Transcription
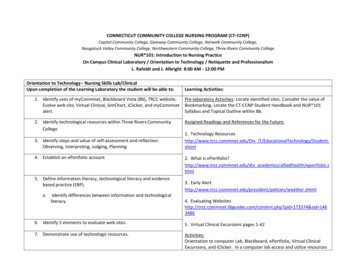
CONNECTICUT COMMUNITY COLLEGE NURSING PROGRAM (CT-CCNP)Capital Community College, Gateway Community College, Norwalk Community College,Naugatuck Valley Community College, Northwestern Community College, Three Rivers Community CollegeNUR*101: Introduction to Nursing PracticeOn Campus Clinical Laboratory / Orientation to Technology / Netiquette and ProfessionalismL. Rafeldt and J. Albright 8:00 AM - 12:00 PMOrientation to Technology-- Nursing Skills Lab/ClinicalUpon completion of the Learning Laboratory the student will be able to:Learning Activities:1. Identify uses of myCommnet, Blackboard Vista (Bb), TRCC website,Evolve web site, Virtual Clinical, SimChart, iClicker, and myCommnetalert.Pre-laboratory Activities: Locate identified sites. Consider the value ofBookmarking. Locate the CT-CCNP Student Handbook and NUR*101Syllabus and Topical Outline within Bb.2. Identify technological resources within Three Rivers CommunityCollegeAssigned Readings and References for the Future:3. Identify steps and value of self-assessment and reflection:Observing, Interpreting, Judging, Planning4. Establish an ePortfolio account5. Define information literacy, technological literacy and evidencebased practice (EBP).a.Identify differences between information and technologicalliteracy.1. Technology Resourceshttp://www.trcc.commnet.edu/Div IT/EducationalTechnology/Student.shtml2. What is ePortfolio?http://www.trcc.commnet.edu/div academics/alliedhealth/eportfolio.shtml3. Early s/weather.shtml4. Evaluating php?pid 173574&sid 14634866. Identify 5 elements to evaluate web sites.5. Virtual Clinical Excursions pages 1-427. Demonstrate use of technologic resources.Activities:Orientation to computer Lab, Blackboard, ePortfolio, Virtual ClinicalExcursions, and iClicker. In a computer lab access and utilize resources
within myCommnet, Blackboard, and set up an ePortfolio account.Assignment:Create your first N101 portfolio—include your definition of nursing,create a guest view, and submit an invitation to view the guest view ofyour first portfolio to lrafeldt@trcc.commnet.edu and a peer. Look forfeedback.
Welcome / Orientation
HOURS3 hoursLiliRafeldtUNIT OBJECTIVESUnit : Therapeutic andProfessional CommunicationIdentify the elements of effectivecommunicationIdentify the different forms ofcommunicationExplain the nursing focus in each ofthe four phases of communicationDescribe the importance of effectivecommunication in the delivery ofnursing careIdentify behaviors and techniquesthat impact client/nursecommunicationDemonstrate communicationtechniques for healthcareprofessionals that enhance andpromote client/nurse relationshipsand the delivery of holistic careDescribe effective communicationbetween healthcare professionalsIdentify nursing outcomes ofeffective and therapeuticcommunicationCONTENTA. Elements of effective communication1. Sender2. Receiver3. Message4. FeedbackAssigned Readings:A. Potter & Perry, Fundamentals ofNursing 8th edition, chapter 24B. Phases of Communication1. Pre-interactiona. Goalsb. Focus2. Introductorya. Goalsb. Focus3. Workinga. Goalsb. Focus4. Terminationa. Goalsb. FocusB. Perry & Potter, Clinical NursingSkills & Techniques 7th edition,pages 27-43C. Characteristics of verbal communication1. Pace and Intonation2. Simplicity3. Clarity and brevity4. Timing and relevance5. Adaptability6. Credibility7. HumorDiscuss the application of therapeuticcommunication techniques in eachphase of the nursing processD. Characteristics of nonverbal communication1. Reinforcement or contraction of verbalcommunication2. Personal Appearance3. Posture and Gait4. Facial Expression5. GesturesApply the nursing process to clientsE. Factors influencing CommunicationIdentify barriers to therapeuticcommunicationLEARNING ACTIVITIESC. Foundations of Psychiatric MentalHealth Nursing, A Clinical Approach6th edition, pages 174-194D. Nursing Diagnosis HandbookAckley, pages 229-237Review preparation power point priorto class.In class: Interpretation of picturestory—predicting outcomesDiscuss how communication haschanged in the 21st centuryDiscuss impact of language barriersand possible interventionsHIPAA principlesCase Study: Communication BarriersEVALUATIONExamNursing Skills t /ReflectionsClinical ProcessRecording
with specific barriers to effectivecommunication1.1.2.3.4.Nature of relationshipSocial vs. professionalLevel of trustPower differentialsIndividual factors: Clienta. Developmental/Lifespani. Age/Stageb. Socio-culturali. Languageii. Customsiii. Level of educationiv. Attitudes, beliefs, valuesc. Mood and emotional/mental stated. Personality Characteristicse. Physical health factorsf. Pain/Comfort5. Client perceptions6. Environmental factorsa. Noiseb. Privacyc. DistractionsF. Communication techniques that demonstrateand accomplish therapeutic communication:1. Active listening2. Acceptance3. Respect4. Clarification5. Support and Comfort6. Delivery of information7. Diversion8. Assistance with problem solving9. AssertivenessG. Barriers to effective communication1. Specific client communication problemsa. Aphasiai. Expressiveii. Receptiveb. Language Differencedc. Alterations in mental statusi. ConfusionReflective practiceCase Studies/Use of ProcessRecording FormDevelop a Process Recording of anurse/client interactionUse of SBAR, preconferencepreparation sheetiClicker questionsAfter classReview Process Recording andcontent of unit. Utilizing principle ofreviewing within 24 hours to increaserecall, application and learningAre you using a system oforganization to retrieve content foreasier application of learning in thefuture? Help is available in thenursing lab and through faculty too!
ii. UnresponsivenessH. Communication as part of the phases of thenursing process1. Assessment2. Analysis/Diagnosis3. Planning4. Implementation5. EvaluationI. Desired outcomes for communication betweennurse and client/families1. Value of Process Recordings for growthin communication skillsJ. Process, Structure and Outcomes ofcommunication among health care providers1. SBARa. Situationb. Backgroundc. Assessmentd. Recommendation
CONNECTICUT COMMUNITY COLLEGE NURSING PROGRAM (CT-CCNP)Capital Community College, Gateway Community College, Norwalk Community College,Naugatuck Valley Community College, Three Rivers Community CollegeNUR*101: Introduction to Nursing PracticeOn Campus Clinical LaboratoryL. Rafeldt*Note to students: Assigned reading and videos to be completed prior to laboratory attendance.Practice with CT-CCNP Core Value of CommunicationUpon completion of the Learning Laboratory the student will be able to:1. Identify why core value of communication is important to nursingpractice.2. Discuss professional communication of the registered nurse.3. Identify value of self assessment and reflection: Observing,Interpreting, Judging, and Planning.4. Practice therapeutic communication.Learning Activities:Assigned Readings:Perry & Potter, Clinical Nursing Skills & Techniques 7th edition,pages 27-30Activities:Therapeutic Communication Activity / Process Recording
HOURS2 hoursNancyRymutUNIT OBJECTIVESUnit : Contemporary NursingPracticeDiscuss various definitions ofnursingCONTENTA. Caring: An Introduction to Nursing1. Definition of nursing2. Historical perspectivesExplain the use of critical thinkingrelated to the nursing process.B. Holism: Societal influences on nursingDiscuss historical leaders in nursingC. Professionalism: The Role of the NurseDiscuss educational preparation forprofessional nursingD. Safe and Competent Practice1. Nursing Education2. Nursing Practicea. Nurse Practice Actsb. Practice Settingsc. ANA Code of EthicsDiscuss the role that caring plays inbuilding a nurse client relationshipDiscuss contemporary roles of theregistered nurseDescribe the philosophy of thenursing program.Identify the core values of thenursing programLEARNING ACTIVITIESAssigned Readings:Potter & PerryChapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5Lewis Chapter 1Student HandbookA. Core ValuesB. Program PhilosophyFormulate definition of nursing andpost in Chap378.htmE. Critical Thinking: Trends in NursingF. Communication: Connecticut CommunityColleges Nursing Program (CT-CCNP)Philosophy and Core ATIONExam OneePortfolio
CONNECTICUT COMMUNITY COLLEGE NURSING PROGRAM (CT-CCNP)Capital Community College, Gateway Community College, Norwalk Community College,Naugatuck Valley Community College, Three Rivers Community CollegeNUR*101: Introduction to Nursing PracticeOn Campus Clinical Laboratory –L. Rafeldt with P. Williams*Note to students: Assigned reading and videos to be completed prior to laboratory attendance.Skills to support CT-CCNP Core Values and Evidence Based Practice of the 21st Century-- Nursing Skills Lab/ClinicalUpon completion of the Learning Laboratory the student will be able to:Learning Activities:1. Identify course content, core values, (Critical Thinking, Safe andCompetent Practice, Holism, Caring, Communication,Professionalism) and how they are connected to mathematicalabilities and information literacy skills.Assigned Readings:2. Discuss professional role of the registered nurse in evidence basedpractice.Finding Articleshttp://www.trcc.commnet.edu/Div IT/Library/databases/Library databases.shtml3. State the importance of organization and lifelong learning as theyrelate to professional nursing.4. Identify strategies to complete searches within CINAHL and Healthand Wellness Data Bases.5. Identify components of a PICO question.The Libraryhttp://www.trcc.commnet.edu/Div IT/Library/Library.shtmlThe Nursing Gatewayhttp://www.trcc.commnet.edu/Div o Tutorialshttp://www.trcc.commnet.edu/Div IT/Library/Resourceguides/videotutorials.shtmlPICO Questions and Levels of ucation/clinquest.html
6. Demonstrate use of technologic resources.Activities:Orientation to Nursing Library Gateway, use of CINAHL and Health andWellness Data Bases, and selected library resources.Practice / Assignments:Utilize resources within the Nursing Library Gateway. Review EvidenceBased Practice (EBP).Complete CINAHL and Health and Wellness Search related to nursingand the Politics of Food.Submit assignment as outlined on Blackboard via ePortfolio. (Create aportfolio, set up a guest view, and send an invitation tolrafeldt@trcc.commnet.edu and pwilliams@trcc.commnet.edu look forfeedback.)
Clinical Orientation
HOURS2 hoursLiliRafeldtUNIT OBJECTIVESUnit: Holism, Caring and CulturalDiversity in NursingCONTENTLEARNING ACTIVITIESDiscuss the relationships betweenhealth, wellness, illness, and diseaseA. Health and holism1. Concepts of Health and well-being2. Models of health and wellnessa. Samplesb. Agent Host Modelc. Health—Illness Continuum3. Factors influencing healtha. Internal / External variablesb. Health Belief modelsc. Illness behaviors4. Holism and nursing practicea. Needs theory—Maslowb. Developmental theory—Ericksonc. Spiritualityd. Communitiese. Interdisciplinary team work5. National trends in health and illnessa. Healthy Peopleb. QSEN-Patient Centered Care6. The nurse’s role in health promotiona. Model healthy lifestyleb. Assess readiness for changec. Promote client involvement in goalsd. Teach self-care strategies toenhance fitness, nutrition,relationships, manage stresse. Reinforce positive behaviorsf. Advocate for changes to promote ahealthy environmentAssigned Readings:A. Potter & Perry, Fundamentals ofNursing 8th edition, chapters 7 and 9ExamB. Medical-Surgical Nursing,Assessment and Management ofClinical Problems 8th edition, byLewis, et.al. pages 20-36SimChart /ReflectionsB. Caring in nursing practice1. Theories on caringa. Benner-primacy of caring, nursing’scaring helps the client to cope aswell as connect the nurse withothers, receiving as well as givinghelpb. Leininger-caring as culturalHow will awareness of other’scultures and your caring behaviorsinfluence client care? How will youuse the LIKE and LEARN (Like,Inquire, Visit and Experience)(Listen, Evaluate, Acknowledge,Recommend, Negotiate) Models.Explain the concept of healthpromotionDiscuss the concept of holism as itrelates to nursing practiceDescribe the variables influencinghealth beliefs and health practicesDescribe health promotion for theindividual and the communityDiscuss the concept of caringDescribe client’s perceptions ofcaring behaviors in a nurseDescribe how nurses demonstratecaring behaviors in practiceDiscuss the nursing process andcritical thinking as they relate tocaringDiscuss demographic trends onhealth and nursingDiscuss health disparities as theyrelate to culture and ethnic diversityC. Review Healthy People 2020 andQSEN (Patient Centered Carewebsites)Prior to class review power points.In class presentation: stories, casestudy / simulation, iClickerquestions.After class reflect on your classroom,lab and clinical experiences.How will you care for yourself?EVALUATIONClinicalperformanceevaluation
competencec. Watson-nursing is an interpersonal,humanistic process helping thepatient strive for the greatest healthpotentiald. Full Spectrum Caring-selfknowledge and ethical knowledge2. Caring behaviorsa. Aware of your values, beliefs andbiases-maintain non-judgmentalattitude and actionsb. Respect human dignityc. Show empathy-routinely useopportunities for conversation tocommunicate genuine interest inwho the patient is, what they areexperiencing and providemeaningful nursing assistanced. Be cultural sensitive and becomecompetente. Understand you obligations: senseof right and wrongf. Advocate for clients3. Caring for selfa. Components of self esteem-real selfand ideal self congruenceb. Self Care Behaviors4. Reflection and critical thinking as theyrelate to caring for self as a developinghealth professional as well as caring forvulnerable populationsC. Cultural Diversity1. Demographics and culture2. Cultural health beliefs and practicesa. Time orientation / personal spaceb. Family and social organizationc. Births / death / other life eventsd. Foodse. Painf. Magico-religious health beliefsg. Scientific / biomedical health beliefAlso reflect on the one singleintervention you could use topromote cultural competence if youare busy-ask the question: “Whatmatters most to them in their illnessand treatment?”
h. Holistic health belief and use of thehealth care system3. Components of a cultural assessmenta. how the person identifies himselfand communicates with othersb. language preferences and toolsc. the degree of acculturationd. role of religione. support systems and primarydecision makerf. relationship with health careg. individuals explanation of illnessh. Use of Purnell wheel of culture4. Culturally competent nursinginterventionsa. Conveying cultural sensitivityb. Preservation and maintenancec. Accommodation and negotiation5. Examples of culture assessments,plans, interventions and evaluations inhealth care
CONNECTICUT COMMUNITY COLLEGE NURSING PROGRAM (CT-CCNP)Capital Community College, Gateway Community College, Norwalk Community College,Naugatuck Valley Community College, Three Rivers Community CollegeNUR*101: Introduction to Nursing PracticeOn Campus Clinical Laboratory –L. Rafeldt with B. Kennedy*Note to students: Assigned reading and videos to be completed prior to laboratory attendance.Skills to support CT-CCNP Core Values and Evidence Based Practice of the 21st Century-- Nursing Skills Lab/ClinicalUpon completion of the Learning Laboratory the student will be able to:Learning Activities:1. Identify readiness for Math Exam, resources for success andindividual preparation plan.Assigned Readings:Review Med. Math Preparation and Practice Test Handout, SelfEvaluation in Pickar and Abernethy, Dosage and CalculationsActivities:Math Tips for Success and Strategies to Decrease Math TestingAnxiety—presented by Professor Brian KennedyPractice and Preparation for N101 Math Exam:Complete 5 problems from Pickar and Sample tests in 15 minutes eachday.
HOURS3 hoursJudyAlbrightUNIT OBJECTIVESUnit : Health Protection andSafetyUtilize the chain of infection todiscuss client risk factorsDescribe assessment data withinflammatory response vs. infectiousresponseDiscuss interventions to prevent thetransmission of pathogensCompare medical and surgicalasepsisDemonstrate use of personalprotective equipment in contact,droplet, and airborne isolationDiscuss rationale for standardprecautionsDemonstrate correct technique forhand hygieneDemonstrate correct application andremoval of clean glovesIdentify the role of the Center forDisease Control in infectionmanagement and environmentalsafetyDiscuss the nurse’s role in earlyidentification of data that mightsuggest epidemic or bioterrorismactivityDiscuss risks to safety based ondevelopmental stage, lifestyle, andpathophysiologyDiscuss interventions to reducephysical hazards in the health care,home, and community environmentsCONTENTA. Infection1. Normal body defenses2. Risk factors for infection3. Chain of infection4. Immunitya. Activeb. passive5. Use of the Nursing Process in infectioncontrolB. Safety1. Factors that affect safetya. developmental / cultureb. individual / pathophysiologyc. environmental2. Public safety and bioterrorisma. chemicalb. biologicalc. nuclear3. Promoting safety in health carea. JCAHO 2010 National Patientsafety goals and sentinel eventsb. QSEN (Quality & Safety Ed forNurses)4. Nursing Process and safetya. Assessment: risk assessment toolsb. Diagnosing: risk for injury, risk forpoisoning, deficient knowledge(accident prevention)c. planning and implementation: callbells, falls, burns, fire safety,reduction of electrical hazards, bed,chair monitoring devices andrestraintsd. evaluation: in clinical settings andthe homeLEARNING ACTIVITIESAssigned Readings:Potter & Perry Text: Chapter 28“Infection Prevention and Control”(stop at Surgical Asepsis) andChapter 27 “Patient Safety”Use the Center of Disease Controlwebsite to access guidelines forinfection control. (See NursingLibrary Gateway or ppt)Complete the CT HospitalAssociation client orientation packetand posttest (CHA Test within Blackboard Vista)Review the QSEN link about prelicensure knowledge, skills andvalues of safe nursing practice.http://www.qsen.org/ksas prelicensure.php#safetyReview JCAHO 2012 NationalPatient Safety Goals for hospitals andlong term care.http://www.jointcommission.org/standards information/npsgs.aspxReview sentinel event link.http://www.jointcommission.org/sentinel event.aspxReview National Patient SafetyGoals on Prevention of InfectionEVALUATIONExamNursing Skills t /Reflections
CONNECTICUT COMMUNITY COLLEGE NURSING PROGRAM (CT-CCNP)Capital Community College, Gateway Community College, Norwalk Community College,Naugatuck Valley Community College, Three Rivers Community CollegeNUR*101: Introduction to Nursing PracticeOn Campus Clinical LaboratoryJudy Albright*Note to students: Assigned reading and videos to be completed prior to laboratory attendance.Medical Asepsis and Precautions1. Demonstrate principles of basic medical asepsis:a. Hand washing with water and Hand hygiene with waterlessantiseptic agentsb. Donning and removing clean gloves.2. Identify clinical settings where basic medical asepsis would beapplied.3. Discuss the importance of standard and transmission basedprecautions.4.Identify clinical situations when personal protective equipment(PPE) is used:a. Glovesb. Masksc.Eye Protectiond. Gownse. Exposure5. Demonstrate competence related to OSHA standardsAssigned Pre-laboratory Readings:Perry & Potter Skills: Chapter 7 “Medical Asepsis” and Chapter13 “Safety”Assigned Pre-laboratory Activities:Skills videos: Under Basic Skills Videos, “Basic InfectionControl” all videos.Lab Activities:View video clip from CDC.Utilize “Glo-Germs” and a black light to validate students’ handhygiene / washing techniques.Students rotate between client stations requiring identificationof PPEs to be used and demonstration of use for clients with:MRSA, C-diff, VREM, Chicken Pox, other.
HOURS2 hoursLiliRafeldtUNIT OBJECTIVESUnit: Critical Thinking and theNursing ProcessDiscuss the use of critical thinking inclinical practiceDescribe the relationship of criticalthinking and problem solving to thenursing processDescribe the components of thenursing processIdentify the components of theassessment phase of the nursingprocessDifferentiate between subjective andobjective dataDescribe methods of data collectionIdentify Erik Erickson’s stages ofdevelopment as an approach to thepsychosocial assessment of clientsDescribe the purposes of physicalassessmentIdentify techniques used for physicalassessmentIdentify expected outcomes ofphysical assessmentDiscuss variations in techniques andfindings of physical assessmentbased on ageCompare frameworks for dataorganizationCONTENTA. Critical thinking1. Problem-solving2. Decision-making3. Clinical reasoning4. Skills and Attitudes5. Nursing process overviewB. Assessment1. Data collection—initial, ongoing,comprehensive, focused, special needs(safety, nutritional, pain, functionalability—ADL and IADL, cultural,spiritual health, psychosocial, wellness,family and community)2. Communication—directive interviewing,closed ended questions, open endedquestions3. Types of data—observation, senses,health history, physical assessment,consults and health record data4. Sources of data—patient, significantothers, care givers, health providers andrecords5. Methods of data l, chiefcomplaint or reason for seeking healthcare, history of present illness, client’sperception of health status andexpectations for care, past health history,family and social health history,medication—herb—device use, review ofbody systems and associated functionalabilities)6. Validation of data—congruence ofsubjective and objective data, outside ofthe normal ranges7. Organization of data—nursing and nonnursing modelsLEARNING ACTIVITIESAssigned Readings:Fundamentals of Nursing 8th edition,1.Critical Thinking in NursingPractice, chapter 15EVALUATIONExamNursing Skills LabperformanceClinicalperformanceevaluation2. Nursing Assessment, chapter 16SimChart /Reflections3. Nursing Diagnosis, chapter 174. Planning Nursing Care, chapter 185. Implementing Nursing Care,chapter 196. Evaluation, chapter 2Ackley, p. 2-123 and 906-908Review power point prior to class.Activities:Content presentationVideo clips of critical thinking andnursing process
8. Confidentiality / HIPAADiscuss the process of data analysisand selection of a nursing diagnosisIdentify the components of adiagnostic statementList advantages and disadvantages ofa taxonomy of nursing diagnosesDescribe the use of definingcharacteristics and etiology inindividualizing a nursing diagnosisDifferentiate between a nursingdiagnosis and a medical diagnosisIdentify the activities that take placein the planning phase of the nursingprocessDiscuss the process of priority settingDescribe the guidelines for writinggoalsDiscuss the process of selectingnursing interventionsCompare a concept map to a nursingcare planDiscuss the skills necessary inimplementing nursing interventionsDescribe the evaluation phase of thenursing processC. Diagnosis—Reasoning process to identifyclient problems and strengths1. Analysis of data—nursing diagnoses,medical diagnoses and collaborativeproblems2. Use of defining characteristics torecognize diagnoses; nursing—humanresponse to disease, injury or stressor,medical—disease, illness or injury,collaborative problem—certain diseases,diagnostic tests or treatments that nursesmonitor to detect onset or change in statuswhich require physician who thenprescribes primary interventions3. Types of nursing diagnosis—actual, riskfor, possible, syndrome, wellness4. Diagnostic Reasoning—identifysignificant data, cluster cues, identifygaps or inconsistencies, drawconclusions, identify problem etiologies,verify problems with the patient5. NANDA nursing diagnosis—formatting6. Three-part diagnostic statement for actualdiagnoses7. Two-part diagnostic statement for risk fordiagnoses8. Collaborative Problemsa. InfectionCase studyJeopardyiClicker questions which:Demonstrate Critical thinking usingexamples of:1. Evidence Based Practicethrough Nursing Process2. Holistic Nursing View withFunctional Health PatternFramework as a Sample3. Holistic Nursing View witha Framework through aSystems’ Review4. Clinical Reasoning Rubric5. Application of Erickson(Developmental theorist)Use classroom examples to identifysubjective vs. objective data.Use classroom examples to identifycorrectly written goals.Identify independent, dependent andinterdependent nursing interventions.Develop nursing care plan. Comparelinear format with a concept map.Practice with SimChart concept map.D. Planning1. Types of care plansa. Collaborative care plans/CriticalPathwaysb. Standardized care plansc. Individualized care plansd. Special discharge or teaching planse. Student care plansf. Mind-mapping care plansg. Electronic health record generated2. Priority setting—safety first, Maslow,Compare school framework for datacollection and nursing care planswith clinical setting forms.
3.4.5.6.7.8.problem urgency, future consequences,patient preferenceWriting over all goals and expectedoutcome statementsa. Short-term vs. long-term outcomesb. Initial and ongoing planningc. Discharge planning begins atassessment—with collaborationd. NOC—Nursing OutcomeClassificationsTypes of nursing interventions—independent, dependent andcollaborative, observation, prevention,treatment and health promotion, NIC—Nursing Intervention ClassificationsConnection between diagnostic etiology,desired outcome, individual clientpreferences, available resources andchoice of interventionEvidence based practice—clinicalpractice guidelines and degree ofevidence (strongest—meta-analysis ofrandomized clinical trails, weakest—expert opinion)Working with the client—for successIndividualizing client interventions—forsuccess in meeting the desired outcomesE. Implementation1. Critical thinking and skills needed forimplementation2. Safe and Competent Practice—firstpriority3. Compliance with principles of HIPAA4. Overlaps with all phases of the nursingprocess5. Check and reinforce your knowledge andabilities6. Organize your work—with realistic goalsand outcomes, prepare supplies andequipment, establish feedback points7. Cultural sensitivity—check your
assumptions—be nonjudgmental butrealize that some client attitudes may notchange. Know the client’s main concerns8. Individualized client care—assess theclient’s readiness, explain what you willdo and what the client will feel9. Remember to provide privacy10. Talk openly and regularly about the goalsand outcomes11. Documentation12. Future behaviors and skills that you aredeveloping in school—doing,coordination, collaboration, delegating(right task, right circumstance, rightperson, right communication, rightsupervision), recordingF. Evaluation1. Collecting data—the client is the nurse’sfirst priority2. Comparing data with expected cognitive,affective, psychomotor and changes inbody systems and function goals andoutcomes3. Identifying if goal and outcomes are met,not met or partially met4. Reflection and revision of care if clientgoal and outcomes are not met5. Evaluating collaborative problems—andcontinuing to monitor6. There is a difference between outcomeand process evaluation7. Evaluating the quality of nursing carea. Quality Assurance (QA)b. Quality Improvement (QI)c. Nursing audit8. Documentation and reporting9. Reflecting on use of the nursingprocess
CONNECTICUT COMMUNITY COLLEGE NURSING PROGRAM (CT-CCNP)Capital Community College, Gateway Community College, Norwalk Community College,Naugatuck Valley Community College, Three Rivers Community CollegeNUR*101: Introduction to Nursing PracticeOn Campus Clinical LaboratoryLili Rafeldt*Note to students: Assigned reading and videos to be completed prior to laboratory attendance.Application of Nursing Process through the Electronic Medical Record / SimChartUpon completion of the Learning Laboratory the student will be able to:1. Discuss the use of critical thinking in clinical practice.2. Describe the components of the nursing process.3. Review assigned case study to collect data needed to completeElectronic Medical Record (EMR): Nursing Assessment.4. Use assigned case study to collect data needed to complete EMR:Laboratory and Diagnostic Studies, Medication Therapy,Pathophysiology Map.5. Use appropriate references/resources to complete lab rationalesfor abnormal values, medication information, and pathophysiologymap in EMR form.6. Complete EMR: data analysis page and compare to a mind map.7. Complete CLEW: nursing care plan page with a nursing diagnosisand a collaborative problem.8. Verbalize understanding of how to complete SimChart: reflection onthe clinical learning experience page.Learning Activities:Assigned Readings:Nursing diagnosis Handbook, An Evidence-Based Guide toPlanning Care 9th edition, pages 1-12, 119-124, 548-555 (Bringto lab.)In each of the clinical groups divide which student will bringone of the N101 texts to lab for group useCase study assignment from NP theory class – students tocomplete nursing assessment in preparation for labFaculty instruction and small group discussion to completeSimChart (an electronic medical record)Group Presentations-as assigned related to use of nursingprocess when developing SimChartAfter Class Assignment:Complete SimChart and Nursing Care Plan from Assigned CaseStudy.Simulation experience/VCE Lesson 2 & 3--Chapter 15/16 CriticalThinking in Nursing Process, Chapter 16-20 Planning andApplication of the Nur
Capital Community College, Gateway Community College, Norwalk Community College, Naugatuck Valley Community College, Northwestern Community College, Three Rivers Community College NUR*101: Introduction to Nursing Practice On Campus Clinical Laboratory / Orientation to Technology / Netiquette and Professionalism L. Rafeldt and J. Albright 8:00 .










