Transcription
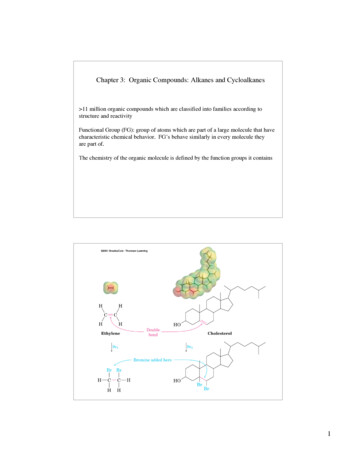
Chapter 3: Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes 11 million organic compounds which are classified into families according tostructure and reactivityFunctional Group (FG): group of atoms which are part of a large molecule that havecharacteristic chemical behavior. FG’s behave similarly in every molecule theyare part of.The chemistry of the organic molecule is defined by the function groups it contains1
C CAlkanesCarbon-heteroatom single bondsCarbon - Carbon Multiple BondsbasicC CC XAlkenesX F, Cl, Br, IAlkyl HalideC NaminesHC CC O CC OAlkynesalcoholsHHHC HthiolsC CHethersC S CC SC CCacidicsulfides(disulfides)HArenesCarbon-nitrogen multiple bondsCarbonyl-oxygen double bonds (carbonyls)OOHCaldehydeOOCHcarboxylic acidCOCesterketonesNClCimine(Schiff base)acid chlorideOOCbasicacidicOOCOCC C NCnitrile(cyano group)anhydridesOCNamideopsinLys-NH2HOrhodopsinH Lys- opsinNH2
Alkanes and Alkane IsomersAlkanes: organic compounds with only C-C and C-H single (s) bonds.general formula for alkanes: CnH(2n 2)Saturated hydrocarbonsHydrocarbons: contains only carbon and hydrogenSaturated" contains only single bondsIsomers: compounds with the same chemical formula, but different arrangement of atomsConstitutional isomer: have different connectivities (not limited to alkanes)C4H10C2H6OC5H12OHbutanolstraight-chain or normal hydrocarbonsn-butaneOdiethyl etherbranched hydrocarbonsn-pentaneSystematic Nomenclature (IUPAC System)Prefix-Parent-SuffixParent- number of carbonsPrefix- substituentsSuffix- functional groups3
Naming AlkanesGeneral Formula: CnH(2n 2)suffix: -aneParent 5H12C6H14C7H16C8H18C9H20C10H22Alkyl substituents (group): carbon chains which are asubstructue of a moleculeone carbon groupoff a main chainR Rest of the molecule -ROctyl9CH3(CH2)7CH2-RNonyl10CH3(CH2)8CH2-RDecyl4
Rules for Systematic Nomenclature of Alkanes1. Find the parent chaina. Identify the longest continuous carbon chain as the parent chain.CH3CH2CH3CH7 carbons hept-HCCH2CH2CH2CH3CH3b. If more than one different chains are of equal length (numberof carbons), choose the one with the greater number ofbranch points (substituents) as the parent.CH3CH3CH3HCCHCH2CH2CH2CH3CH3CHCH2CH22 branch pts.2.a.CHCH3CH2CH3CH31 branch pt.Numbering the carbons of the parent chainNumber the carbon atoms of the parent chain so that anybranch points have the lowest possible number1 CH37 CH36 CH22 CH2CH3CH34HCCH2CH2CH256CH3CH3CH37branch pts. at carbons 3 and 4b.CH5HCCH2CH2CH2324CH3CH31branch pts. at carbons 4 and 5If there is branching equidistant from both ends of theparent chain, number so the second branch point has thelowest 28branch pts. at carbons 3, 6, ch pts. at carbons 3,4,75
3. Substituentsa. Identify and number the substituents and listthem in alphabetical 1Parent C-9 nonane3- ethyl4-methyl4,7-dimethyl7-methylb. If there are two substituents on the same carbon,assign them the same number.4. Write out the namea. Write out the name as a single word:hyphens (-) separate prefixescommas (,) separate numbersb. Substituents are listed in alphabetical order4c. If two or more identical substituents are present use theprefixes:di- for twotri- for threetetra- for fournote: these prefixes (di-, tri-, tetra-, etc.) are not used foralphabetizing purposes9CH38CH2H3CCH2CH33- 316
5. Complex Substituents (substituents with branching)a. Named by applying the four previous rules withsome modificationb. Number the complex substituent separately from theparent. Begin numbering at the point of attachmentto the parent chain.c. Complex substituents are set off by parenthesis.CH2CH312CH3 methyl-4-(1-methylpropyl)decaneCH3Nonsystematic (trivial) hylethyl)4-Carbons:H3CCH3CHH3CParentChainH3CCH2CH c-butyl(1-methylpropyl)5- 3CH3H3CCH CH2 tyl-, )CParentChainCH3tert-pentyl-, tert-amyl(1,1-dimethylpropyl)Alphabetizing trivial names:Iso- and neo are part of the alkyl group name and are used for alphabetizing.sec- and tert- are not included in the alphabetical methyldecane7
Degrees of SubstitutionPrimary (1 ) Carbon: carbon which is bonded to only one other carbonSecondary (2 ) Carbon: carbon which is bonded to two other carbonsTertiary (3 ) Carbon: carbon which is bonded to three other carbonsQuarternary (4 ) Carbon: carbon whohc is bonded to four other carbonsHOsecondaryalcoholPrimary (1 ˇ)Secondary (2 ˇ)Tertiary (3 ˇ)Quarternary (4 ˇ)1 Hydrogens- hydrogens on a primary carbon. -CH3 (methyl group)2 Hydrogens- hydrogens on a secondary carbon. -CH2- (methylene group)3 Hydrogens- hydrogens on a tertiary carbon. CH (methane group)CH3H3CCH2CHCH3CH2Cmethyl group: 1 hydrogensmethylene group: 2 hydrogensmethine group: 3 hydrogensCH3CH3Applied to other functional tanol1 alcoholssec-butanol2 alcoholtert-butanol3 alcohol8
Alkanes show: regular increase in bp and mp as the molecularweight increase. Branching lowers the bp or alkanesn-pentane bp 36.1 Ci-penatane bp 27.9 Cneo-pentane bp 9.5 CVan der Waals Forces: small temporary dipoles that are a result of aDistortion of the electron clouds. There is an attraction betweenmolecules as result of these temporary ChainDecaneCyclodecaneCyclodecyl9
Naming Cycloalkanes1. Parent ChainGeneral Formula: CnH(2n)a. Use the cycloalkane as the parent chain if it has a greater number ofcarbons than any alkyl substituent.b. If an alkyl chain off the cycloalkane has a greater number of carbons,then use the alkyl chain as the parent and the cycloalkane as acycloalkyl- ne2. Numbering the Cycloalkanea. When numbering the carbons of a cycloalkane, start with a substitutedcarbon so that the substituted carbons have the lowest numbers (sum).6CH315422CH311,3-Dimethylcyclohexane6533 H31,2,4-Trimethylcyclohexane(1 2 4 7)54CH33612CH3-not1,3,4-Trimethylcyclohexane(1 3 4 8)2. b. When two or more different substituents are present, number accordingto alphabetical -1-methylcyclohexaneHalogen SubstituentsHalogen substituents are treated exactly like alkyl 2-methylcyclobutaneCl10
ndin E1OHOOHOesteronetestosterone11
The chemistry of the organic molecule is defined by the function groups it contains . 2 CC CC CC C CC C HH H HH Alkenes Alkynes Arenes CC Alkanes Carbon - Carbon Multiple Bonds CX X F, Cl, Br, I Alkyl Halide Carbon-heteroatom single bonds CO COC alcohol sethr H CN amines CS H CS thiols sulfides (disulfides) acidic basic HO opsin