Transcription
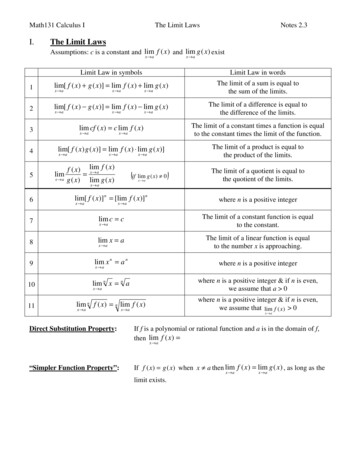
Math131 Calculus II.The Limit LawsNotes 2.3The Limit LawsAssumptions: c is a constant and lim f ( x ) and lim g ( x ) existx aLimit Law in symbolsx aLimit Law in words1lim[ f ( x ) g ( x )] lim f ( x ) lim g ( x)The limit of a sum is equal tothe sum of the limits.2lim[ f ( x ) g ( x )] lim f ( x ) lim g ( x )The limit of a difference is equal tothe difference of the limits.3lim cf ( x) c lim f ( x)The limit of a constant times a function is equalto the constant times the limit of the function.4lim[ f ( x ) g ( x )] lim f ( x ) lim g ( x)]The limit of a product is equal tothe product of the limits.5x ax ax ax ax ax ax ax ax alimx ax ax af ( x)f ( x ) lim x ag ( x ) lim g ( x)(if lim g ( x) 0)x aThe limit of a quotient is equal tothe quotient of the limits.x a6lim[ f ( x)] n [lim f ( x )] nwhere n is a positive integer7lim c cThe limit of a constant function is equalto the constant.8lim x aThe limit of a linear function is equalto the number x is approaching.9lim x n a nwhere n is a positive integer10lim n x n awhere n is a positive integer & if n is even,we assume that a 011lim n f ( x ) n lim f ( x )where n is a positive integer & if n is even,we assume that lim f ( x ) 0x ax ax ax ax ax ax ax ax aDirect Substitution Property:If f is a polynomial or rational function and a is in the domain of f,then lim f ( x ) x a“Simpler Function Property”:If f ( x) g ( x) when x a then lim f ( x ) lim g ( x ) , as long as thex alimit exists.x a
Math131 Calculus Iex#1Notes 2.3Given lim f ( x) 2 , lim g ( x) 1 , lim h( x) 3 use the Limit Laws find lim f ( x )h( x ) x 2 g ( x)x 3ex#2x 3x 32Evaluate lim 22 x 1 , if it exists, by using the Limit Laws.x 2ex#3page 2Evaluate:x 6x 4lim 2 x 2 3 x 5x 1ex#4Evaluate:1 (1 x) 2limx 0xex#5Evaluate:limh 0h 4 2hx 3
Math131 Calculus INotes 2.3page 3Two Interesting Functions1.Absolute Value FunctionDefinition: x x if x 0 x if x 0Geometrically:The absolute value of a number indicates its distance from another number.x c a means the number x is exactly units away from the number .x c a means:The number x is within units of the number .How to solve equations and inequalities involving absolute value:Solve: 3x 2 7Solve: x - 5 2What does x - 5 2 mean geometrically? 2.The Greatest Integer FunctionDefinition:[[x]] the largest integer that isless than or equal to x.ex 6ex 7ex 8ex 9[[ 5 ]] [[ 5.999 ]] [[ 3 ]] [[ -2.6 ]] Theorem 1:lim f ( x) L if and only if lim f ( x) L lim f ( x)x ax a x a xex#10 Prove that the lim does not exist.x 0 x
Math131 Calculus INotes 2.3page 4ex#11 What is lim [[ x ]] ?x 3 Theorem 2:If f ( x) g ( x) when x is near a (except possibly at a) and the limits of f and g bothexist as x approaches a then lim f ( x ) lim g ( x ) .x ax a 1ex12 Find lim x 2 sin . To find this limit, let’s start by graphing it. Use your graphing calculator.x 0x The Squeeze Theorem:If f ( x) g ( x) h( x) when x is near a (except possibly at a) andlim f ( x) lim h( x) L then lim g ( x) Lx ax ax a
Math131 Calculus ILimits at Infinity & Horizontal AsymptotesNotes 2.6Definitions of Limits at Large NumbersnumbersLet f be a function defined on some interval (a, ).Then lim f ( x ) L means that the values of f(x) canx numbersLargeLargeNEGATIVEPOSITIVEDefinition in WordsHorizontal Asymptotex be made arbitrarily close to L by taking x sufficientlylarge in a positive direction.corresponding number N such that if x N thenLet f be a function defined on some interval(- ,a). ). Then lim f ( x) L means that theLet f be a function defined on some interval(- ,a). Then lim f ( x) L if for every ε 0 therevalues of f(x) can be made arbitrarily close to L bytaking x sufficiently large in a negative direction.is a corresponding number N such that if x N thenx DefinitionVertical AsymptotePrecise Mathematical DefinitionLet f be a function defined on some interval (a, ).Then lim f ( x ) L if for every ε 0 there is af ( x) L εx f ( x) L εWhat this can look like The line y L is ahorizontal asymptoteof the curve y f(x) ifeither is true:1. lim f ( x) Lx or2. lim f ( x) Lx The line x a is avertical asymptoteof the curve y f(x)if at least one of thefollowing is true:1. lim f ( x) x a2. lim f ( x) x a3. lim f ( x) x a4. lim f ( x) x a5. lim f ( x) x a6. lim f ( x) x aTheorem1 0x x r If r 0 is a rational number then lim If r 0 is a rational number such that x r is defined for all x then lim1 0x x r
Math131 Calculus INotes 2.63x x 5ex#1Find the limit: limex#2Find the limit: limex#3Find the limit: limex#4Find the limit: lim cos xx3 2xx 5 x 3 x 2 4x x 9 x 2 x 3xpage 2
Math131 Calculus Iex#5Notes 2.6Find the vertical and horizontal asymptotes of the graph of the function: f ( x) page 32x 2 13x 5
,g r4-, -CR.\.1. o\ {-i y!! rP Lr: - orot a\r.eAC."or*o " .-\ob\o\k-i g\ e.dovoqFroA\.cfc\.6;l 'a-,.--- o.-.o'""q -r xi 6o A o co \v* e -o{\ a j s,p-
J-Or e\ge !Y\o \ t!SS
a\rtsocsh (/Js ea!-5 ,2.- - ,o ,\Xr1\\i6\io.i!iov\I P @ *J4''.t .A" {1A'(\5 Q) A.5 l A 'IAtL, ) AC.\- * AeM -S) 6. c l { - - ( e .!4-e
the product of the limits. 5 lim ( ) lim ( ) ( ) ( ) lim g x f x g x f x x a x a x a ( lim ( ) 0) if g x x a The limit of a quotient is equal to the quotient of the limits. 6 n x a n x a f x f x lim[ ( )] [lim