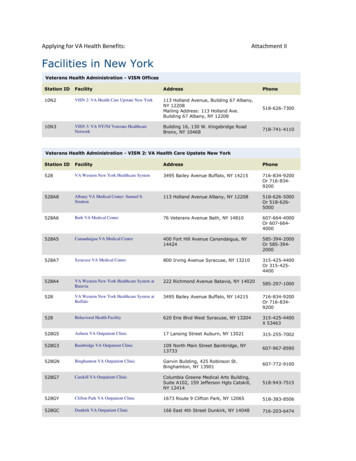
Transcription
Introduction to OptionsBy: Peter Findley and Sreesha VamanInvestment Analysis GroupWhat Is An Option? One contract is the right to buy or sell 100shares The price of the option depends on the priceof the underlying, plus a risk premium It is an option, it is not a binding contract Call Option: Right to buy a share Put Option: Right to sell a share Options traded the same as stocks1
What Makes Up An Option? The strike price is the price at which you can buyor sell shares Expiration date is the last day you can exercise anoption– Automatically executed on this day Underlying asset is the stock on which the optionis written Price of the option is how much investor pays forthe right to buy or sell (a.k.a. premium) Options can be either “American” or “European”– American-style options can be executed on any day– European-style options can be executed only on theexpiration dateWhat Is Contained In An Option?CALL Right to buy 100 shares Holder of option can buy sharesat the strike price Thus, seller of option MUST sellshares at strike price ifexercised Calls are in-the-money if thestrike price is below the stockprice Calls are out-of-the- money ifthe strike price is greater thanthe stock price Calls are at-the-money if thestrike price is equal to the stockpricePUT Right to sell 100 shares Holder of option can sell sharesat strike price Thus, seller of option MUST buyshares at strike price ifexercised Portfolio protection Puts are in-the-money if thestrike price is greater than thestock price Puts are out-of-the- money ifthe strike price is less than thestock price Puts are at-the-money if thestrike price is equal to the stockprice2
How Do I Find The Price Of An Option?Three components of the price of an option: Intrinsic Value: value of the option ifexercised now Volatility: premium for protection againstprice fluctuations in the underlying stock Time Value: value of buying option insteadof stock– Money saved on initial outlay can earn interestWhat Are The Payoffs For A Call?Payoff on OptionPayoff on OptionCKPrice of StockPrice of StockKCLONG CALLSHORT CALL Initially, buyer pays out price Initially, writer receives priceof Call (C)of Call (C) Value of long Call increasesas value of Stock increases Value of short Call decreasesas value of Stock increases3
What Are The Payoffs For A Put?Payoff on OptionPPayoff on OptionPPrice of StockKPrice of StockKLONG PUT Initially, buyer pays out priceof Put (P)SHORT PUT Initially, writer receivesprice of Put (P) Value of long Put decreasesas value of Stock increases Value of short Put increasesas value of Stock increasesHow Do I Use Options? Portfolio Insurance Speculation/Leverage Hedging (Which is actually a type of insurance!) Risk Control Targeted returns4
What Are Some Basic Calls Strategies?Bullish Call SpreadPayoff on OptionsBearish Call SpreadPayoff on OptionsK2Price of StockK1K1Price of StockK2 Buy Call at K 1 Write Call at K 1 Write Call at K 2 Buy Call at K 2 Lower Cost of Portfolio, but that Take advantage of bearishlimits upsidesentiment by selling a call Best if you think stock will rest Hedge your bearish opinion bybetween K 1 and K 2 at maturitylimiting downsideYOU Draw the Diagram: Put SpreadsBullish Put Spread isthe same as BullishCall Spread, using PutsPayoff on OptionsBearish Put Spread isthe same as BearishCall Spread, using PutsPayoff on OptionsPrice of StockK1K2Price of StockK1K25
YOU Draw the Diagram: Put SpreadsBuy Put at K 1, Sell Put at K2. Use to maximize putportfolio during bull marketPayoff on OptionsSell Put at K 1, Buy Put at K 2.Use to maximize put portfolioduring bear marketPayoff on OptionsPrice of StockK1Price of StockK1K2K2What Is A Straddle?Payoff on OptionsStraddleIf you think that the underlying asset isvolatile, but you don’t know whichdirection, you can hedge yourself bybuying both a Put and a Call at strikeK. You will make more money as thestock price moves away from K.KPrice of StockK1 K2StranglesThis is the same as a straddle, but withtwo different strike prices. This way,you can offset your costs by buying acheaper call option or a cheaper putoption, depending on how far apartyou want the options to be.6
How Else Can I Use A Straddle?StripsPayoff on OptionsIf you think that the price of theunderlying is going to increase, youcan buy two calls and, for protection,buy one put. This takes the view thatthe stock price will go up, but protectsyou if the stock price goes down.StockKStrapsIf you think that the price of theunderlying is going to decrease, youcan buy two puts and, for protection,buy one call. This takes the view thatthe stock price will go down, butprotects you if the stock price goes up.KWhat Is A Butterfly?Payoff on OptionsK1A Butterfly Spread is themost widely used optionscombination. With calls :– Long Call at K1– Short 2 Calls at K2– Long Call at K3K3K2StockFor puts, the butterflyspread is :– Long Put at K1– Short 2 Puts at K2– Long Put at K3Investors make money onthe premiums of the twocalls sold, plus a potentialpayoff on the underlyingstock price from the longpositions.7
YOU Decide: Why Are Options Useful?Risks of an option Unlimited downside risk when shorting(writing) options If they expire worthless, you lose 100%of your invested capital8
Any Questions?9
option, depending on how far apart you want the options to be. K 1 K 2. 7 How Else Can I Use A Straddle? Payoff on Options Stock Strips If you think that the price of the underlying is going to increase, you can buy two calls and, for protection, buy one put. This takes the view that the stock price will go up, but protects you if the stock price goes down. K Straps If you think that the price .