Transcription
1/23/2018Current Diabetes MedicationsRebecca Newberry APRN MSCDENursing Implications and ApplicationsMethodist Center for Diabetes and Nutritional HealthDisclosures Speakers Bureaus/Consulting Board Astrazeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Janssen, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, ValeritasObjectives Explain diabetes medications to patients Apply medication information to various clinicalsettings, including surgical setting Identify various technologies used in diabetesmanagementPhysiology and PathophysiologyBasic Diabetes education process/programUse appropriate languageBasis for understanding diabetes managementLifestyle - diet, activity, monitoringMedication – adherenceFollow up1
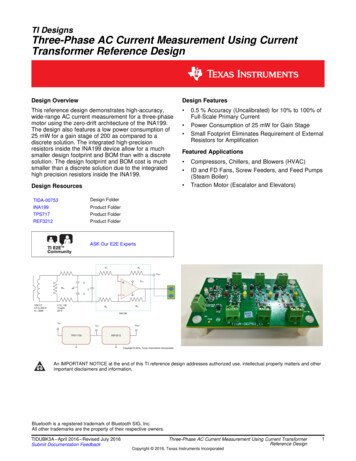
1/23/2018Treating PhysiologyMedication Choices Addressing the various pathologies of diabetes leadsto Combination Therapy Patient centered approach should be used to guide choiceof pharmaceutical agents Continue metformin when possibleDo not mix drugs of same class/similar actionWatch for side effectsBe aware of cost issuesFab Four – Metformin, Actos, GLP1, SGLT2 EfficacyHypoglycemia riskHistory of CV diseaseImpact on weightPotential side effectsRenal effectsDelivery methodCostPatient preferencesMetformin Action – Decreases hepatic glucose output Use – First line med at diagnosis, continue Benefits – No hypo or weight gain, approved forpeds, 10 yrs Cost – generic inexpensive. XR may be more Side effects – nausea, bloating, gas, diarrhea, B12deficiency with long term use To minimize GI effects, use XR, take with mealsSulfonylureas Action – Stimulates sustained insulin release frompancreas Use – After metformin Benefits – effective, available Cost - Low cost generic Side effects – hypoglycemia and weight gain Considerations – Must be taken with meal, timingvery important, QD or BIDMetformin Considerations Obtain GFR before starting If 30, do not use If 30-45, use half maximum dose, evaluate risk/benefit For Dye study Stop on day of study, restart in 48 hours if renal functionstable Risk for lactic acidosisMeglitinides Action – Stimulates rapid insulin release frompancreas Use – Before meals to affect post meal blood sugars Benefits – Short duration of action, less hypoglycemiathan long acting sfu Cost – generic/branded Side effects – hypoglycemia, weight gain2
1/23/2018Thiazolidinediones (TZD) Action- Increases insulin sensitivity Use – Black Box warning – may cause or worsen CHF.Monitor for edema and weight gain. Increased risk for peripheral fractures, bladder cancer Benefits- Only med to work at receptor site Cost – generic/low costGLP-1 Receptor Agonists Actions – Increases insulin release with food, slowsgastric emptying, promotes satiety, suppressesglucagon Use – Black box warning Thyroid C-cell tumor Second line choice Benefits – Decreased hypoglycemia, may help withweight loss, Victoza found to decrease risk of CVdeath, HA, strokeDPP-IV Inhibitors Actions- Prolongs action of gut hormones, increasesinsulin secretion, delays gastric emptying Uses – Second line after metformin. Benefits – No hypoglycemia or weight gain, few sideeffects Cost – Branded only Side effects – headache, flu-like symptomsTZDs Side effects – weight gain, edema Considerations – takes 3 months for full effect, longduration of action when stoppedGLP-1 Cost – Brand name only Side effects – nausea, vomiting, weight loss, injectionsite reactions. Report signs of acute pancreatitis:severe abdominal pain, vomiting. Stop med Considerations – Daily or weekly formulations. Maydecrease need for insulin, sulfonylureasDPP-IVs Considerations- may decrease dose if renal functiondecreased (not Tradjenta). Can cause joint pain,report signs of pancreatitis. Some may increase riskof heart failure.3
1/23/2018SGLT2 InhibitorsSGLT2s Action – Decrease glucose reabsorption in the kidney Uses – Second line, may be limitations to use if GFRdecreased Benefits – no hypoglycemia, may help with weightloss Cost – Branded only Side Effects – Genital mycotic infection, UTI,increased urination, hypotension, ketoacidosis Considerations – Decrease risk of death from CVdisease. Invokana may increase risk of amputation inhigh risk patients, don’t use Farxiga in patients withbladder cancer. Need to increase fluid intake.Practice good genital hygieneAlpha Glucosidase InhibitorsAmylin Analog- Symlin Action – Delays carbohydrate absorptionUse – Not commonly usedBenefits – Oral med, works with dietCost – GenericSide effects – GI upset, gas, abdominal crampingConsiderations – Start low dose. Caution withliver/kidney problems. Hypoglycemia riskSymlin Side Effects – nausea, weight loss Considerations – needs to be injected with insulinbefore meals Actions – Suppresses glucagon, slows gastricemptying, promotes satiety Use – Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, on insulin. Black boxwarning – severe hypoglycemic risk, decrease insulindose when starting Benefits – Decreases insulin requirments, may helpwith weight loss Cost – Branded onlyDopamine Receptor Agonist Action – Resets circadian rhythm, helping to decreaseinsulin resistance Use – Not first or second line Benefits – May decrease other medication doses Cost – Branded (Quick Release bromocriptine) Side Effects – Nausea, headache, fatigue,hypotension, dizziness4
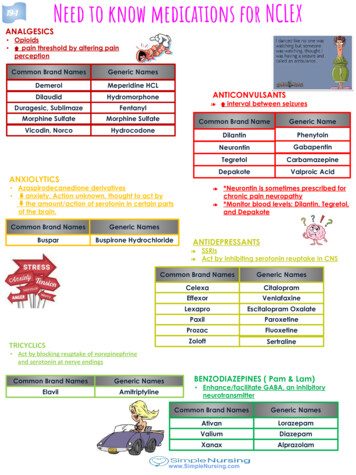
1/23/2018Cycloset Considerations – Take 6 tabs within 2 hour ofwakeningWelchol Considerations – Do not use if history of bowelobstruction, triglycerides over 500, or pancreatitis.Insulin Cost – Are “generics” and “biosimilars”, but still notinexpensive. Many new formulations are Brandname. Side effects – Hypoglycemia, weight gain Considerations – Education is vital for patients to useappropriately. Injection technique, timing of dosing,etc. Need to be aware of different formulations,onset of action, duration.Bile Acid Sequestrants Action – Decreases cholesterol and blood glucoseUse – Not first or second lineBenefits – Dual action, lowers LDL 15-30%Cost – Brand nameSide effects – GI issues, diarrhea. Can decreaseabsorption of certain meds, soluble vitaminsInsulin Action – Replaces insulin to take glucose into cell formetabolism Uses – All types of diabetes, used first or second line.Usually effective in bringing blood sugars down. Benefits – Works quickly, dosing can beindividualized, many choices of formulationsTechnology in Diabetes Management Meters for glucose testing Continuous Sensors Insulin Delivery Systems5
1/23/2018Technology in Diabetes Management Rapid evolution in recent yearsPatient drivenIssues related to security, safety, privacyClinicians need to be knowledgeableSystems set up to use newest technologyTechnology in Diabetes Management Continuous Glucose Sensors Measures intracellular fluid glucose levels, correlates toblood glucose Consists of sensor, transmitter, display Sensors changed every 7-10 days Dexcom, Medtronic Enlite, Freestyle FlashInsulin Delivery Systems V-Go – mechanical delivery device, takes the place ofinsulin injections. Device filled with insulin, changedevery 24 hours. Set basal dosing, not able to bechanged. Bolus dosing done per “clicks” on thedevice6
1/23/2018Insulin Delivery Systems Insulin Pumps Omni Pod – Tubeless, insulin delivered by pod attached tobody, controlled by separate PDM (Personal Data Manager). Tandem – uses tube, touchscreen display and adjustment.Updates done by computer. Medtronic 670-G system – Pump and Sensor are connected, can be usedin “Automatic mode” to deliver basal insulin automatically,based on blood sugar reading. Still need to bolus mealtimeinsulin.Use of Pump in Hospital Policies vary by institution Need to assure patient has ability to handle Continuous insulin dosing, using pump If possible, keep pump on patient May need to stop for safety Staff need to understand basic pump functions –basal rates, bolus ratios etc7
1/23/2018Peri-Operative Considerations Goals Reduce overall morbidity/mortalityAvoid severe hyper or hypo glycemiaMaintain electrolyte/fluid balancePrevent ketoacidosisPre Op Oral meds – stop day of surgery, resume wheneating/drinking normally Injectables – stop day of surgery, resume whenappropriate Basal (Long acting) insulin – Lantus, Levemir,Basaglar, Tresiba, Toujeo, NPHGuidelines Vary per institution Surgery Research and Practice 2015:284063 Guidelines for Perioperative Management of theDiabetic Patient Individualized based on medical history, glycemiccontrol, procedure plannedPre Op Bolus (rapid or mealtime) insulin – Novolog, Humalog,Apidra, Regular Stop day of surgery Use as correction (sliding scale) when BS tested Resume appropriate dose when eating normally Partial dose day before/day of surgery,Cancelling Surgery No evidence based guideline No surgery on patients in compromised metabolicstate (DKA) 400-500 mg/dl Variables – patient, procedure, surgeonIntra Op BG range 140-170 – lowest risk of adverse outcomes Monitor frequently IV insulin or Insulin infusion IV insulin active for 1 hour, serum half life of 7 minutes8
1/23/2018Post Op Variables affect glycemic control Physiologic stress, NPO status Diligent BG testingUse correction (sliding scale) based on BS resultsResume basal insulin asapResume orals/injectables as toleratedNursing Approach to Patient withDiabetesNursing Approach to Patient withDiabetes Non judgmental approach NOT a lifestyle disease – understand physiology Assess issues regarding management Barriers to non adherence Treat with compassion Educate Use resources NEVER give up on a patientReferences Educate yourself Diabetes field is rapidly changing Be open to new information Patient often great source of information Diabetes Resources ADA and ADA Pro Diabetes in Control Methodist Center for Diabetes and Nutritional Health 8111 Dodge Street, Suite 332 Standards Of Medical Care in Diabetes. Diabetes Care41:Supplement 1. American Diabetes Association,January 2018. “Guideline for Perioperative Management of theDiabetic Patient”. Sudhakaran, S, et al, SurgeryResearch and Practice 2015:294063, May 19, 2015.402-354-8797Questions?9
Nursing Implications and Applications Rebecca Newberry APRN MS CDE Methodist Center for Diabetes and Nutritional Health Speakers Bureaus/Consulting Board Astrazeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Janssen, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Valeritas Disclosures Explain diabetes medications to patients Apply medication information to various clinical settings, including surgical setting Identify various .