Transcription
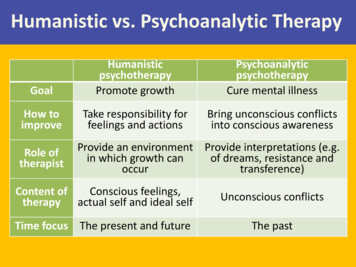
Humanistic vs. Psychoanalytic TherapyGoalHumanisticpsychotherapyPromote growthPsychoanalyticpsychotherapyCure mental illnessHow toimproveTake responsibility forfeelings and actionsBring unconscious conflictsinto conscious awarenessRole oftherapistProvide an environment Provide interpretations (e.g.in which growth canof dreams, resistance andoccurtransference)Content ofConscious feelings,therapy actual self and ideal selfUnconscious conflictsTime focus The present and futureThe past
Group Therapies(Emerged from humanistic movement) Provides a socialatmosphere thatis similar to thereal world Groups are costeffective Groups providecommonality (e.g.“I’m not the onlyone with thisproblem”) Making a publicstatement abouttarget behaviormeans one ismore likely tofollow through. Feedback /diversity ofperspectives Normally consists of6-9 people attending a90-minute session Often focus onstigmatized or hardto-discuss illnesses. AIDS, Anorexia andalcoholism are twoconditions which oftenlead to support groups.Not everyone can bein a group (e.g.,issues, interpersonalskills)Confidentiality moredifficult to maintainHarder to build trustand safetyGroup leaders haveless control / notalways properlytrainedNot enough time todeal with each personthoroughlyThere are concernswith conformity andpeer pressure
Other TherapiesFamily therapy treats the family as a system.Therapy guides family members toward positiverelationships and improved communication.Community psychology is a relatively newspecialty area concerned with how individuals relate tosociety.Two main areas of focus:1. How people can become more activecontributors in their communities?2. How community issues can impact thehealth and wellness of individuals?Self-Help Groups are led by group membersinstead of a therapist, and focus more on support ratherthan working on goals during the session. They can bemuch larger than group therapy, with less interaction.
Commonalities AmongPsychotherapiesThree commonalities shared by all forms ofpsychotherapies are the following:1. A hope for“therapeutic alliance” - The emotionaldemoralizedbond between therapist and clientpeople.2. A newperspective.3. An empathic,trusting andcaringrelationship.
Behavior Therapies Therapy that applies learningprinciples to the elimination ofunwanted behaviors. The behaviors are the problems- sowe must change the behaviors.
Classical Conditioning TechniquesCounterconditioning:Mary Cover Jones A behavioral therapy that conditionsnew responses to stimuli that initiallytrigger unwanted behaviors.Based on classical conditioning andincludes exposure therapy andaversive conditioning.
Exposure TherapyThe Far Side 1986 FARWORKS. Reprinted with Permission. All Rights Reserved. Used to treat phobias Expose patients tothings they fear andavoid. Through repeatedexposures, anxietylessens because theyhabituate to the thingsfeared.
Systematic Desensitization (Wolpe) A type of counterconditioning thatassociates (step 1) a pleasantrelaxed state with (step 2)gradually increasing anxietytriggering stimuli.Progressiveexposure iskey
Exposure Therapy - (Flooding)Thomas Stampfl Uses in vivo exposure (actualexposure to feared stimulus.) Patient confronted with asituation in which the stimulusthat provoked the originaltrauma is present. Therapist usually offers verylittle assistance or reassuranceother than to help the patientto use relaxation techniques inorder to calm themselves.
Pit Bull guy
Systematic DesensitizationHow would I use systematicdesensitization to reduce my fear ofclowns?
Virtual Technology Exposure Therapy
Aversive Conditioning(Aversion training) A type of counterconditioning thatassociates an unpleasant state with anunwanted behavior.
Aversion Therapy gonehorribly, horribly wrong
Aversive ConditioningWhat are some ways youcan change the behaviorsof your friends withaversive conditioning?
Behavioral TherapyUseful in treating:DepressionADHDAnxiety (Phobias/OCD)ObesityInsomniaChronic fatigueCriticisms: Dehumanizing - techniques are sterile, standardized,and mechanistic. Lack the promotion of internal growth Lack of one specific theory to guide therapists intreatment.
Classical Conditioning inTherapy - Homework Explain the contributions ofMary Cover Jones, and explainhow Joseph Wolpe expandedand adapted her work fortherapeutic benefit.
Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning TechniquesUsed to INCREASE AdaptiveBehaviors: Shaping--successive approximations oftarget behavior are rewarded (includesrole-playing, behavior rehearsal,assertiveness training)
Operant ConditioningToken Economy: an operantconditioning procedure that rewardsa desired behavior.A patient exchanges a token of somesort, earned for exhibiting the desiredbehavior, for various privileges or treats.
Criticisms of operant conditioningfor behavior modification What happens when the reinforcersstop? (overjustification effect) Is it right for one person to controlanother person’s behavior?
Cognitive Therapy(CBT - CognitiveBehavioral Therapy)Key figures:Albert EllisAaron Beck Behaviorism focused onobservable behavior (J.B.Watson, B.F. Skinner) Albert Bandura reopened the door tocognitions with modeling The Cognitive Revolutionin therapy – 1960s Core assumption:Conscious thoughts aremost influential to ourpsychological well-being Goal: Change unhealthythought patterns tonew, more constructiveways of thinking
Cognitive Therapy Cognitive Therapy: focuses on faultythinking and beliefs– Improvement comes from insight intonegative self-talk (unrealistic things aperson has been telling himself orherself)– Cognitive Restructuring (process ofchanging destructive thoughts orinappropriate interpretations)
Cognitive TherapyThrough Functional analysis the therapist might help theclient identify her automatic negative thought patterns.(cognitive distortion)In thecognitiveperspective,the cause ofdepressionare not badevents, butourthoughtsabout thoseevents.
Cognitive Therapy (CBT - Cognitive Behavioral Therapy) Behaviorism focused on observable behavior (J.B. Watson, B.F. Skinner) Albert Bandura re-opened the door to cognitions with modeling The Cognitive Revolution in therapy -1960s Core assumption: Conscious thoughts are most influential to our psychological well-being










