Transcription
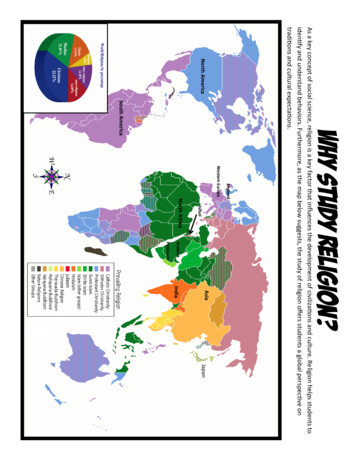
Why study Religion?EnglandWestern EuropeIsraelNorth AfricaPeninsulaArabianIndiaAsiaJapanAs a key concept of social science, religion is a key factor that influences the development of civilizations and culture. Religion helps students toidentify and understand behaviors. Furthermore, as the map below suggests, the study of religion offers students a global perspective ontraditions and cultural expectations.North AmericaSouth America
World ReligionsLook at the World Religions Map provided to answer questions on aseparate piece of paper.1. List the three types of Christianity on this map.2. Which type of Christianity is most practiced in Western Europe?3. Which type of Christianity is practiced in Mexico and South America?4. List the two major branches (called sects) of Islam.5. The people of modern Saudi Arabia (The Arabian Peninsula) and North Africaare mostly which sect of Islam? Sunni or Shiite (also called Shia)?6. Find India: Which religion is mostly practiced in India?7. Buddhism is practiced mostly on which continent?8. In Israel (just north of the Red Sea), you will see red. Which religion does thered represent? Also, be informed that there are highly concentrated pocketsof this religion in major cities on the east coast of the United States.9. If Catholic Christianity or Catholicism originated in Europe, what mightexplain why South America and Europe are both majority Catholic?10. What may explain why England and North America are mostly comprised ofProtestant Christians?11. Provide evidence from the map or pie chart that supports the claim thatstudents should have a basic education about varying religions in order tounderstand the world from which they live.
World Religions Answer KeyLook at the World Religions Map provided to answer questions.1. List the three types of Christianity on this map. Protestant, Catholic andOrthodox Christianity2. Which type of Christianity is most practiced in Western Europe? Catholic3. Which type of Christianity is practiced in Mexico and South America? Catholic4. List the two major branches (called sects) of Islam. Shiite/Shia and Sunni5. The people of modern Saudi Arabia (The Arabian Peninsula) and North Africaare mostly which sect of Islam? Sunni or Shiite (also called Shia)?6. Find India: Which religion is mostly practiced in India? Hinduism7. Buddhism is practiced mostly on which continent? Asia8. In Israel (just north of the Red Sea), you will see red. Which religion does thered represent? Also, be informed that there are highly concentrated pocketsof this religion in major cities on the east coast of the United States. Judaism9. If Catholic Christianity originated in Europe, what might explain why SouthAmerica and Europe are both majority Catholic? The Spanish conquistadorsand missionaries brought Catholicism to this region.10. What may explain why England and North America are mostly comprised ofProtestant Christians? The English immigrated top North America.11. Provide evidence from the map or pie chart that supports the claim thatstudents should have a basic education about varying religions in order tounderstand the world from which they live. According to the map, one cansee that large parts of the world practice varying religions. One could inferthat in order to understand the behaviors of these people, one should knowthe basics of their religion. Also one can see from the chart that whileChristianity is the majority religion, other religions like Islam and Hinduismcomprise a higher percentage than Christians.
Common Core LiteracyChristianity, Judaism and Islam : A Fact SheetChristianity, Islam, and Judaism are all monotheistic (believe in one god) religions. All three religions were broadlyfounded on the continent of Asia in the geographic region called the Middle East. These three faiths share commonhistory and traditions. All three have a respect for the Bible, especially the Hebrew Bible or “Old Testament” as allthree religions believe in many of the same prophets (messengers of God) such as Abraham and Moses. They allmaintain that there is one God and that Jerusalem is a holy city. However, Christianity, Islam and Judaism also differsignificantly in both belief and practice. The belief in Jesus is at the forefront of their differences. While Christiansbelieve he is a messiah (savior) and the son of God, Muslims acknowledge him as a prophet only. Still, most Jews denythat he was a prophet or messiah. The following chart is intended to be a brief overview for understanding the basicsof these ancient religions and their shared history.ChristianityBeliefs about GodOriginationTextsJudaismIslamMonotheistic (believe in one god) MonotheisticMonotheisticHoly Trinity (One God in threepersons) God the Father Godthe Son God the Holy SpiritAllah Arabic word for God.One God Yaweh (Hebrew namefor God as used in Bible)The Middle East - Roman province The Middle Eastof Palestine.The religion of the Hebrews.Based on life and teachings ofTraces of Judaism are dated backJesus of Nazareth, c. 30 CE.as far as c. 1300 BCE in AncientBabylonia.The Middle East - Mecca, SaudiArabia.Bible Hebrew Bible (referred toas Old Testament) and the NewTestament.Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and theTalmud.Qur'an or Koran (Scripture) andthe Hadith (tradition).The Old Testament or HebrewBible - Comprised of thirty-ninebooks . The texts are about law,history, prophecy, and wisdom ofthe ancient people of Israel.The Hebrew Bible - Comprised ofthirty-nine books. Torah (Hebrew:'Law'), Nevi'im ('Prophets') andKetuvim ('Writings'). The texts areabout law, history, prophecy, andwisdom of the ancient people ofIsrael.Qur’an - Believed to be the wordof God as dictated to Muhammadby the angel Gabriel.Called ChristiansCalled JewsCalled MuslimsChristians practice ChristianityJews practice JudaismMuslims practice IslamChristians believe he was the sonof God, as God made in flesh (partof the holy trinity). They considerhim to be the Jewish messiah(savior of the world)Jews do not believe he is theJewish messiah. He in also notconsidered a prophet.Muslims believe he was amessenger of god or, prophet.Based on teachings of theProphet (messenger of God)Muhammad; founded 622 CE.Hadith - Collection of traditionscontaining sayings of the prophetMuhammad that, with accountsFor example: The tenof his daily practice (the Sunna),commandments are laws given to For example: The tenconstitute the major source ofthe Ancient Israelites by God.commandments are laws given to guidance for Muslims apart fromthe Ancient Israelites by God.the Qur’an.The New Testament -Teachings ofJesus and his earliest followers .Talmud - A body of Jewish civiland ceremonial law, customs andculture.FollowersBeliefs aboutJesusMuslims believe he was amessenger of god or, prophet.Copyright 2015 Instructomania Pavlovich
Christianity, Judaism and Islam: A Fact SheetChristianityJudaismIslamPlace of Worshipchurch or chapelsynagogue or templemosqueFundamentaldisagreementsChristians do not viewMuhammad as a prophet.Christians believe Jesus was themessiah (savior) that wasprophesized about in theHebrew Bible.Jews do not view Muhammadas a prophet, nor do they viewJesus as a messiah or son ofGod. Jews are still awaiting amessiah or savior.Muslims believe thatMuhammad was the lastprophet and that Jesus wasalso a prophet, but not the sonof God.AdherentsApproximately 2 billionApproximately 14 millionApproximately 1.3 billionCatholic -. Approximately 53%of Christians.Orthodox - 10% of JewsShia - 10 to 13% of populationEastern Orthodox –Approximately 9% ofChristians.Protestant – Approximately33% of Christians.Major BranchesCatholic - Original “RomanCatholic” form of Christianity.Greek Orthodox (1054) - Afterthe Great Schism (adisagreement over theselection of a pope).Protestant (1500s) - After theProtestant Reformationinitiated mostly by MartinLuther.Common ReligiousSymbolsThe crossReform - Approximately 35% of Sunni - Approximately 90% ofJewspopulation.Conservative JudaismApproximately 20 % of Jews30 % of Jewish population doesnot affiliate with adenomination.Orthodox (1800 CE) - BelieveThe difference between Shiaboth the written and oral Torah and Sunni is about therepresent the word of God.leadership of Islam (in itsoriginal boundaries).Reform (approximately 1926) Jewish traditions and ancientShia -Believe God chose Alilaws were modernized to be(Muhammad’s blood relative)more compatible withto be Muhammad's successor.participation in WesternHence he was the firstCulture (including use ofacceptable caliph (head ofmodern technology).state) of Islam.Conservative (1850)- Inbetween Orthodox and ReformJews. They seek to conservethe traditional elements ofJudaism, while also allowing forsome modernization.Sunni (c. 650 CE) - Deny that ablood relative of Muhammadneeded to be the leader ofIslam, hence leaders before Aliwere acceptable.The star of DavidThe crescent moon and starCopyright 2015 Instructomania Pavlovich
Common Core LiteracyKey Vocabulary: Judaism, Christianity and IslamWordLetterDefinition1. MonotheismA. Hebrew name for God as used in Bible.2 MessiahB. Original “Roman Catholic” form of Christianity.3. ProphetC. Name for people who practice Christianity.4. ChurchD. Arabic word for God.5. SynagogueE. Name for people who practice Islam.6. MosqueF. Jewish place of worship.7. BibleG. Collection of traditions containing sayings of the prophet Muhammad that, with accounts of his daily practice(the Sunna), constitute the major source of guidance for Muslims apart from the Qur’an.8. TorahH. Believe both the written and oral Torah represent the word of God.9. Qur’an (Koran)I. Teachings of Jesus and his earliest followers.10. HadithJ. Jewish traditions and ancient laws were modernized to be more compatible with participation in WesternCulture (including use of modern technology).11. ChristiansK. After the Protestant Reformation initiated mostly by Martin Luther.12. MuslimsL. Deny that a blood relative of Muhammad needed to be the leader of Islam, hence leaders before Ali wereacceptable.13. JewsM. Name for people who practice Judaism.14. Old TestamentN. One God in three persons :God the Father God the Son God the Holy Spirit .15. New TestamentQ. Believe God chose Ali (Muhammad’s blood relative) to be Muhammad's successor. Hence he was the firstacceptable caliph (head of state) of Islam.16. CatholicR. Jewish holy text. Means Hebrew Law.17. ProtestantS. Comprised of thirty-nine books . The texts are about law, history, prophecy, and wisdom of the ancient peopleof Israel.18. Greek OrthodoxT. Means messenger of God.19. SunniU. After the Great Schism (a disagreement over the selection of a pope).20. ShiaV. Christian place of worship.21. ConservativeJudaismW. Savior of the world.22. Reform JudaismX. In between Orthodox and Reform Jews. They seek to conserve the traditional elements of Judaism, while alsoallowing for some modernization.23. Orthodox JudaismY. The belief in one god.24. AllahZ. Christians believe he was the son of God, as God made in flesh (part of the holy trinity). They consider him to bethe Jewish messiah (savior of the world).25. YawehO. Christian holy text, comprised of New and Old Testaments.26. Holy TrinityP. Muslim place of worship.27. JesusAA. Muslim holy book or Scripture.Copyright 2015 Instructomania Pavlovich
ANSWER Key Vocabulary: Judaism, Christianity and IslamWordLetterDefinition1. MonotheismY.A. Hebrew name for God as used in Bible.2 MessiahW.B. Original “Roman Catholic” form of Christianity.3. ProphetT.C. Name for people who practice Christianity.4. ChurchV.D. Arabic word for God.5. SynagogueF.E. Name for people who practice Islam.6. MosqueP.F. Jewish place of worship.7. BibleO.G. Collection of traditions containing sayings of the prophet Muhammad that, with accounts of his daily practice(the Sunna), constitute the major source of guidance for Muslims apart from the Qur’an.8. TorahR.H. Believe both the written and oral Torah represent the word of God.9. Qur’an (Koran)AA.I. Teachings of Jesus and his earliest followers.10. HadithG.J. Jewish traditions and ancient laws were modernized to be more compatible with participation in WesternCulture (including use of modern technology).11. ChristiansC.K. After the Protestant Reformation initiated mostly by Martin Luther.12. MuslimsE.L. Deny that a blood relative of Muhammad needed to be the leader of Islam, hence leaders before Ali wereacceptable.13. JewsM.M. Name for people who practice Judaism.14. Old TestamentS.N. One God in three persons :God the Father God the Son God the Holy Spirit .15. New TestamentI.Q. Believe God chose Ali (Muhammad’s blood relative) to be Muhammad's successor. Hence he was the firstacceptable caliph (head of state) of Islam.16. CatholicB.R. Jewish holy text. Means Hebrew Law.17. ProtestantK.S. Comprised of thirty-nine books . The texts are about law, history, prophecy, and wisdom of the ancient peopleof Israel.18. Greek OrthodoxU.T. Means messenger of God.19. SunniL.U. After the Great Schism (a disagreement over the selection of a pope).20. ShiaQ.V. Christian place of worship.21. ConservativeJudaismX.W. Savior of the world.22. Reform JudaismJ.X. In between Orthodox and Reform Jews. They seek to conserve the traditional elements of Judaism, while alsoallowing for some modernization.23. Orthodox JudaismH.Y. The belief in one god.24. AllahD.Z. Christians believe he was the son of God, as God made in flesh (part of the holy trinity). They consider him to bethe Jewish messiah (savior of the world).25. YawehA.O. Christian holy text, comprised of New and Old Testaments.26. Holy TrinityN.P. Muslim place of worship.27. JesusZ.AA. Muslim holy book or Scripture.Copyright 2015 Instructomania Pavlovich
Common Core Writing and Critical ThinkingChristianity, Judaism and Islam: A Comparison ChartList five similarities of all three religionsChristianityJudaismIslamDescribe Five DifferencesDescribe Five DifferencesDescribe Five n: (In a sentence, what conclusion can be drawn?)Copyright 2015 Instructomania Pavlovich
Wager This!An easy, fantastic review game for all ages, K-12 which also utilizes math skills.Materials needed - Student: A piece of paper and pen/pencil. Teacher: Material that you would like studentsto review such as, homework questions, test questions or anything that is a short answer. This is also fun todo with a PowerPoint of prepared questions. This game can be played individually, with a partner or a team.Paper set up - Students set up their paper as follows.NameWager ThisAnswersTeacher maywant to havestudents numberas they go, sothey haveenough room towrite answers.1.score 100The score at the beginningis up to the teacher. Forelementary starting with 10or 50 is good, secondarystarting with 100 is great!2.3.4.5.6.Here is how it works:STEP 1: Before teacher asks a review question, students “wager” part of their total score (shown above as100). A wager is like a “bet” that the student/s will respond correctly. Students are only allowed to wager upto half of their total. Assuming students are given 100 points to begin with, for the first question, they canonly wager 1-50 points (student choice.) After “wagering” their points, teacher reads the review questionand they write down their answer.STEP 2: If the student/s responds correctly then he/she adds the amount wagered to the total, if he/sheresponds wrong he/she subtracts from the total. Then, before question two, students place a wager up tohalf of their own new total and play continues on.For example: If the student wagered 50 points initially, and they responded correctly they would have a newtotal of 150 points. Which means he/she could wager up to 75 points for the second question.Step 3: Students share scores at end of game. In my experience, students keep each other in check prettywell, so cheating has not been a major concern.Copyright 2015 Instructomania Pavlovich
Common Core!Includes a world religionsmap activity.Includes a similarities anddifferences comparisonchart activity and keyvocabulary matching.Includes a fun,easy class game!Includes a two pagereading with key factsabout Islam, Judaism andChristianity
A common CoreActivity Set!ComparingReligionsChristianity, Judaism, Hinduism,Buddhism and Islam
World Religions Look at the World Religions Map provided to answer questions on a separate piece of paper. 1. List the three types of hristianity on this map. 2. Which type of hristianity is most practiced in Western Europe? 3. Which type of hristianity is practiced in Mexico and South Amer







![[Page 1 – front cover] [Show cover CLEAN GET- AWAY 978-1 .](/img/13/9781984892973-6648.jpg)