Transcription
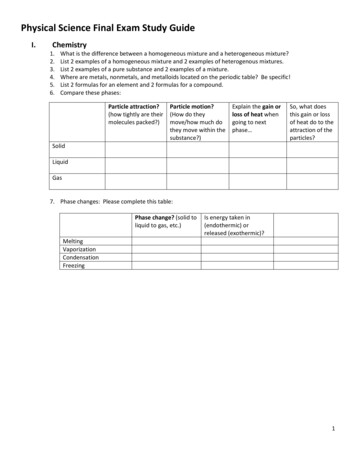
Physical Science Final Exam Study GuideI.Chemistry1.2.3.4.5.6.What is the difference between a homogeneous mixture and a heterogeneous mixture?List 2 examples of a homogeneous mixture and 2 examples of heterogenous mixtures.List 2 examples of a pure substance and 2 examples of a mixture.Where are metals, nonmetals, and metalloids located on the periodic table? Be specific!List 2 formulas for an element and 2 formulas for a compound.Compare these phases:Particle attraction?(how tightly are theirmolecules packed?)Particle motion?(How do theymove/how much dothey move within thesubstance?)Explain the gain orloss of heat whengoing to nextphase So, what doesthis gain or lossof heat do to theattraction of theparticles?SolidLiquidGas7. Phase changes: Please complete this table:Phase change? (solid toliquid to gas, etc.)Is energy taken in(endothermic) orreleased ng1
8. Compare evaporation, vaporization, and boiling. Watch this Youtube video:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v 9KjMe92gr-oSee this table to help with your comparisonVaporizationBoilingEvaporationThis is the only one that isan ACTUAL phase changeEnergy is NOT involvedwith this process.This is not technically aphase change, but it iswhen a liquid changes to agas due to changes inpressure.This is when the particleson a surface are exposedto wind and a liquidchanges into a gas belowits “boiling point”This is the phase change ofa liquid turning to a gas.9. Compare the formation of a solution and the formation of a compound. Which is a chemical process andwhich is a physical process?10. A solution forms due to forces of (CHOOSE ONE) (gravity, attraction, or energy) between the two typesof particles that make up solutions. These two types of particles are (CHOOSETWO) (protons, neutrons, solutes, solvents).11. A material is due to the LACK of ATTRACTION between particles.2
12. Please answer the following questions based on this solubility curve:a. Which is more soluble, NaNO3 or KCl?b. How does the line drawn for a particular substance relate to the saturation of a solution of thatsubstance?c. How many grams of NH4Cl will dissolve in 100 grams of 90 C Water?d. How many grams of NH4Cl will dissolve in 50 grams of 90 C water?e. How many grams of KClO3 will dissolve in 300 grams of 30 C water?f. How would you make a saturated solution of KNO3 at 60 C in 50 grams of water?g. If I asked you to make a saturated solution of KCl in 100 grams of water, what other piece of informationwould you need before you could start?13. Complete this table:Cannot hold anymore solute inthat given solventat that giventemperature.Holds moresolute than thatsolvent canusually hold atthat temperature.Holds less solutethan that solventcan hold at rsaturatedDiluteConcentrated3
14. Explain how you could separate a mixture using solubility, density, boiling point, and magnetic properties.15. Please complete this table:MetalState of matterat roomtemperatureDensity (high orlow)Melting pointsare normally Boiling pointsare normally vity?Nonmetal16. Compare some physical and chemical properties of:Physical propertiesSaltMetalloidDefinition, if necessaryChemical Properties4
SugarBaking sodaCorn starchRubbing alcoholWater17. Complete this table:ChargeMass?LocationProtonElectronNeutron18. Compare the number of protons, neutrons, electrons, and mass number in neutral atoms vs. ions19. Explain how the different mass numbers of isotopes contributes to the average atomic mass for a givenelement.20. Show 3 ways to write the symbol for a carbon isotope that has a mass number of 12.21. Draw Bohr models of Sodium and Hydrogen.22. Draw dot diagrams for chlorine, helium, and argon.23. How many valence electrons do the following atoms have? Be, K, B, Si, As, Te, I, Kr24. What are these atoms’ oxidation numbers?25. Why are tin and lead sometimes written Sn (II) and Pb (III) or Pb (II) (having Roman Numerals besidethem)?26. Which group contains the most reactive metals and which one is the most reactive?27. Which group contains the most reactive nonmetals and which one in the most reactive?28. Complete this table:Their Electrons areFormed between(shared/transferred, which type ofetc.)atoms? (metals,nonmetals, etc.)NaClCO2KBrIonicCovalentMetallic29. Write the formulas or the names for the following compounds. Make sure you follow the correct rulesfor ionic vs. covalent (molecular) compounds.sodium hydroxideP4S5lithium oxideSi2Br6B2SiMgBr2iron (III) phosphidechlorine dioxide5
dinitrogen trioxideZn(OH)2PbOiodine pentafluoride30. Please BALANCE and CLASSIFY these reactions:1. 2 K 2 H2O ----- 2 KOH H22. HCl NaOH ---- H2O NaCl3. KNO3 ---- KNO2 O24. 2 C2H2 5 O2 ----- 4 CO2 2 H2O5. C4H8 6 O2 ---- 4 CO2 4 H2O6. Hg O2 ---- HgO31. How does the Law of Conservation of Matter relate to balancing chemical equations?32. Match these acids and bases with their eSodiumHydroxideAmmoniumHydroxideAcetic AcidPotassiumHydroxideSulfuricAcidCitric (OH)2Ba(OH)2NH4OHHClH2SO4C2H4O2HNO36
C6H8O7NaHCO3NaOHKOHCa(OH)2Mg(OH)2Ba(OH)2NH4OH35. Arrhenius theory of acids and bases:AcidsBasesNeutralProduce more OH- ions in solution than H Produce more H ions in solution than OH- ionsProduce equal amounts of H ions and OH- ions in solutionpH below 7pH above 7pH equal to 7Reactive with metalsReactive with fats/oils36. What is a neutralization reaction?37. Which 2 things are formed in a neutralization reaction?38. Complete the table below with the correct information about each type of radioactive emission.Charge AtomicCan beMassThis decayThis decayThese areSymbolstopped(large/small)?Increases thereduces the mass Electromagneticbyatomic number byof an atom by 4Waves released1and the atomicfrom thenumber by 2nucleus with analpha or betaparticle.AlphaBetaGamma39. Complete the following nuclear reactions:a. 6027Co 0-1e Radiation typeb. 211 Fr 20785Radiation type7
c. 8235 KrRadiation type40. Complete this table using the concepts you have learned about Fission and Fusion:FissionFusiontwo or more nuclei join together to form a more-massive nucleusUraniumlarge nucleus splits into two smaller nucleienergy is releasedChernobylnot currently used to provideelectrical energyno radioactive waste productsoccurs in the sun’s coreradioactive waste productsrequires temperatures over 100,000,000 Cfuels 20 percent of the electrical energy used in the United Statesnot currently used to provideelectrical energy41. Complete these half-life problems:II.Physics42. Draw and label a diagram which shows the difference between distance and displacement.43. Which is a scalar quantity and which is a vector quantity:Scalar quantitySpeedVelocityDistanceDisplacementV ector quantity8
44. The symbol for velocity is The symbol for time isThe symbol for distance is The equation for velocity isThe unit for velocity isThe unit for time isThe unit for distance is45. Please calculate the answers to these problems:12349
46. Momentum problems:1. Calculate the momentum of a 0.15 kg ball that is moving toward home plate at a velocity of 40m/s.2. Which has greater momentum, a 2.0kg hockey puck moving east at 2.5m/s or a 1.3kg hockey puckmoving south at 3.0m/s?47.48.49.50.51.52.53.54.55.How do you determine the weight of an object?A small rocket weighs 14.7 N. What is the mass?A net force of 25 N is applied to a 10 kg mass. What is the acceleration given to the mass?How is air resistance related to terminal velocity?Define friction.Give examples of static, sliding, rolling, and fluid friction.What is inertia and how is it related to mass? Think of Newton’s first Law!Draw 1 diagram to show balanced forces and another diagram to show unbalanced forces.Think about the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration to answer these:a. The greater the force on an object, the greater its change in (acceleration/ motion/mass) (choose one)b. The same amount of force applied to an object with less mass results in greater (acceleration/motion/mass) (choose one)56. State Newton’s 2nd Law and give 2 examples.57. State Newton’s 3rd Law and give 2 examples.58. Compare thermal energy, heat, and temperature:TemperatureThermal EnergyHeatTOTAL energy of all ofthe particles of anobject – this includesmass and kineticenergy.Thermal energymoving from awarmer object to acooler objectA measure of theaverage kineticenergy of an object.59. Compare conduction, convection, and radiation as methods of energy transfer:ConductionConvectionInvolves wavesInvolves currentsInvolves direct contactA metal spoon in a pot ofsoup.Boiling waterA toaster toasting bread.radiation60. How are kinetic energy and potential energy related on a roller coaster’s top of the first hill and bottom of thefirst hill?61. Work requires .62. When work is done on an object , the result is an increase in its and is accompanied bya decrease in energy somewhere else.63. What is the equation for calculating the amount of work done on an object?64. How are power and work related? (give the equation for calculating power)10
65. The 2 simple machines that are a modified version of the inclined plane are and.66. Which 2 simple machines are variations of a lever?67. If work input is not equal to work output for a machine, how does the Law of Conservation of Energy explain this“lost” energy?68. Why is no machine 100 % efficient, or greater than 100 % efficient?69. Give the formula for calculating efficiency of a machine.70. Calculate the efficiency of a machine that places the caps on plastic soda bottles requires 25 kJ of input work.The output work of the machine is 23 kJ.71. Determine the ideal and actual mechanical advantage for the following machine: A lever has an effort armwith a length of 2 m and a resistance arm with a length of 0.5 m. When 900 N of force are applied to the lever, a1750-N load is raised 0.3 m.72. Draw and label a longitudinal (compressional) wave with the parts: amplitude, rarefaction, compression, andwavelength.73. What is the equation for calculating wave problems involving velocity, frequency, and wavelength.74. How is energy related to the amplitude of a wave?75. Draw and label a transverse wave with its parts: crest, trough, amplitude, and wavelength76. How do transverse and longitudinal waves move particles as related to wave direction?77. Please complete this table comparing wave behaviors:ReflectionRefractionDiffractionBeing able to hear arounda corner is due to thiswave behaviorSONAR is due to thiswave behaviorThings can look bigger,bent, or broken in waterRADAR is due to this wavebehavior78. Opposite charges (attract/repel) and like charges (attract/repel) (choose one in each set of parenthesis)79. Please complete this table regarding methods of charging objects:ConductionFrictionInductionTransferred from rubbingthe force field of a highlynegatively charged object pushesthe electrons away from nearbyobjects causing them to become chargedtransferred by direct contact w/another objectHair standing on end w/ Van deGraff machinestatically charged balloon attractssmall pieces of torn up paperGetting shocked from walking onthe carpet80. Draw both a series and a parallel circuit diagram with resistors and batteries. Please label the parts of thediagrams11
81. Show the difference between an open circuit and a closed circuit by drawing a simple diagram. Please labelwhich is open and which is closed.82. List Ohm’s law equation and the Power equation. Explain what each of the letters represent.83. Explain the difference between a series and a parallel circuit.84. Explain how the flow of electricity through series and parallel circuits is affected by voltage andresistance .think about the circuits lab what happened when you added more light bulbs? What wouldhappen if we added more voltage?85. More current exists in a wire when (resistance/voltage) is low.86. Explain how changes in composition, length, temperature, and diameter of a wire would affect the current in acircuit.87. Complete this table regarding resistance:Increases resistanceIncreasing the lengthof a wireIncreasing thetemperatureIncreasing thediameter of a wireDecreases resistance88. For a magnet to be magnetized, the Magnetic domains must be (random/lined-up) (choose one).89. How do you demagnetize a magnet?90. Magnets (repel/attract) because force comes out of (North/South ) Pole and goes into the (North/South) Pole(choose one from each set of parenthesis)91. Magnets (repel/attract) (choose one) because the forces are pushing (toward/away) from each other (chooseone from each set of parenthesis)92. An electric current produces a magnetic field. (True or False)93. Describe what an Electromagnet is.94. An electric generator converts (mechanical/electrical) energy into (mechanical/electrical).95. A motor converts (mechanical/electrical) energy into (mechanical/electrical).96. Explain how electricity and magnetism are related to ATM or credit cards, speakers, automatic sprinklers, andtraffic signal triggers.12
13
Physical Science Final Exam Study Guide I. Chemistry 1. What is the difference between a homogeneous mixture and a heterogeneous mixture? 2. List 2 examples of a homogeneous mixture and 2 examples of heterogenous mixtures. 3. List 2 examples of a pure substance and 2 examples of a mixture. 4.










