Systemsb. Description of ML andbackground to the technologyc. General functions of ML andits uses in applications ofSmart Systemsd. Relationships with AI, BigData and areas of applicatione. Knowledge of NeuralNetworksGuidanceBig Data has given rise to a new field of AI and that is MachineLearning. With the rise of Big Data, ML has emerged as oneof the best problem-solving technologies. Candidates shoulddemonstrate an awareness and understanding of ML, itsrelationship with AI and Big Data, its purpose, and its areas ofapplication as well as how it is used in data analytics and smartsystems.2.7 Explain Blockchain and its purpose.Indicative contenta. Definition, function andpurpose of BlockchainTechnologyGuidanceSmart Systems rely on a number of enabling technologies fortheir development, implementation and use. Blockchain is one ofthese enabling technologies. Candidates should be able to defineBlockchain and explain its purpose and consequently its role inSmart Systems. They should also be able to evaluate benefits ofthis technology and any challenges it might provoke.11
3. ApplicationsLearners will be able to:3.1 Explain smart homes.Indicative contenta. Smart homes and Smarthome devicesb. Advantages, disadvantagesand challenges of smarthome devicesc. Components of smart homeautomationGuidanceCandidates should be able to define smart homes, the devices andcomponents of smart home automation and have the ability todiscuss the advantages and disadvantages of smart home devicesand have an awareness of any challenges they might present.3.2 Explain smart appliances.Indicative contenta. Definition of smartappliancesb. Advantages anddisadvantages of smartappliances and theirapplicationc. Types of appliancesGuidanceCandidates should be able to identify applications of smartappliances and demonstrate an understanding of what smartappliances are, and the advantages and disadvantages they have.3.3 Explain smart things.Indicative contenta. Smart things and theirbenefitsb. Advantages anddisadvantages of SmartthingsGuidanceCandidates should demonstrate an understanding of smart thingsand the advantages and disadvantages of their development anduse.12
3.4 Explain healthcare applications.Indicative contenta. Smart health applicationsb. Types of applicationsc. Devices and componentsused in the development ofsmart health applicationsd. Challenges and risks inhealth applicationsGuidanceCandidates should have the ability to identify a variety of smarthealth applications and areas for their use as well as evaluatethe validity in their development and use. An awareness of anychallenges and ethical implications for their development and useshould be paramount.3.5 Describe smart spaces.Indicative contenta. Description of smart spacesb. Identification of how smartspaces change the role ofmobile devicesc. Examples of smart spacesd. Security and privacy issuesin smart space environmentse. Enabling technologies forsmart spacesGuidanceAn ability to describe and identify examples of smart spaces shouldbe part of the learning. In smart spaces where devices constantlycommunicate with each other, issues of privacy and security tendto arise. Sensor networks are key to the creation of smart spaces,but they can also impose privacy and security issues, candidatesshould have an awareness of these issues in relation to smartspaces and how they might be prevented.
4. Impacts and ChallengesLearners will be able to:4.1 Explain the ethical considerations.Indicative contenta. Social and environmentalimpactb. Privacy issuesc. Design and developmentissuesd. Energy consumptione. Resourcesf. Security issuesg. Psychological wellbeingGuidanceDue to the nature of Smart Systems, candidates shoulddemonstrate an awareness of the ethical considerations in boththe development and use of Smart Systems and their social andenvironmental impact. Candidates will discuss ethical issues thatmight arise using examples to support their discussions.4.2 Explain sustainability and economic impacts.Indicative contenta. How sustainable are smartsystems?b. Economic impact due tothe development and use ofsmart systemsGuidanceWith the increase in consumption of energy, there is a need toconserve energy wherever possible. Candidates should be ableto discuss, evaluate and have an awareness of the cost andsustainability implications for the development and use of SmartSystems.4.3 Explain privacy concerns.Indicative contenta. Identifying and explainingprivacy concerns with thedevelopment and applicationof Smart SystemsGuidanceSmart systems devices have many advantages in industrial andsocial contexts, however, there are also a number of privacy issuesthat may arise with their development and use. Candidates shoulddemonstrate an awareness of these privacy concerns and havethe ability to identify these concerns and be mindful of possiblestrategies to address these issues.13
4.4 Explain security concerns.Indicative contenta. Identifying security concernsin smart systemsb. Their challenges and impactGuidanceThe domain of Smart Systems has a number of securitychallenges, of which candidates are expected to have anawareness. They should have the ability to identify the securitychallenges with respect to the enabling technologies in thedevelopment of smart systems.4.5 Identify application standards.Indicative contenta. Identifying and describingapplication standardsb. Regulations and standardsapplicable to the designand development of SmartSystemsGuidanceCandidates should have the ability to identify and describeany relevant application standards and why and how they areimplemented.4.6 Describe legal aspects of application.Indicative contenta. Identifying and describinglegal aspects of applicationGuidanceCandidates should have knowledge of legal aspects of applicationas well as the ability to identify and describe relevant legal aspectsof application.
5. Cyber Physical Systems SecurityLearners will be able to:5.1 Explain Operational Technology (OT) and Information Technology (IT) security.Indicative contenta. OT Security vs. IT securityb. OT security’s common usesc. Differences between OT andIT securityd. Purpose of OT and IT securityGuidanceCandidates should demonstrate knowledge of OT and IT securityand the differences between these system securities and theirpurpose.5.2 Describe the challenges of Operational Technology (OT) security.Indicative contenta. Challenges of OT securityGuidanceCandidates should be able to identify and discuss the challenges ofOT security.5.3 Explain Cyber Physical Systems (CPS) risk management.Indicative contenta. Definition and explanation ofthe purpose of CPS securityrisk managementb. Security concernsc. Elements of the riskmanagement processGuidanceThe domain of Smart Systems has a number of securitychallenges, candidates should demonstrate an understanding ofwhat CPS risk management is and be able to discuss its purposeand importance. The ability to identify and discuss elements of therisk management process in CPS is also required.14
Examination FormatThis module is assessed through completion of an invigilated written exam.Type Four written questions from a choice of six, each with equal marksDuration Two hoursSupervised YesOpen Book No (no materials can be taken into the examination room)Passmark 10/25 (40%)Delivery Paper format onlyAdjustments and/or additional time can be requested in line with the BCS reasonable adjustments policyfor candidates with a disability or other special considerations.Question WeightingCandidates will choose four questions from a choice of six. All questions are equally weighted and worth 25marks.18
Recommended ReadingTitle: Cyber physical systems security: Analysis, challenges andsolutionsAuthor: Y. Ashibani and Q. MahmoudAvailable at: S0167404817300809?via%3Dihub [Accessed 9 July 2021]Title: Artificial Intelligence: A Very Short IntroductionAuthor: M. BodenPublisher:: Oxford University PressDate: 2018ISBN: 978-0199602919Title: Framework for Cyber-Physical Systems: Volume 1, OverviewAuthor: Cyber-Physical Systems Public Working GroupAvailable at: ons/NIST.SP.1500-201.pdf [Accessed 9 July 2021]Title: Big Data: Using SMART Big Data, Analytics and Metrics To MakeBetter Decisions and Improve PerformanceAuthor: B. MarrPublisher: WileyDate: 2015ISBN: 978-1118965832Title: Handbook of Industry 4.0 and SMART SystemsAuthor: D. Pascual, P. Daponte and A. KumarPublisher: CRC PressDate: 2019ISBN: 978-113831629419
Title: Data Analytics and Big DataAuthor: S. SedkaouiPublisher: ISTE LondonDate: 2018ISBN: 978-0128023082Using BCS BooksAccredited Training Organisations may include excerpts from BCS books in the course materials. If youwish to use excerpts from the books you will need a license from BCS. To request a license, please contactthe Head of Publishing at BCS outlining the material you wish to copy and its intended use.Document Change HistoryAny changes made to the syllabus shall be clearly documented with a change history log. This shall includethe latest version number, date of the amendment and changes made. The purpose is to identify quicklywhat changes have been made.Version NumberChanges MadeVersion 1.0August 2021Document created21
CONTACTFor further information please contact:BCSThe Chartered Institute for IT3 Newbridge SquareSwindonSN1 1BYT 44 (0)1793 417 445www.bcs.org 2021 Reserved. BCS, The Chartered Institute for ITAll rights reserved. No part of this material protected by this copyright may be reproduced or utilised in any form,or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or by any information storage andretrieval system without prior authorisation and credit to BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT.Although BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT has used reasonable endeavours in compiling the document it does notguarantee nor shall it be responsible for reliance upon the contents of the document and shall not be liable for anyfalse, inaccurate or incomplete information. Any reliance placed upon the contents by the reader is at the reader’ssole risk and BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT shall not be liable for any consequences of such reliance.Copyright BCS 2021BCS Level 5 Diploma in Smart Systems v1.0
1.1 Define and explain the purpose of Smart Systems. 1.2 Indicative content a. The background and historical perspective of the Smart Systems domain b. Smart Services c. Smart Industry d. Smart Manufacturing, etc. Guidance Smart Systems are the next generation of computing and information systems that use a number of enabling technologies