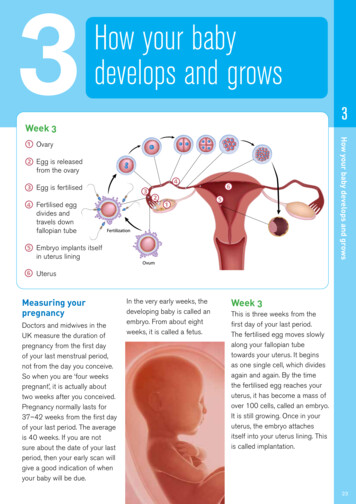
Transcription
ISUOG Basic TrainingUmbilical and Uterine Artery Doppler StudiesJuriy WladimiroffBasictrainingEditabletext here
Learning objectivesAt the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to perform, assess and report an umbilical arteryDoppler examination correctly describe how to perform, assess and report a Doppler examinationof the uterine arteries correctlyBasictrainingEditabletext here
Key questions1. What technique is required to perform a clinically useful Dopplerexamination of the umbilical artery ?2. What are the main pitfalls to be aware of when using Doppler tosample the umbilical artery?3. What technique is required to perform a clinically useful Dopplerexamination of both uterine arteries?4. What are the main pitfalls to be aware of when using Doppler tosample the uterine arteries?BasictrainingEditabletext here
umbilical and uterine DopplerBasictrainingEditabletext here
Bhide A, Acharya G, Bilardo CM, Brezinka C, Cafici D, Hernandez- Andrade E, Kalache K, Kingdom J, Kiserud T,Lee W, Lees C, Leung KY, Malinger G, Mari G, Prefumo F, Sepulveda W and Trudinger B. on behalf of the ISUOGClinical Standards CommitteeBasictrainingEditabletext here
Some general rules before you start know your US equipment have some knowledge of fluid dynamics have some knowledge of hemodynamics have some knowledge of fetal physiology know what you want to measure know which indices to use know when and when not to use DopplerBasictrainingEditabletext here
Fetal circulation high heart ratelow blood pressurelow peripheral resistance (placenta)placental circulation constant(does not respond to vasoactive substances) with advancing gestation fetal BP andarteriolarplacental bed flow increase, peripheralresistance decreasesBasictrainingEditabletext here
Fetal and maternal vesselsFetal side umbilical artery middle cerebral artery ductus venosus umbilical veinBasictrainingEditabletext hereMaternal side uterine arteries
Indications for Doppler in pregnancyPlacentation trophoblast invasion of spiral arteriesFetal well-being hypoxaemiaanaemiachromosomal anomalies (1st trimester)heart anomalies (heart function)MC twinsplacental abruptionpost-term pregnanciesdiabetesBasictrainingEditabletext here
Umbilical artery DopplerBasictrainingEditabletext here
Umbilical artery Doppler1.2.visualise the cord, select a free loop, not too close to the fetal cord insertionor the placental insertionzoom up/magnify the area of cordBasictrainingEditabletext here
Umbilical artery Doppler3. switch on the colour Doppler modality (not compulsory)BasictrainingEditabletext here
Umbilical artery Doppler3a. optimize the colour flow mapping (CFM) scaleBasictrainingEditabletext here
Umbilical artery Doppler4. place the sample gate on the umbilical arteryBasictrainingEditabletext here
Umbilical artery Doppler5. start the pulsed Doppler functionBasictrainingEditabletext here
Umbilical artery DopplerLaurin 1987BasictrainingEditabletext here
2D/pulsed Doppler 2D image in freeze mode provides better Doppler signalsBasictrainingEditabletext here
Irregular umbilical artery flow velocitypattern due to fetal breathing movementsBasictrainingEditabletext here
Umbilical cord Doppler16 weeks24 weeks32 weeks40 weeksresistance in the placenta falls progressively with advancinggestationBasictrainingEditabletext here
Umbilical artery in pathologicalpregnancieshigh PIabsent end diastolic flowreversed end diastolic flowBasictrainingEditabletext here
Abnormal UA findingsElevated UA indexREDVBaschat AA, Gembruch U,UOG 2003; 21: 124-7BasictrainingEditabletext hereTrudinger BJ, Giles WB,Br J Obstet Gynaecol, 1996; 105: 487-9.70% of villous vesselsare underperfused
Variation in umbilical artery waveforms there is a significant difference in Doppler indices when measured at the fetalend, in a free cord loop or at the placental end of the umbilical cord for the sake of simplicity and consistency, measurements should be made in afree cord loop in multiple pregnancies, and/or when comparing repeated measurementslongitudinally, recordings from fixed sites (fetal end, placental end or intraabdominal portion) may be more reliable reference ranges used should be appropriate for the site of interrogationBasictrainingEditabletext here
When is umbilical arteryassessment indicated? reduced fetal growth velocity/fetal growth restriction (FGR) MC twins fetal hydrops EDF ( ve, absent or reversed) more sensitive than PIBasictrainingEditabletext here
Uterine artery DopplerBasictrainingEditabletext here
BasictrainingEditabletext here
Trophoblast invasionuterine arteryBasictrainingEditabletext here
BasictrainingEditabletext here
Uterine artery Doppler - technique trans-abdominally, the probe is placed longitudinally in the lower lateralquadrant of the abdomen, and angled medially colour flow mapping is useful to identify the uterine artery as it appears tocross the external iliac artery sample volume is placed 1 cm downstream from the crossover point if the uterine artery branches before the intersection of the external iliacartery, the sample volume should be placed on the main artery just beforethe bifurcationBasictrainingEditabletext here
Uterine artery measurementBasictrainingEditabletext here
Normal uterine artery waveformBasictrainingEditabletext here
Abnormal uterine artery waveformnote notch (arrow) implying increased resistance in the uterine arteryBasictrainingEditabletext here
Normal range uterine artery PIBasictrainingEditabletext here
Uterine artery screening at 22-24 wkslow risk for PE and IUGRBasictrainingEditabletext herehigh risk for PE and IUGR
Abnormal uterineartery waveformsafter 20-24 weeksBasictrainingEditabletext here
Uterine arteryBasictrainingEditabletext here
Clinical applicationsBasictrainingEditabletext here
BasictrainingEditabletext here
BasictrainingEditabletext here
When are uterine arterymeasurements indicated? suspicion of placental insufficiency / FGR FGR in previous pregnancy mothers with LES, factor V Leiden or other factors related to poorplacentationBasictrainingEditabletext here
Repeatability of transabdominal uterineartery measurementBasictrainingEditabletext herePapageorghiou et al UOG 2001
Increased impedance to flow in the uterine arteries in pregnancies attendingfor routine antenatal care identifies approximately 40% (L.R. 6) of those whosubsequently develop PE and approximately 20%(L.R. 3,5) of those whodevelop fetal growth restrictionBasictrainingEditabletext here
Pre-eclampsia screeningBasictrainingEditabletext hereCnossen JS et al 2008
Uteroplacental failure- sequential well being changesGrowth Cerebralblood flow (MCA)Moderate/severeRedistribution (MCA )Fetal size 5th centile(HC/AC)Abnormal venousblood flow (DV)Umbilical artery PI AFIBasictrainingEditabletext hereOligohydramnios
Take home messages Doppler investigations give insight into fetal and pregnancy pathophysiology Doppler is one of the major breakthroughs in Fetal Medicine Doppler can be used in all trimesters for different indications It can be used as a screening or a diagnostic tool, according to thecircumstances In the 2nd and 3rd trimesters it can indicate abnormal placentation, fetalhypoxemia, fetal anemia and impending heart failure Operators should use it skillfully and with knowledge of its potentials,limitations and dangersBasictrainingEditabletext here
Thank you for your attentionBasictrainingEditabletext here
Editable text hereBasic training there is a significant difference in Doppler indices when measured at the fetal end, in a free cord loop or at the placental end of the umbilical cord