Transcription
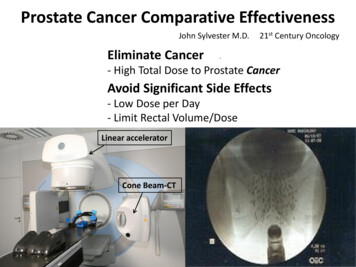
Prostate Cancer Comparative EffectivenessJohn Sylvester M.D.Eliminate Cancer21st Century Oncology-- High Total Dose to Prostate CancerAvoid Significant Side Effects- Low Dose per Day- Limit Rectal Volume/DoseLinear acceleratorCone Beam-CT
Partin TablesStudy of 5,000 patients that underwent Radical ProstatectomyRisk of microscopic diseaseT Stage (DRE)ECEGleason ScoreSVPSALymphNodes
TRUS Volume Study
Transperineal InterstitialPermanentProstate Brachytherapy(seed implant)05/00Seattle Prostate Institute
Quality & Experience is CriticalSeeds Insideand outsideof prostateProstateFull DoseRadiationInside andoutside ofprostateDay 1 post-implant dosimetry
Post OperativeDischarge to home 1 hour later with: Alpha-blockers, NSAIDs, AntibioticsIce bag on perineum 20minutes on/off repeat all dayLight lunch, normal dinnerPost-op dosimetry CT the next day.Return to work in 3-4 daysAvoid strenuous activities and sex for 2 weeksAvoid upright bike seat 2 months
Cone Beam-CT Image Guided-IMRT (BEAM)Linear acceleratorCone Beam-CT
Multiple fields ( 100-200)Doses4 field: 68 Gy3dCrt: 74 GyIMRT: 78 GyIGRT: 81 Gy
Prostate Cancer IMRT /- IGRTChan LW et al IJROBP ;69,No 3 2007,abstr.#2242 Normal structures significantly spared(e.g. rectum V70 19% vs 1.7%) Side effects Graded 1 (very mild)-5 (severe) Acute grade 2 toxicity (mild) :Rectal 80% vs 13% p 0.004.Bladder 60% vs. 13%, p 0.014. No grade 3-5 toxicity Conclusion: IMRT with daily image (IGRT) results in lowerdose to normal structures which means less side effects
Rectal BalloonRectal Balloon1)2)3)4)Lower rectal doseLess movementNormal dietLower small bowel doseCBCTIGIMRTCone-beam CTImage GuidedIntensity ModulatedRadiation Therapy
SpaceOARFDA approved 2:1 randomized trialSpaceOAR
RISK GroupsLowIntermediatePSA 10Gleason 7T1c-T2aPSA 10.1-20.0 ng/mland/or Gleason 7and/or Stage T2bHighPSA 20 ng/mlGleason 8-10Stage T2c,T3Don’t Use MSKCC Nomogram to compare results!!!
5-YR Relapse-free Survival Low riskusually seedsIntermed. ebrt High risk seedsebrt seeds veland Clinic (IJROBP ;2008)-------------89%-----------SeedsSylvester Seattle (IJROBP 1;2007)--------------80% (15-yr)68% (15-yr)SeedsSylvester Seattle (Brachy 5;2009)---------------92% (9-YR)--------SeedsFrank.Sylvester (Cancer99.1% itutional study IJROBP Feb 2009---------------86%HDRDemanes- (UCLA JCO 2009 ) (10-yr)92%87%63%RPMayo Clinic RP82% 10-yr65% (10yr)55% (10yr)RPJHU RP (Hernandez J Urol 2007)94%76%54%RPCleveland Clinic RP86% (10yr)79% (5yr)EBRTProtons- IJROBP 78,3 s146 ASTRO 2010 (10-yr)92%69%-----------IMRTMSKCC (81Gy)89% (8yr)78% (8yr)67% (8yr)ImmuneBaylor Prostatak 76Gy IMRTHiFUCryo(IJROBP 2009)Epub 2011)(J. Urol April 2008)(IJROBP 69,3,2007)J Urol; 176, Oct 20062006100% ( 6yr) 95% ( 6yr)80% ( 6yr)HiFU European Urology 65 (2014)76% (8yr)63% (8yr)57% (8yr)Dhar et al BJU int, 2011 Jul 1 (Epub)79.4%61.4%58%
HIFUDickinson et al; Mar 2016 Urology 569 patients 8 hospitals academic registry 29% required re-treatment 5-yr relapse free survivalLow risk 87%Intermediate 63%High risk 58% Impotency 71% Incontinence 12%
Comparative Analysis of Prostate Specific Antigen Free Survival Outcomes for Patientswith Low, Intermediate and High Risk Prostate Cancer Treated By Radical Therapy.Results of the Prostate Cancer Results Study Group.Grimm, Sylvester et al IJROBP 2009. Updated BJU Int 2012;109(sup1):22-29LOW RISK RESULTS% PSA Progression FreeTreatment Success100EBRT43023252237901933329 4331243814 2113 83918401 422735321028362 26Brachy512Robot RP798015Surgery7034 Years from Treatment 60EBRT & SeedsSeedsSurgeryEBRTCRYOHIFUProtonsHDR1112 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Prostate Cancer Results Study Group Numbers within symbols refer to references12/11/202016John Sylvester MD21st Century Oncology
Comparative Analysis of Prostate Specific Antigen Free Survival Outcomes for Patientswith Low, Intermediate and High Risk Prostate Cancer Treated By Radical Therapy.Results of the Prostate Cancer Results Study Group.Grimm, Sylvester et al IJROBP 2009 Updated BJU Int 2012;109(sup1):22-29INTERMEDIATE RISK RESULTS EBRT & SeedsBrachy% PSA Progression FreeTreatment Success10033149024 23 133516 436 45396 121819 579 262541110 1160EBRT40384234370 3415 4480Robot RP3732Hypo rachySeeds AloneSurgeryEBRTCRYOHIFUEBRT, Seeds ADT Years from Treatment 1Seeds ADTEBRT & Seeds789 10 11 12 13 14 15 Prostate Cancer Results Study Group Numbers within symbols refer to referencesProtons17John Sylvester MD21st Century Oncology
Comparative Analysis of Prostate Specific Antigen Free Survival Outcomes for Patients withLow, Intermediate and High Risk Prostate Cancer Treated By Radical Therapy.Results of the Prostate Cancer Results Study Group.Grimm, Sylvester et al IJROBP 2009 Updated BJU Int 2012;109(sup1):22-29HIGH RISK RESULTS EBRT, Seeds & ADT% PSA Progression FreeTreatment Success201619 1838 22451094108EBRT & ADT17349 41362510110644481EBRT & Seeds43 32210123747Hypo EBRT10442824533 2139EBRT117 6 26103354631Surgery30107102 15105 Years from Treatment ProtonsHDR23 29 Prostate Cancer Results Study Group Numbers within symbols refer to references12/11/2020Brachy49EBRT Seeds ADTRobot RPHiFUJohn Sylvester MD21st Century Oncology
ASCENDE-RT RCT TrialFor the Brachytherapy Blast Issue this month, Dr. Mira Keyes has graciouslywritten a summary of the ASCENDE-RT RCT trial, PI Dr. James Morris, thatwas presented both at the ASCO GU Symposium this year, as well as theApril ABS meeting in Orlando. This RCT is a "game changer" in themanagement of intermediate- and high-risk prostate patients. All GUoncologists should be very familiar with the study design and results. Inthis study of nearly 400 men, both groups received 12 months of ADT andpelvic RT to 46 Gy. They were than randomized to either an EBRT boost of32 Gy (total EBRT dose of 78 Gy) or an LDR-PB boost of 110 Gy. At over 6years of follow-up the PSA PFS curves dramatically diverge with a 50%reduction in the failure rates for those who received a LDR-PB boost. Theabsolute difference at 9 years for the intermediate-risk LDR-PB group was24%, and for the high-risk group 20% (P 0.001 - 0.05). The prevalence ofGU 3 toxicities were 8.6% vs 2.2% for LDR vs EBRT - primarily urethralstrictures in which 50% resolved with dilatation. These results arestaggering and practice changing. We thank the vision and leadership of Dr.Morris and the British Columbia Cancer Agency for conducting this sentinelwork. At the ABS, we predict this RCT, as well as the results of other criticalstudies, will solidify the importance of dose escalation with BT.Daniel Petereit, MD, FASTRODavid K. Gaffney, MD, PhD, FASTRO, FACR
ASCENDE-RT RCT Trial
Radical prostatectomy, external beam radiotherapy, or EBRT with Brachytherapy boostand disease progression and mortality in patients with Gleason score 9-10 cancerKishan et al JAMA march 6, 2018 .vol 319, N9 1,809 patients at 12 teriary medical centers 5-year Prostate cancer specific mortality:3% Brachy boost, 13% EBRT, 12% Surgery 5-Year metastatic disease:8% Brachy boost, 24% Surgery, 24% EBRT 7.5-year overall mortality:10% Brachy boost, 18% EBRT, 17% surgery Only 41% of EBRT patients received greater than 70Gy and 2years ADT
Acute Temporary Side Effects – IMRT (Beam) Obstructive Urinary Symptoms few weeks s/p tx--- Usually mild Retention (Catheter)--- much less than 1% of patients Increase BM frequency--- common Diarrhea--- Mainly if lymph nodes treated Fatigue--- usually mild
Brachytherapy (Seeds) Obstructive urinary symptoms –moderateCatheter 6-35% of patients ( 2-4 weeks)Alpha blockers usually for 3- 6 monthsPain with Urination 24-72 hoursTime off work 1-2 daysDiarrhea – very rareFatigue – usually mild if anyO.R. Procedure and anesthesia
Possible Late / Long Term Side Effects- Rectal: bleeding 1 yr s/p treatment.- More frequent BM’s, looser stools, moresensitivity to roughage in diet- Impotency: age and current function dependent- Reduced volume ejaculate- Bladder: Permanent frequency urgency- Radiation induced malignancies (rare)- Dysuria (burning sensation during urination)- Stricture (restricted flow)- Incontinence - rare
Later Possible Side EffectsIMRT (81Gy) (Beam)MSKCCSeedsMSKCCProtons(EuropeanUrology 60 (2011)Pp 908-916)(Zelefsky et al J Urol 2010 Dec)(Zelefsky et al J Urol 2010 Dec)Number Patients281448Grade 2 rectal1.4%5.1%HighesttoxicityGrade 3 Rectal0%1.1%HighesttoxicityGrade 4 rectal0%0%Grade 2 GU4.3%(Stricture- tx Flomax)15.6%Grade 3 GU1.4%2.2%
Late Gastrointestinal Toxicities FollowingRadiation Therapy for Prostate CancerKim et al European Urology 60 (2011) 908-816Proton Beam therapy hashigher gastrointestinalToxicity any otherradiation optionJohn Sylvester M.D. 21st Century Oncology-Lakewood Ranch Oncology Center
John Sylvester M.D. 21st Century Oncology-Lakewood Ranch Oncology Center
HRQOL: UCLA-PCIProstatectomy vs brachytherapy vs EBRT (not IMRT)Measured QOL 2.5 years post treatmentHigher the bar better the function* poor functioningUsed 3dCrt , (Modern IMRT has less side eds /- EBRTEBRTOld form of EBRTControlscontrols6040*200UrinaryFunction BowelBowelFunction SexualFunctionUrinarySexual(Surgery & Seed patients are younger than ebrt pts)*-Statistical SignificanceDavis JW, et al. J Urol. 2001;166:947-952.
At 5 Years, Brachytherapy Shows Quality-of-life Advantages over RadicalProstatectomy for Favorable-risk Prostate CancerCrook et al JCO;September 1, 2011, Volume 2, Issue 13P 0.05 significant********
New Radiation Therapy Innovations Stranded Seeds:- prevents seed migration Cs-131 Seedshorter 1/2life- maybe shorter duration sideeffect? Rectal Balloon- reduces rectal side effects and prostatemotion·CT/MRI Fusion planning– reduces side effectsJohn Sylvester M.D. 21st Century Oncology-Lakewood Ranch Oncology Center
HRQOL: UCLA-PCI Prostatectomy vs brachytherapy vs EBRT (not IMRT) Measured QOL 2.5 years post treatment Higher the bar better the function * poor functioning Davis JW, et al. J Urol. 2001;166:947-952. * * * *-Statistical Significance (Surgery & Seed patients are younger than ebrt pts) Used 3dCrt , (Modern IMRT has less side effects) Urinary .











