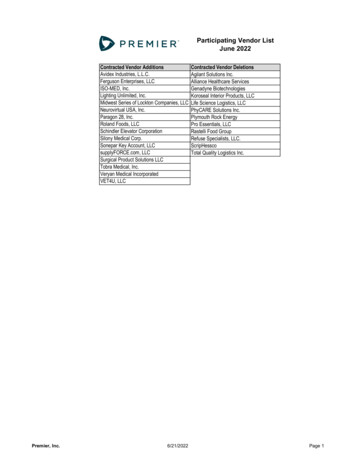
Transcription
Association of BritishInsurersSectionXX1Are you buying privatemedical insurance?Take a look at this guidebefore you decide2017abi.org.ukabi.org.uk@British Insurers@British Insurers
2Contents1 About this guide2 Understanding what you are buying3 What is private medical insurance?4 How do I buy private medical insurance?5 Will I need to give details about my health?6 How do I choose the right cover?7 What is and is not covered?8 What if I have a disability?9 How could my product change over time?10 What if I want to change to a new insurer?11 What do I need to remember?12 What protection do I have?abi.org.uk@British Insurers
3Section OneAbout this guideThis guide is for individuals who are thinking about buyingprivate medical insurance (PMI) for themselves and their families.We have designed this guide to help you understand more about whatPMI in the UK is, why people buy it, and how it works, so that you will beable to make an informed choice before you buy a policy.As well as this guide, the information you receive from insurers offeringPMI will tell you more about the products that you are consideringbuying. They outline what is, and is not, covered. Remember thatdifferent products from different companies will vary. If you have anyquestions, your insurance company will be able to answer them and youcan also consult an independent financial adviser.abi.org.uk@British InsurersIf you get PMI as a benefit throughyour employer, your employer willhave all the information aboutyour insurance cover which may bedifferent from the generalinformation detailed in this guidefor individuals purchasing PMI. Forexample, the cooling-off periodwill not apply if your employer haspurchased the insurance for you.
4Section TwoUnderstanding whatyou are buyingBuying private medical insurance is similar tobuying any other type of insurance policy.Private medical insurance is available in a range ofcover levels and premium levels designed to meet theneeds of different customers. For example, yourchoices may include: types of treatment, levels ofcover for those treatments, how you access care,where treatment is provided, and your contributiontowards the treatment cost (the excess). Take the timeto understand the cover available to help you make aninformed choice.You should: compare the benefits of each insurer compare any cover limits or monetary amounts consider your own health needs consider what benefits are available to helpkeep you in good health ask questions about how the cover worksIf your employer has purchased the cover on yourbehalf, they will have made these decisions foryou. Your employer will have all the informationabout your insurance cover.If you are buying a PMI policy for yourself (and yourfamily), make sure that you understand what you arecovered for and the limits that will apply if you make aclaim; read the policy terms and conditions. Youshould contact the insurer who will be happy to talkyou through the cover available to you. You can alsoconsult an independent financial adviser.For example, you might want to know: Are there monetary limits on the policy - how muchtowards the cost of a treatment, or course oftreatments, do you want covered? How does an excess work – will it be applied perclaim or per policy year? What cover is there for cancer - what treatments arecovered and for which stages of the disease? Is there a no claims discount – what will happen tomy future premiums if I make a claim?There can be limits on cover for drug treatments. Youmight want to ask about these. A drug treatment thatyour insurer has covered might not be available on theNHS when your PMI cover ends. Your insurer willcontact you as you approach the end of cover aboutthe options available to you so you can discuss it withyour specialist. These could be: Return to the NHS and receive the treatment there,if available Return to the NHS and receive alternative treatment Pay for the treatment privately on a self-pay basisabi.org.uk@British Insurers
5Section ThreeWhat is privatemedical insurance?Private medical insurance is designed to coverthe cost of private medical investigations andtreatment for ‘acute conditions’ that start afteryour policy begins.WHY BUY PRIVATE MEDICALINSURANCE?An acute condition is a disease, illness or injury that islikely to respond quickly to treatment that aims toreturn you to the state of health you were inimmediately before suffering the disease, illness orinjury, or which leads to your full recovery. Yourinsurer can tell you about their cover for this andwhether or not they will provide any cover for longerterm conditions (typically referred to as‘chronic conditions’).Timely access to healthcare Prompt referral to a consultantA chronic condition is a disease, illness, or injury thathas one or more of the following characteristics: it needs long-term monitoring, control or relief ofsymptoms it requires rehabilitation it continues indefinitely it has no known cure or is likely to come backSome policies may cover certain types of, orelements of, long-term treatment or treatment forchronic conditions, but this is not usually the mainpurpose of PMI.PMI is designed to work alongside, not to replace, allthe services offered by the NHS and customers cancontinue to use the NHS.abi.org.uk@British InsurersPeople buy this type of insurance to have: Quick admission to hospital Treatment at a convenient time and placeChoice of healthcare Direct care by a consultant Advanced treatment options, such as access to somecancer drugs that are not available on the NHSHigh-quality private clinic and hospitalaccommodation Privacy of an en-suite room Home amenities, such as TV Comfort and cleanlinessHOW DOES PRIVATE MEDICALINSURANCE WORK?Although policies can be different, medical treatmentusually has to start with a referral by your GP forspecialist treatment. Before you arrange any privatetreatment, you should call your insurance company tocheck that you are covered for the treatment and todiscuss your options for accessing care.Stay in touch with your insurer at each stage of yourtreatment. Your insurer will confirm your cover. It islikely that treatments for some illnesses, includingpre-existing conditions (conditions from which you arealready suffering, or have already had before yourpolicy started) will not be covered by a private medicalinsurance policy (see section 4 of this guide).
6Section FourHow do I buy privatemedical insurance?Private medical insurance is provided only byinsurers and may be bought: direct from the insurer through an independent adviser through an agent (bank, building society or retailoutlet, such as a supermarket)You can apply for insurance: over the phone face-to-face online by postThe method of application may vary by insurer. If youare using the internet, try searching for key words suchas ‘health insurance’ as well as ‘medical insurance’.An insurer, or a tied agent who sells policies on aninsurer’s behalf, is only able to discuss that insurer’sown policies. An independent adviser offers policiesfrom a range of insurers.Independent advisers give you recommendationsafter assessing your needs. They are responsible toyou for the advice they give. If you buy direct from aninsurer or an insurer’s agent, they will also assess yourneeds, but they can only give you advice on which oftheir own policies best suits you.Your adviser must explain whether they are: independent advising on a range of insurers a representative of one insurerabi.org.uk@British InsurersIf you buy direct from an insurer or insurer’s agentwithout receiving advice, it is your responsibility tochoose a policy that is right for you.You will be asked to fill in an application, and may beasked for information about your health. Yourapplication, or any declaration you make to yourinsurer, is very important. In fact, it forms the basis ofyour contract with your insurer. You must answer anyquestions you are asked as fully and as accurately asyou can, to the best of your knowledge and belief. If youdo not, your insurer may reduce your claim or refuse topay and cancel your policy. If you are unsure whethersomething is important, it is best to tell your insurer.Once your application has been accepted you will betold when cover will start.CANCELLATION PERIODYour insurer will send you policy documents whenyour policy has been set up. You have at least 14 daysfrom the day you receive them to decide whether theproduct is suitable for you. This is commonly knownas a ‘cooling-off period’. If you want to cancel yourpolicy, you must do so within the stated period andtell the insurer that you want to cancel your cover. Ifyou have made any payments you will usually receivea full refund unless you have made a claim.
7Section FiveWill I need togive details aboutmy health?You will not normally be covered for anyillnesses you are currently suffering from, orhave already had. These are known as ‘preexisting conditions’. You must answer allquestions as fully and as accurately as you can,to the best of your knowledge and belief.There are two main methods that PMI companies useto deal with your application for cover. These are: full medical underwriting moratorium underwritingAll PMI companies will offer you the full medicalunderwriting option. Only some companies offer themoratorium option.abi.org.uk@British InsurersFULL MEDICAL UNDERWRITING(MEDICAL HISTORY DECLARATION)You are asked to give details of your medical history.The insurer may write to your doctor for moreinformation, but they do not do so in every case. Youmust give all the information you are asked for. If youdo not, your insurer may reduce your claim or refuseto pay and cancel your policy. In some cases, insurersmay also decline offering any cover.If you are not sure whether to mention something, it isbest to do so. If you have a medical condition that islikely to come back, the insurer will issue a policy, butthat condition (and any related to it) might not becovered. Depending on a number of factors, thecondition may never be covered, or not covered for aset period of time.
8Section FiveMORATORIUM UNDERWRITINGYou are not asked to give details of your medical history.Instead, the insurer does not cover treatment for anypre-existing medical condition that you have receivedtreatment for, diagnostic tests for, taken medication for,asked advice on or had symptoms of, in the yearsimmediately before your policy started. In other words,you will not be covered for any condition that existed inthe past few years. This time period can vary acrossdifferent insurers.These conditions may automatically become eligiblefor cover. But this will only happen when you do nothave symptoms of, or receive treatment, medication,tests and advice (from your GP, a healthcareprofessional or a specialist) for that condition, or arelated condition, usually for a continuous period oftwo years after your policy has started. This timeperiod can vary across different insurers.abi.org.uk@British InsurersYou do not need to tell the insurer about your medicalhistory when you take out the policy. If you claim,however, your insurer might ask for medical notes thatare needed to decide if your claim can be covered.There are some conditions, for example chronicconditions, that will probably never be covered. This isbecause you will always need treatment, medication,tests or advice for them. You should not delay gettingmedical advice or treatment, simply to get coverunder the moratorium terms.If you have general health check-ups simply in theinterests of maintaining good health, and not for anyparticular condition, then your insurer will disregardthese check-ups when applying the moratorium.Your insurer will give you information explaining howtheir moratorium works. You may also want to ask theinsurer or adviser, to explain this.
9Section SixHow do I choosethe right cover?You should check to see if you already have PMIcover. Some employers include PMI as part oftheir benefits package. A club or professionalorganisation might also have arrangements tooffer you (and your family members) cover.If this is not the case and you want to take out coveryourself, you need to think about what benefits aremost important to you. You will need to decide whatsort of cover you want. There are a number of thingsyou will have to consider: What are your health requirements? How much do you want to spend? Are you prepared to pay towards yourinvestigations and treatment?abi.org.uk@British Insurers Do you want your cover to include seeing aspecialist and having diagnostic tests (for example,X-rays and blood tests) as an outpatient? Do you want a choice of hospitals, or would you behappy to have any treatment that you might needin a hospital available from a limited range chosenby your insurance company? What are you not covered for?The answers you give to questions such as these couldhave a significant effect on how much you pay (seesection 9). The more your cover includes, the higheryour premiums are likely to be. Most policies offercover for inpatient and day patient treatment, but donot always include cover for outpatient treatment anddiagnostic tests.
10Section SixThe following diagram is an example of how you might get private treatment.Visit your GPYour GP refers you for investigations ortreatment*.*Call your insurance company to check that you arecovered for the specialist and hospital treatment,and to discuss your options for accessing care.Remember to stay in touch with your insurer at eachstage of your treatment.GP refers you for specialist treatmentThis usually includes initial consultations anddiagnostic tests.Your specialist needs to refer you to hospitalfor more investigations or treatment.OutpatienttreatmentStart to claimHospitalThis may be a private hospital or privatefacilities within an NHS hospital.After leaving hospital you will usually have afollow-up visit to your specialist.Follow-up visitSpecialist consultation and a review of yourtreatment.HOW YOURECEIVETREATMENTFALLS INTO ONEOF THREECATEGORIES.abi.org.uk@British InsurersOutpatientA patient who attends ahospital, consultingroom, or outpatientclinic and is notadmitted as a daypatient or inpatient.Inpatient orDay patienttreatmentIf your policy includes outpatienttreatment and your claim iseligible, you can claim after yourGP has referred you to a specialist.OutpatienttreatmentDay patientA patient who isadmitted to a hospital orday patient unit becausethey need a period ofmedically supervisedrecovery but does notstay in a bed overnight.InpatientA patient who isadmitted to hospitaland who occupies a bedovernight or longer, formedical reasons.
11Section SevenWhat is and isnot covered?Private medical insurance is designed to covertreatment for curable, short-term illness orinjury. These are commonly called ‘acuteconditions’. Some long-term illnesses andtreatments are rarely covered.Private medical insurance is not designed to cover thelong-term treatment of chronic conditions for anumber of reasons: The private-hospital sector’s main purpose is totreat conditions that can be cured, or mostly cured,quickly. A large part of the NHS’s funding is to care forpatients with long-term conditions. So, for example,patients with diabetes can go to clinics, be regularlymonitored and have their insulin needs met. Thiswill often happen locally, in a primary-care settingsuch as their GP surgery.As well as the practical reasons mentioned above,insurers also have to balance how much cover theyprovide with what you are willing to pay for that cover. So,insurers do not usually cover the treatment of long-term(chronic) conditions. This is because, if they did, theirpremiums would become too expensive for most people.WHAT YOUR PMI MIGHT COVERUsually includedInpatient testsSurgery as aninpatient or daypatientHospitalaccommodationand nursing careSometimesincluded(as part of thepolicy or if youask for it)Outpatient testsOutpatientconsultations andtreatment with aspecialistTherapy, for example, physiotherapyand complementary therapyabi.org.uk@British InsurersCash payment tothe customer fortreatmentreceived as anNHS inpatient
12Section SevenThe following conditions or treatments arenormally not included in your cover: Consultations with a general practitioner (GP) Accident and Emergency admissions Drug abuse HIV/AIDS Normal pregnancy Gender reassignment Mobility aids, such as wheelchairs Organ transplant Injuries you get from dangerous hobbies (oftencalled ‘hazardous pursuits’) Conditions you had before taking out the insurance(commonly known as ‘pre-existing conditions’ – seesection 5) Long-term treatment and chronic conditions Dental services Prescription drugs and dressings, after leavinghospital or as an outpatient Deliberately self-inflicted injuries Infertility Cosmetic treatment Experimental or unproven treatment or drugs Kidney dialysis War risksabi.org.uk@British InsurersYour insurer will provide you with the terms andconditions of your policy at the point of sale or assoon as possible thereafter, but in any event beforethe conclusion of the contract. Your insurer may alsogive you a policy summary before or straight afteryour insurance contract starts. The summary of yourpolicy is designed to highlight any important orunusual limits of the policy, as well as the mainmonetary limits. Please read your full policydocument as the summary will not explain the fullpolicy terms and conditions.
13Section EightWhat if I havea disability?You will not be refused cover because you have adisability. As with other pre-existing conditions,your insurer might not include cover fortreatment that is needed because of yourdisability. However, the law requires that it mustbe reasonable and fair for them to do this.abi.org.uk@British InsurersIf you sign a declaration about your medical history,you must give all relevant information about yourdisability. If your policy does not cover pre-existingconditions, an existing medical condition causing thedisability, or arising from it, will not be covered.
14Section NineHow could my productchange over time?When taking out a PMI policy, and upon renewal,check that you have the right cover in place tomeet your needs. Over time your product maychange for a number of reasons such as: Methods used to diagnose conditions becomemore advanced and are used more, so doctors areable to identify some conditions earlier andpatients can be treated more quickly New drugs, such as those for the treatment ofcancer, become availableabi.org.uk@British Insurers The technology used in surgery becomes moreadvanced As you get older you are more likely to needtreatment; your premiums could increase with yourage to reflect thisInsurers take into account a number of factors toassess your risk, to provide you with the best cover atthe best price. Depending on changes to your riskprofile and any evolution in the cover provided, thepremiums you pay may change at renewal.
15Section TenWhat if I wantto change to anew insurer?You can change your PMI provider. If you want toswitch to a different insurer there are four mainthings you need to consider.COMPARING YOUR COVEREven if your personal medical exclusions stay thesame with your new insurer, the overall cover is likelyto be different.You should: compare the benefits of each insurer compare any cover limits or monetary amounts ask questions about how the cover works, includingyour options to access carePAPERWORKPaperwork varies from one company to another, butthere is likely to be an application form to sign andyou might need to provide a copy of the policycertificate from your current insurer as proof of yourcurrent cover.abi.org.uk@British InsurersWHEN YOU CHOOSE TO SWITCHUsually, private medical insurance is offered throughan annual contract. If you are thinking of switching toanother insurer, it is best to consider doing this at yourrenewal date, otherwise you may incur a fee forswitching provider before the insurance contract hascome to an end.PRE-EXISTING CONDITIONSSome insurers will keep your current personalexclusions (what is not included in your cover) whichmeans any treatment for these conditions will beexcluded from your new cover. They will not add anynew ones. However, some insurers might not coverillnesses or injuries you have had in the recent past orany condition that you suffer from now, even if theseare covered by your current insurer. You shouldcompare the benefits, policy terms and cover limitsfrom different providers carefully, so that you get thecover that is right for you.
16Section ElevenWhat do I needto remember?Before you change insurers you should check the benefits, policy terms andunderwriting position carefully to understand the consequences. The cover offeredmay not be the same.Check that you have the cover that is right for you. Remember that you may have achoice of options.You must give full and accurate information to your insurer or adviser. If you do not,your insurer may reduce your claim or refuse to pay and cancel your policy.You should read all the policy documents carefully, now and in the future. Keep alldocuments safe.You need to keep your payments up to date. If you do not, your cover will stop andonly eligible treatment costs from before the cancellation date will be paid.You will be sent details of changes to benefits, rules, premiums in the previous year andproposed premiums for the forthcoming year before your renewal date. Your policy willnot be cancelled just because you have claimed or your health has got worse.abi.org.uk@British Insurers
17Section TwelveWhat protectiondo I have?REGULATIONCOMPENSATIONThe Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and thePrudential Regulation Authority (PRA) regulate privatemedical insurance policies and any advice you receiveabout them.The Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS)is the UK’s legal fund for customers of authorisedfinancial services firms. The FSCS can paycompensation if a firm cannot, or is likely to beunable, to pay claims against it due to insolvency. TheFSCS is an independent organisation, set up under theFinancial Services and Markets Act 2000.Website: www.fscs.org.ukCOMPLAINTSIf you are unhappy with the way you have beentreated by an insurer when taking out an insurancepolicy or when making a claim, you can make acomplaint directly to the insurer.If you are not happy with the insurer's response, youcan take your complaint to the FinancialOmbudsman Service (FOS), an independent bodywhich aims to settle complaints between consumersand businesses providing financial services. Moredetails on the FOS can be found on their ITYUnder current legislation, all insurers treat personalsensitive information confidentially, including medicaldetails. When you are asked for information, you willbe told what it will be used for, who it may be given toand in what circumstances. You can ask to see anyinformation an insurer has about you.Anonymised aggregated statistical information issometimes given to outside organisations, so they cancarry out research.Insurers might use email to communicate with you. Ifyou choose to communicate with your insurer in thisway, you must make sure your email address is privateand cannot be used or seen by anyone else.abi.org.uk@British Insurers
18Section XXabi.org.uk@British InsurersAssociation of British InsurersOne America Square, 17 Crosswall,London EC3N 2LBT: 020 7600 3333 I abi.org.uk
Buying private medical insurance is similar to . buying any other type of insurance policy. Private medical insurance is available in a range of . cover levels and premium levels designed to meet the needs of different customers. For example, your choices may include: types of treatment, levels of cover for those treatments, how you access care,