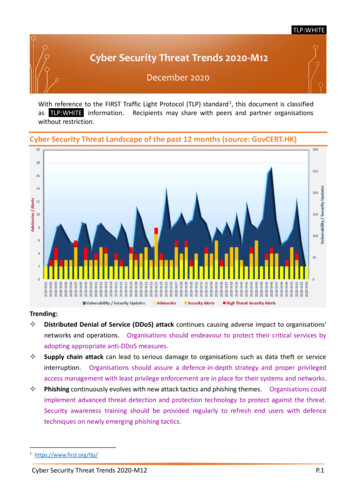
Transcription
Draft syllabus of Cyber Security Course for Undergraduate and Post-Graduation alongwith Credit schemeIntroductionThe evolution of Information Communication Technology (ICT) and growing securityconcerns demands flexible and generally comprehensive approach to the issue of CyberSecurity. The rapid growth of ICT has raised various complex questions which need to beaddressed. A need has been felt to address Cyber Security broadly but in sufficient depth sothat even students from non-technical streams will develop a more complete picture of theCyber Security issues. The syllabus has been prepared with an aim to create more aware,responsive and responsible digital citizens, thereby contributing effectively to overall healthyCyber Security posture and ecosystem. This course attempts to make the students familiarwith Indian cyber eco-system to understand international developments in the area of cybersecurity.Terms of Reference2.Terms of Reference (TOR) for drafting the proposed syllabus.(a) Cyber Security as a subject need to be incorporated at Graduation and Post-Graduationlevel in all the streams.(b) A separate syllabus for Graduation and Post-Graduation program to be prepared.(c) The syllabus should incorporate all the essential elements of Cyber Security so thestudents at the Graduation and Post-Graduation level understand the essence and conceptof Cyber Security as a whole.(d) The syllabus of Cyber Security at Graduation level to be pitched at basic and mid-levelwhile the syllabus at Post Graduation level should cover mid and advanced level concept,duly considering the fact that Post Graduation students would have exposure to the basicconcepts of Cyber Security in the preceding degree.(e) The syllabus should have sufficient depth so that even students from the non-technicalstreams can develop a complete picture of the Cyber Security.Essentials Components of Cyber Security3.People, Process and Technology are the important pillars of the Cyber Security, as tohow, effectively the aspects related to these components fit into the curriculum considering thecyber threat landscape forms part of the content structuring and syllabus formation. With thisbackdrop, the following aspects, as tabulated below, have been taken into consideration in thesyllabus formation: -Page 1 of 10
Sl. )(q)ContentEssential components of Cyber SecurityCyber Security threat landscapeCybercrime and its typesRemedial and mitigation measuresReporting of CybercrimeCyber LawData privacy and securityE-Commerce, Digital payments and its securityOverview of Social media and its securityCyber Security of digital devicesTools and technology for Cyber SecurityCyber Security plan and crisis managementSecurity controlsRisk based assessment, audit and complianceCyber Security best practices and do’s and don’tsPlatforms to report and combat cybercrimePractical hands-onLevelBasicBasicBasic – AdvancedAdvancedAdvancedMediumBasicBasic-Medium andAdvancedProgram Educational Objectives (PEOs)4.The exposure of the students to cyber Security program at Graduate and Post Graduatelevel should lead to the following: (a)Learn the foundations of Cyber Security and threat landscape.(b)To equip students with the technical knowledge and skills needed to protect anddefend against cyber threats.(c)To develop skills in students that can help them plan, implement, and monitorcyber security mechanisms to ensure the protection of information technology assets.(d)To expose students to governance, regulatory, legal, economic, environmental,social and ethical contexts of Cyber Security.(e)To expose students to responsible use of online Social media network.(f)To systematically educate the necessity to understand the impact of cybercrimesand threats with solutions in a global and societal context.(g)To select suitable ethical principles and commit to professional responsibilitiesand human values and contribute value and wealth for the benefit of the society.Program Specific Outcomes (PSOs)Page 2 of 10
5.Upon completion of the degree program, students will be able to:a. Understand the Cyber Security threat landscape.b. Develop a deeper understanding and familiarity with various types ofcyberattacks, cybercrimes, vulnerabilities and remedies thereto.c. Analyse and evaluate existing legal framework and laws on Cyber Security.d. Analyse and evaluate the digital payment system security and remedialmeasures against digital payment frauds.e. Analyse and evaluate the importance of personal data its privacy and security.f. Analyse and evaluate the security aspects of social media platform and ethicalaspects associated with use of social media.g. Analyse and evaluate the cyber security risks.h. Based on the Risk assessment, plan suitable security controls and audit andcompliance.i. Evaluate and communicate the human role in security systems with an emphasison ethics, social engineering vulnerabilities and training.j. Increase awareness about cyber-attack vectors and safety against cyber-frauds.k. Take measures for self-cyber-protection as well as societal cyber-protection.Syllabus for Undergraduate Program6.The proposed syllabus for Graduation level academic program is as under: -ModuleModule-IModule-IICyber Security Program at Graduation LevelModule NameModule ContentIntroduction toDefining Cyberspace andCyber SecurityOverview of Computer and Webtechnology, Architecture ofcyberspace, Communication andweb technology, Internet, Worldwide web, Advent of internet,Internet infrastructure for datatransfer and governance, Internetsociety,Regulationofcyberspace, Concept of CyberSecurity, Issues and challengesof Cyber Security.Cybercrime and Classification of cybercrimes,Cyber lawCommoncybercrimescybercrime targeting computers ,cybercrime against woman andchildren, financial frauds, socialengineering attacks, malware andransomware attacks, zero dayandzeroclickattacks.,Cybercriminals modus-operandi, Reporting of cybercrimes,RemedialandmitigationPage 3 of 10LearningOutcomesAfter completion ofthis module, studentswould be able tounderstandtheconcept of CyberSecurity and issuesandchallengesassociated with it.Students, at the endof this module,should be able tounderstand thecybercrimes, theirnature, legalremedies and as tohow report thecrimes throughavailable platformsand procedures.
PracticalModule-IIIPracticalModule IVmeasures, Legal perspective ofcybercrime, IT Act,2000 and itsamendments, Cybercrime andoffences, Organisations dealingwith Cybercrime and CyberSecurity in India, Case studies1.Checklist for reporting cybercrime at Cybercrime Police Station.2.Checklist for reporting cybercrime online.3.Reporting phishing emails.4.Demonstration of email phishing attack and preventive measures.SocialMedia Introduction to Social networks. On completion ofOverviewand Types of Social media, Social this module, studentsSecuritymedia platforms, Social media shouldappreciatemonitoring, Hashtag, Viral various privacy andcontent, Social media marketing, security concerns onSocialmediaprivacy, online Social mediaChallenges, opportunities and and understand thepitfalls in online social network, reporting procedureSecurity issues related to social ofinappropriatemedia, Flagging and reporting of content, underlyinginappropriate content, Laws legal aspects andregardingpostingof best practices for theinappropriate content, Best use of Social mediapractices for the use of Social platform.media, Case studies1.Facebook privacy security settings.2.Basic checklist, privacy and security settings for popular Socialmedia platforms.3.Reporting and redressal mechanism for violations and misuse ofSocial media platforms.E-Commerce and Electronic Commerce definition, After the completionDigital Payments Main componentsof E- of this module,Commerce, Elements of E- students would beCommercesecurity,E- able to understandCommerce threats, E-Commerce the basic conceptssecuritybestpractices, relatedtoEIntroduction to digital payments, CommerceandComponents of digital payment digitalpayments.and stake holders, Modes of They will becomedigitalpaymentsBanking familiar to variousCards,UnifiedPayment digitalpaymentInterface(UPI),e-Wallets, modes and relatedUnstructuredSupplementary CyberSecurityService Data (USSD), Aadhar aspects,RBIenabledpayments,Digital guidelinesandpayment related common frauds preventive measuresand preventive measures. RBI againstdigitalguidelines on digital payment payment frauds.and customer protection inPage 4 of 10
unauthorisedbankingtransactions.Relevent Configuring security settings in Mobile Wallets and UPIs.2.Checklist for secure net banking,Module V DigitalDevices End Point device and Mobile Students,afterSecurity,Tools phone security, Password policy, completion of thisand Technologies Security patch management, module will be ableforCyber Data backup, Downloading and to understand theSecuritymanagement of third party basicsecuritysoftware, Device security policy, aspects related toCyber Security best practices, ComputerandSignificance of host firewall and Mobiles. They willAnt-virus, Management of host be able to use basicfirewall and Anti-virus, Wi-Fi toolsandsecurity, Configuration of basic technologiestosecurity policy and permissions. protect their devices.Practical1.Setting, configuring and managing three password policy in thecomputer (BIOS, Administrator and Standard User).2.Setting and configuring two factor authentication in the Mobilephone.3.Security patch management and updates in Computer andMobiles.4.Managing Application permissions in Mobile phone.5.Installation and configuration of computer Anti-virus.6.Installation and configuration of Computer Host Firewall.7.WiFi security management in computer and mobile.References1.Cyber Crime Impact in the New Millennium, by Marine R. C,Auther Press.2.Cyber Security Understanding Cyber Crimes, ComputerForensics and Legal Perspectives by Sumit Belapure and NinaGodbole, Wiley India Pvt. Ltd.3.Security in the Digital Age: Social Media Security Threats andVulnerabilities by Henry A. Oliver, Create Space IndependentPublishing Platform.4.Electronic Commerce by Elias M. Awad, Prentice Hall of IndiaPvt Ltd.5.Cyber Laws: Intellectual Property & E-Commerce Security byKumar K, Dominant Publishers.6.Network Security Bible, Eric Cole, Ronald Krutz, James W.Conley, 2nd Edition, Wiley India Pvt. Ltd.7.Fundamentals of Network Security by E. Maiwald, McGraw Hill.Page 5 of 10
TEACHING SCHEMECyber Security Program at Undergraduate LevelTeaching SchemeSl. No1Course TitleCyber SecurityTotalCreditsL33T P Total- 14- 14Legend:L: LecturesT: TutorialsP: Practical/ProjectsC: CreditsNotes:1 C: 1 Hour for Lecture/Tutorial1 C: 2 Hour for Practical/ProjectsTerms of Reference for Credit Scheme ( 3 1) There are total of 90-96 working days (15 -16 Weeks) in a semester.1 Credit 15 Hours, therefore 3 Credits 45 hours (3*15 45)In a week, 3 lectures of theory, each period of one hour duration and 1 practicalsession of two hoursTeaching (3x15) 45 hoursPractical (2x15) 30 hoursTotal 75 hoursNOTE : As far as transaction of these courses at UG and PG level in HEIs is concerned,HEIs may invite /Cyber Security/ Computer/ IT qualified faculty or else Experts fromIndustry/ Subject Matter Experts to take the lectures , practical and tutorials . Theproposed syllabus gives broad guidelines and teachers who would teach the subject willhave enough flexibility to strike the balance between time vis-a-vis depth of coverage.Page 6 of 10
7.The proposed syllabus for Post-Graduation level program is as under: -ModuleModule-IModule-IIPracticalModule-IIICyber Security Program at Post Graduation LevelModule NameModule ContentsLearning OutcomeOverview ofCyber Security increasing threat StudentsafterCyber Securitylandscape,CyberSecurity completing this moduleterminologies- Cyberspace, attack, willbeabletoattack vector, attack surface, threat, understand the basicrisk,vulnerability,exploit, terminologies related toexploitation, hacker., Non-state actors, Cyber Security andCyber terrorism, Protection of end user current Cyber Securitymachine, Critical IT and National threat landscape. TheyCritical Infrastructure, Cyberwarfare, willalsodevelopCase studiesunderstanding about theCyberwarfareandnecessity to strengthenthe Cyber Security ofend user machine,critical IT and nationalcritical infrastructure.CybercrimesCybercrimes targeting Computer After completion of thesystems - data diddling attacks, module, students willspyware, logic bombs, DoS, DDoS, havecompleteAPTs, virus, Trojans, ransomware, data understanding of thebreach., Online scams and frauds- cyber-attacks that targetemail scams, Phishing, Vishing, computers, mobiles andSmishing, Online job fraud, Online persons. They will alsosextortion, Debit/credit card fraud, develop understandingOnline payment fraud, Cyberbullying, about the type andwebsite defacement, Cyber-squatting, nature of cybercrimesPharming,Cyberespionage, and as to how reportCryptojacking, Darknet- illegal trades, these crimes throughdrug trafficking, human trafficking., the prescribed legal andSocial Media Scams & Frauds- Government channels.impersonation, identity theft, jobscams, misinformation, fake news.,Cybercrime against persons- cybergrooming, child pornography, cyberstalking., Social Engineering attacks,Cyber Police stations, Crime reportingprocedure, Case studies1.Platforms for reporting cybercrimes.2.Checklist for reporting cybercrime online.Cyber LawCybercrime and legal landscape around Studentsafterthe world, IT Act,2000 and its completing this modulePage 7 of 10
amendments. Limitations of IT Act,2000. Cybercrime and punishments,Cyber Laws and Legal and ethicalaspects related to new technologiesAI/ML, IoT, Blockchain, Darknet andSocial media, Cyber Laws of othercountries, Case studiesModule IVPracticalData Privacyand DataSecurityDefining data,meta-data,big data,nonpersonal data.Data protection,Dataprivacy and data security, Personal dataprotection bill and its compliance, Dataprotection principles, Big data securityissues and challenges, Data protectionregulations of other countries- lInformation Protection and ElectronicDocuments Act (PIPEDA).,will understand thelegal framework thatexist in India forcybercrimesandpenaltiesandpunishments for suchcrimes, It will alsoexpose students tolimitations of existingIT Act,2000 legalframework that isfollowedinothercountries and legal andethical aspects relatedto new technologies.After completing thismodule, students willunderstand the aspectsrelated to personal dataprivacy and security.They will also getinsight into the DataProtectionBill,2019and data privacy andsecurity issues relatedtoSocialmediaplatforms.Social media- data privacy andsecurity issues.1. Setting privacy settings on social media platforms.2. Do’s and Don’ts for posting content on Social media platform.Module VPractical3. Registering compliant on a Social media platform.Cyber SecurityCyber Security Plan- Cyber SecurityManagement,policy, cyber crises management plan.,Compliance and Business continuity, Risk assessment,GovernanceTypes of security controls and theirgoals, Cyber Security audit andcompliance, National Cyber Securitypolicy and strategy.1.Studentsaftercompleting this modulewill understand themain components ofCyber Security plan.They will also getinsight into risk-basedassessment,requirementof security controls andneed for cyber securityaudit and compliance.Prepare password policy for computer and mobile device.Page 8 of 10
References2.List out security controls for computer and implement technical securitycontrols in the personal computer.3.List out security controls for mobile phone and implement technicalsecurity controls in the personal mobile phone.4.Log into computer system as administrator and check the securitypolicies in the system1.Cyber Security Understanding Cyber Crimes, Computer Forensics andLegal Perspectives by Sumit Belapure and Nina Godbole, Wiley India Pvt.Ltd.2.Information Warfare and Security by Dorothy F. Denning, AddisonWesley3.Security in the Digital Age: Social Media Security Threats andVulnerabilities by Henry A. Oliver, Create Space Independent PublishingPlatform.4.Data Privacy Principles and Practice by Natraj Venkataramanan andAshwin Shriram, CRC Press.5.Information Security Governance, Guidance for Information SecurityManagers by W. KragBrothy, 1st Edition, Wiley Publication.6.Auditing IT Infrastructures for Compliance By Martin Weiss, MichaelG. Solomon, 2nd Edition, Jones Bartlett Learning.Practical Work8. The practical list has been suggested for the applicable modules; however, the faculty mayexpand the list as per the syllabus content duly taking into consideration the emerging nature ofcyber threats and incumbent protective measures to guard against such threats.Page 9 of 10
TEACHING SCHEMECyber Security Program at Postgraduate LevelTeaching SchemeSl. No1Course TitleCyber SecurityTotalCreditsL33T P- 1- 1Total44Legend:L: LecturesT: TutorialsP: Practical/ProjectsC: CreditsNotes:1 C: 1 Hour for Lecture/Tutorial1 C: 2 Hour for Practical/ProjectsTerms of Reference for Credit Scheme ( 3 1) There are total of 90-96 working days (15 -16 Weeks) in a semester.1 Credit 15 Hours, therefore 3 Credits 45 hours (3*15 45)In a week, 3 lectures of theory, each period of one hour duration and 1 practical sessionof two hoursTeaching (3x15) 45 hoursPractical (2x15) 30 hoursTotal 75 hoursNOTE : As far as transaction of these courses at UG and PG level in HEIs is concerned,HEIs may invite /Cyber Security/ Computer/ IT qualified faculty or else Experts fromIndustry/ Subject Matter Experts to take the lectures , practical and tutorials . Theproposed syllabus gives broad guidelines and teachers who would teach the subject will haveenough flexibility to strike the balance between time vis-a-vis depth of coverage.Page 10 of 10
concepts of Cyber Security in the preceding degree. (e) The syllabus should have sufficient depth so that even students from the non-technical streams can develop a complete picture of the Cyber Security. Essentials Components of Cyber Security 3. People, Process and Technology are the important pillars of the Cyber Security, as to