Transcription
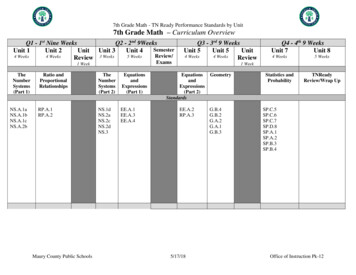
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by Unit7th Grade Math – Curriculum OverviewQ1 - 1st Nine WeeksQ2 - 2nd 9WeeksSemesterUnit 1Unit 2Unit Unit 3Unit 4Review/4 Weeks4 Weeks5 WeeksReview 3 WeeksExams1 WeekTheNumberSystems(Part 1)NS.A.1aNS.A.1bNS.A.1cNS.A.2bRatio andProportionalRelationshipsTheNumberSystems(Part 2)EquationsandExpressions(Part EE.A.4Maury County Public SchoolsQ3 - 3rd 9 WeeksUnit 5Unit 5Unit4 Weeks4 WeeksReviewQ4 - 4th 9 WeeksUnit 7Unit 84 Weeks5 WeeksStatistics andProbabilityTNReadyReview/Wrap Up1 WeekEquationsandExpressions(Part P.B.3SP.B.4Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by UnitUnit 1: Number Systems- Part 1#of Days- 15-20“I Can” StatementsStandardsNumber Systems7.NS.A.1 Apply and extend previous understandings of additionand subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; representaddition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number linediagram.7. NS.A.1a Describe situations in which opposite quantitiescombine to make 0.7. NS.A.1b Understand p q as the number located a distance q from p, in the positive or negative direction depending on whetherq is positive or negative. Show that a number and its opposite havea sum of 0 (are additive inverses). Interpret sums of rationalnumbers by describing real world contexts.7.NS.A.1c Understand subtraction of rational numbers as addingthe additive inverse, p – q p (–q). Show that the distancebetween two rational numbers on the number line is the absolutevalue of their difference, and apply this principle in real-worldcontexts.7. NS.A.2 Apply and extend previous understandings ofmultiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and dividerational numbers.7.NS.A.2.b Understand that integers can be divided, provided thatthe divisor is not zero, and every quotient of integers (with nonzero divisor) is a rational number. If p and q are integers then –(p/q) (–p)/q p/(–q). Interpret quotients of rational numbers bydescribing real-world contexts.Maury County Public SchoolsI can apply the rules of signed numbers to problems involvingdecimals and fractions.I can represent rational numbers on the number line.I can show that the distance between two integers on a number lineis the absolute value of their difference.I can use a number line or positive/negative chips to show that aninteger and its opposite will always have a sum of zero.I can use a number line to show addition as a specific distance from aparticular number in one direction or the other, depending on thesign of the value being added.I can describe real-world situations represented by the subtraction ofintegers.( i.e.- temperature, football yardage)I can apply the rules of signed numbers to multiplication and divisionproblems.I can use the relationship between multiplication and division todevelop procedures for dividing integers.I can justify that a number cannot be divided by zero.I can describe real-world situations represented by the division ofintegers.I can interpret the quotient in relation to the original problem.I can justify why the following is true: (1/2) 1/2 1/ 2.5/17/18Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by UnitSections/Topics - to be completed by individual teacher or during PDwith 7th grade math teachers. Pre-assessment Section 1 Topic Section 2 Topic Section 3 Topic Quiz Section 4 Topic Section 5 Topic Section 6 Topic Quiz Section 7 Topic Section 8 Topic Section 9 Topic Unit Review Unit TestAcademic Vocabulary:Maury County Public SchoolsActivities/Resources/MaterialsResources Found On 7th grade Dropbox Request to be added to Dropbox resources by emailingbhodge@mauryk12.orgIReady:Short Tasks (Found on www.mathshell.org) Supporting MCD Lessons- 6th Grade - Adding and Subtracting Directed Numbers (CD) - Finding Factors for Multiples (CD) -Interpreting Multiplication and Division (CD) -Translating Between FDP (CD) -Using Standard Algorithms for Number Opera-tions (CD)Math Shell: Taxi CabsExtra Resources TNCore Tasks Number System Tasks (Summer 2013Training Resources, tab 1, pages 14-19) Add/Subtract Rational Numbers Task Arc (7.NS.1) Holt Textbook 2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-11, 3-2, 3-7, 3-8 Online Textbook Eureka Math – Module 2, Lessons 1-9 Holt Textbook2-4, 2-5, 3-3, 3-4, 3-5, 3-9, 3-10, 3-11Online Textbook Eureka Math – Module 2, Lessons 10-16Engage NY: Lesson 4 Efficiently Adding Integers and Other Rational NumbersEngage NY: Lesson 7 Addition and Subtraction of Rational NumbersEngage NY: Lesson 8 Applying the Properties of Operations to Add and SubtractRational NumbersConnected Math: Accentuate the Negative 7.NS.1a-d Investigations 1, 2 & 4Engage NY: Lesson 11 Multiply Signed NumbersEngage NY: Lesson 12 Division of IntegersEngage NY: Lesson 13 Converting Between Fractions and Decimals Using EquivalentFractionsEngage NY: Lesson 14 Converting Rational Numbers to Decimals Using LongDivision 5/17/18Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by UnitUnit 2Ratio and Proportional Relationships – Part 1# of Days- 25“I Can” StatementsStandardsRatios and Proportions7.RP.A.1 - Compute unit rates associated with ratios of fractions,including ratios of lengths, areas, and other quantities measured inlike or different units. For example, if a person walks 1/2 mile ineach 1/4 hour, compute the unit rate as the complex fraction1/2/1/4 miles per hour, equivalently 2 miles per hour.I can compute a unit rate by repeating a given rate.I can compute a unit rate by multiplying or dividing both quantities by thesame factor.I can compute unit rates in several contexts.I can apply unit rates to real situations.I can convert units in real situations.7.RP.A.2a- Decide whether two quantities are in a proportionalrelationship (e.g., by testing for equivalent ratios in a table orgraphing on a coordinate plane and observing whether the graph isa straight line through the origin).7.RP.A.2b- Identify the constant of proportionality (unit rate) intables, graphs, equations, diagrams, and verbal descriptions ofproportional relationships.I can determine whether two quantities are proportional by examining therelationship given in a table, graph, diagram, or as a verbal description.(Focus on testing for proportionality using unit rates.)7.RP.A.2c- Represent proportional relationships by equations. Forexample, if total cost t is proportional to the number n of itemspurchased at a constant price p, the relationship between the totalcost and the number of items can be expressed as t pn.7.RP.A.2d- Explain what a point (x, y) on the graph of a proportionalrelationship means in terms of the situation, with special attentionto the points (0, 0) and (1, r) where r is the unit rate.I can write an equation that represents a direct proportional relationship.(Inverse is not taught at this time)Maury County Public SchoolsI can identify the unit rate (constant of proportionality also known as slope)given a proportional relationship in the form of a table, graph, diagram, orverbal description.I can use proportional relationships to solve real world problems involvingmultiple steps including problems dealing with tax, interest, discounts, markups, commission, tips, fees, and percent change.5/17/18Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by UnitSections/Topics- to be completed by individual teacher or during PD with7th grade math teachers Pre-assessment Section 1 Topic Section 2 Topic Section 3 Topic Quiz Section 4 Topic Section 5 Topic Section 6 Topic Quiz Section 7 Topic Section 8 Topic Section 9 Topic Unit Review Unit TestActivities/Resources/MaterialsResources Found On 7th Grade DropboxIReady:Short Tasks (Found on www.mathshell.org) MDC Lessons -Classifying Proportion and Non-Proportion Situations (CD) -Comparing Solutions for Proportional Problems (CD) -Representing Road Race (PS) Supporting MDC Lessons 6th Grade -Maximizing Profit: Selling Soup (PS) -Using Proportional Reasoning (CD)Extra Resources Holt Textbook 4-1, 4-2, 4-3, 4-4 All Chapter 5 Holt Textbook4-8, 4-9, 4-10, 6-2, 6-4, 6-5, 6-6, 6-7DropboxDP, IP, L, NL ResourceOnline TextbookEureka Math – Module 1, Lessons 1-10TNCore TasksWalking(TNCore Task 7.RP.2a, b, c)Coupon Book Sales(TNCore Task 7.RP.2, a, b, c, d, 7.EE.4a)Capture-Recapture(TNCore Task 7.RP.2c, 7.EE.3)Gas TankAcademic Vocabulary:Maury County Public Schools5/17/18Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by UnitUnit 3Number Systems – Part 2# of Days- 15“I Can” StatementsStandardsNumber Systems7.NS.A.1d- Apply properties of operations as strategies to add andsubtract rational numbers.7.NS.A.2a- Understand that multiplication is extended fromfractions to rational numbers by requiring that operations continueto satisfy the properties of operations, particularly the distributiveproperty, leading to products such as (–1)(–1) 1 and the rules formultiplying signed products of rational numbers by describing realworld contexts.7.NS.A.2c- Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiplyand divide rational numbers.7.NS.A.2d- Convert a rational number to a decimal using longdivision; know that the decimal form of a rational numberterminates in 0s or eventually repeats.7.NS.A.3- Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving thefour operations with rational numbers. (Computations with rationalnumbers extend the rules for manipulating fractions to complexfractions.)Maury County Public SchoolsI can rewrite a subtraction problem as an addition problem by usingthe additive inverse.I can use the properties of operations to add and subtract rationalnumbers.I can interpret the addition of integers by relating values to real-worldsituations.I can use patterns and properties to explore the multiplication ofintegers.I can use patterns and properties to develop procedures formultiplying integers.I can use distributive property to verify the properties of integers.I can describe real-world situations represented by the multiplicationof integers.I can generalize the procedures for multiplying and dividing integersto all rational numbers.I can use long division to convert a rational number to a decimal.I can verify that a number is rational based on its decimal equivalent.I can describe and give examples of both terminating and repeatingdecimals.I can solve real-world problems involving the addition, subtraction,multiplication, and/or division of rational numbers.5/17/18Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by UnitSections/Topics- to be completed by individual teacher or during PD with7th grade math teachers Pre-assessment Section 1 Topic Section 2 Topic Section 3 Topic Quiz Section 4 Topic Section 5 Topic Section 6 Topic Quiz Section 7 Topic Section 8 Topic Section 9 Topic Unit Review Unit TestActivities/Resources/MaterialsResources Found On 7th Grade DropboxIReady:Short Tasks (Found on www.mathshell.org) Illustrative Math: 7.NS.1 TNCore Assessment Task: High and Low Elevations(NS.A.1) TNCore Assessment Task: Video Game Ratings(NS.A.1&2) Math Shell: Taxi CabsExtra Resources Holt Textbook 2-4, 2-5, 3-3, 3-4, 3-5, 3-9, 3-10, 3-11 Online Textbook Eureka Math – Module 2, Lessons 10-16 Engage NY: Lesson 11 Multiply Signed Numbers Engage NY: Lesson 12 Division of Integers Engage NY: Lesson 13 Converting Between Fractions and DecimalsUsing Equivalent Fractions Engage NY: Lesson 14 Converting Rational Numbers to DecimalsUsing Long Division Connected Math Lessons: 7.NS.2a-d Investigation 3 Math Shell: Using Positive and Negative Numbers in Context Utah Education Network Lesson: Operations with Fractions andDecimals Illustrative Math: Sharing Prize Money TNCore Instructional Tasks: Extending the Number System and TheLeader of the Pack TNCore Assessment Task: eReader Sales (7.NS.A.3) TNCore: Weight of Candles(NS.A.1&3) TNCore: Winter Denmark(NS.A.1&3) TNCore Task Arc: Adding/Subtracting Positive and NegativeRational Numbers7.NS.1 & 3Academic Vocabulary:Maury County Public Schools5/17/18Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by UnitUnit 4: Equations and Expressions – part 1# of Days- 25“I Can” StatementsStandardsExpressions and Equations7.EE.A.1- Apply properties of operations as strategies to add,subtract, factor, and expand linear expressions with rationalcoefficients.7.EE.B.3a- Solve multi-step real-world and mathematicalproblems posed with positive and negative rational numberspresented in any form (whole numbers, fractions, anddecimals). Apply properties of operations to calculate withnumbers in any form; convert between forms as appropriate.7.EE.B.3b- Assess the reasonableness of answers using mentalcomputation and estimation strategies.7.EE.B.4a- Use variables to represent quantities in a realworld or mathematical problem, and construct simpleequations and inequalities to solve problems by reasoningabout the quantities. Solve contextual problems leading toequations of the form px q r and p(x q) r, where p, q,and r are specific rational numbers. Solve equations of theseforms fluently. Compare an algebraic solution to anarithmetic solution, identifying the sequence of theoperations used in each approach. For example, theperimeter of a rectangle is 54 cm. Its length is 6 cm. What isits width?7.EE.B.4b- Solve contextual problems leading to inequalitiesof the form px q r or px q r, where p, q, and r arespecific rational numbers. Graph the solution set of theinequality on a number line and interpret it in the context ofthe problem. For example: As a salesperson, you are paid 50per week plus 3 per sale. This week you want your pay to beat least 100. Write an inequality for the number of sales youneed to make, and describe the solutions. (Note thatinequalities using , , , are included in this standard).Maury County Public SchoolsI can use the commutative and associative properties to add linearexpressions with rational coefficients.I can use the distributive property to add and/or subtract linear expressionwith rational coefficients.I can use the distributive property to factor or expand linear expressionswith rational coefficients.I can solve real-world problems using rational numbers in any form,including those problems involving multiple steps.I can apply the properties of operations to fluently compute with rationalnumbers in any form.I can write an algebraic equation with more than one step to represent areal-world problem.I can solve an algebraic equation with multiple steps by using the propertiesof equality or mathematical reasoning and show or explain my steps.I can write and solve an algebraic inequality to represent a real-worldproblem.I can graph the solution to an inequality on a number line.I can describe the solution to an inequality in relation to the problem.5/17/18Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by UnitSections/Topics - to be completed by individual teacher or during PDwith 7th grade math teachers Pre-assessment Section 1 Topic Section 2 Topic Section 3 Topic Quiz Section 4 Topic Section 5 Topic Section 6 Topic Quiz Section 7 Topic Section 8 Topic Section 9 Topic Unit Review Unit TestActivities/Resources/MaterialsResources Found On 7th Grade DropboxIReady:Extra Resources Holt Textbook 1-4, 1-5, 1-6, 1-7, 1-8, 1-9 Online Textbook Eureka Math – Module 3, Lessons 1-6 More resources to come. Holt Textbook 1-10, 1-11, 6-3, All of Chapter 12 Online Textbook Eureka Math – Module 3, Lessons 7-15 Engage NY Lesson: Writing Products as Sums and Sums asProducts 7.EE.1 & 2 Engage NY: Lesson 4 Writing Products as Sums and Sums asProducts Engage NY: Lesson 6 Collecting Rational Number Like Terms Connected Math Lesson: Moving Straight Ahead Investigation 3 Learn Zillion Lessons: Solving Equations TN Task: Fixing Up The Yard TN Task: Shipping Rates Math Shell: FencingAcademic Vocabulary:Maury County Public Schools5/17/18Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by UnitUnit 5Expressions and Equations – Part 2# of Days- 20“I Can” StatementsStandardsRatios and Proportions7.RP.A.3- Solve real-world and mathematical problemsinvolving the four operations with rational numbers.(Computations with rational numbers extend the rules formanipulating fractions to complex fractions.)I can use proportional relationships to solve real world problems involvingmultiple steps including problems dealing with tax, interest, discounts, markups, commission, tips, fees, and percent change.Expressions and Equations7.EE.A.2- Understand that rewriting an expression in differentforms in a contextual problem can provide multiple ways ofinterpreting the problem and how the quantities in it are related.For example, shoes are on sale at a 25% discount. How is thediscounted price P related to the original cost C of the shoes? C .25C P. In other words, P is 75% of the original cost for C - .25Ccan be written as .75C.Maury County Public SchoolsI can rewrite expressions to make them easier to understand andsolve.I can use equivalent expressions to understand the relationshipsbetween quantities.5/17/18Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by UnitSections/Topics - to be completed by individual teacher or during PDwith 7th grade math teachers Pre-assessment Activities/Resources/MaterialsResources Found On 7th Grade DropboxIReady:Section 1 Topic Section 2 Topic Section 3 Topic Quiz Section 4 Topic Section 5 Topic Section 6 Topic Quiz Section 7 Topic Section 8 Topic Section 9 Topic Unit Review Unit TestExtra Resources Holt Textbook 4-8, 4-9, 4-10, 6-2, 6-4, 6-5, 6-6, 6-7Online Textbook Eureka Math – Module 1, Lessons 11-15 Eureka Math – Module 1, Lessons 16-22 Eureka Math – Module 4, Lessons 1-11 TNCore Tasks Plant Species (TNCore Task 7.RP.1, 7.RP.2. a, b, c, d, 7.RP.3) Track Practice (TNCore Task 7.RP.1) Salsa (TNCore Task 7.EE.3, 7.EE.4a, 7.RP.1, 7.RP.2a, b, c, d)Academic Vocabulary:Maury County Public Schools5/17/18Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by UnitUnit 6Geometry# of Days- 20“I Can” StatementsStandardsGeometry7.G. B.4- Know and use facts about supplementary,complementary, vertical, and adjacent angles in a multi-stepproblem to write and solve simple equations for an unknownangle in a figure.I can state the relationship between supplementary, complementary,and vertical angles.I can use angle relationships to write algebraic equations for unknownangles.I can use algebraic reasoning and angle relationships to solve multistep problems.7.G.A.2- Draw geometric shapes with given conditions. Focuson constructing triangles from three measures of angles orsides, noticing when the conditions determine a uniquetriangle, more than one triangle, or no triangle.I can draw a geometric shape with specific conditions.I can construct a triangle when given three measurements: 3 side lengths, 3angle measurements, or a combination of side and angle measurements.I can determine when three specific measurements will result in one uniquetriangle, more than one possible triangle, or no possible triangles.7.G.A.1- Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometricfigures, including computing actual lengths and areas from ascale drawing and reproducing a scale drawing at a differentscale.I can use a scale drawing to determine the actual dimensions and area of ageometric figure.I can use a different scale to reproduce a similar scale drawing.I can use a scale drawing to compute an actual length or area from a map orpicture.7.G.B.3- Know the formulas for the area and circumference ofa circle and use them to solve problems; give an informalderivation of the relationship between the circumference andarea of a circle.I can state the formula for finding the area and circumference of a circle.I can use the formulas to compute the area and circumference of a circle.I can determine the diameter or radius of a circle when the circumference isgiven.7.G.B.5- Solve real-world and mathematical problemsinvolving area, volume, and surface area of two- and threedimensional objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals,polygons, cubes, and right prisms.I can determine the area of two-dimensional figures.I can determine the surface area and volume of three-dimensional figures.Maury County Public SchoolsI can use a ratio and algebraic reasoning to compare the area andcircumference of a circle.5/17/18Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by UnitSections/Topics - to be completed by individual teacher or during PDwith 7th grade math teachers Pre-assessment Section 1 Topic Section 2 Topic Section 3 Topic Quiz Section 4 Topic Section 5 Topic Section 6 Topic Quiz Section 7 Topic Section 8 Topic Section 9 Topic Unit Review Unit TestActivities/Resources/MaterialsResources Found On 7th Grade DropboxIReady:Short Tasks (Found on www.mathshell.org) MDC Lessons -Applying Angle Theorems (CD) - Describing and Defining Quadrilaterals (PS) -Describing and Defining Triangles (CD) -Designing a 3D Product in 2D: A Sports Bag (PS) -Estimating Volume: The Money Munchers (PS) -Finding Area of Circles (CD) -Maximizing Area: Gold Rush (PS) Extra Resources Holt Textbook 9-2, 9-5, , 8-2 and lab, 9-3, 9-4, 10-1, 10-2, 10-3, 10-4, 10-5, 8-6, 101 Extension Online Textbook Eureka Math – Module 3, Lessons 16-26 Module 6, Lessons 1-4Academic Vocabulary:Maury County Public Schools5/17/18Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by UnitUnit 7Statistics and Probability# of Days- 20“I Can” StatementsStandardsStatistics and Probability7.SP.C.5- Understand that the probability of a chance event is anumber between 0 and 1 that expresses the likelihood of the eventoccurring. Larger numbers indicate greater likelihood. A probabilitynear 0 indicates an unlikely event, a probability around 1/2indicates an event that is neither unlikely nor likely, and aprobability near 1 indicates a likely event.7.SP.C6- Approximate the probability of a chance event by collectingdata on the chance process that produces it and observing its longrun relative frequency, and predict the approximate relativefrequency given the probability. For example, when rolling anumber cube 600 times, predict that a 3 or 6 would be rolled roughly200 times, but probably not exactly 200 times.7.SP.C.7a- Develop a probability model and use it to find probabilities ofevents. Compare probabilities from a model to observed frequencies; if theagreement is not good, explain possible sources of the discrepancy.Develop a uniform probability model by assigning equal probability to alloutcomes, and use the model to determine probabilities of events. Forexample, if a student is selected at random from a class, find theprobability that Jane will be selected and the probability that a girl will beI can define probability as a ratio that compares favorable outcomesto all possible outcomes.I can recognize and explain that probabilities are expressed as anumber between 0 and 1.I can interpret a probability near 0 as unlikely to occur and aprobability near 1 as likely to occur.I can interpret a probability near ½ as being as equally likely to occuras to not occur.I can collect data on a chance process to approximate its probability.I can use probability to predict the number of times a particular eventwill occur given a specific number of trials.I can use variability to explain why the experimental probability willnot always exactly equal the theoretical probability.I can develop a simulation to model a situation in which all events areequally likely to occur.I can use the model to find the sample space and probabilities ofoutcomes that are equally likely to occur.selected.7.SP.C.7b- Develop a probability model (which may not be uniform) byobserving frequencies in data generated from a chance process. Forexample, find the approximate probability that a spinning penny will landheads up or that a tossed paper cup will land open end down. Do theoutcomes for thespinning penny appear to be equally likely based on the observedI can develop a probability model.I can determine whether the probability model is equally likely.frequencies?7.SP.D.8a- Summarize numerical data sets in relation to their context. Givequantitative measures of center (median and/or mean) and variability(range and/or interquartile range), as well as describe any overallMaury County Public SchoolsI can run a simulation and document the probability of a real-lifesimulation.I can create a tree diagram to find all of the possible outcomes5/17/18Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by Unitpattern and any striking deviations from the overall pattern withreference to the context in which the data were gathered.7.SP.D.8b- Know and relate the choice of measures of center(median and/or mean) and variability (range and/or interquartilerange) to the shape of the data distribution and the context inwhich the data were gathered.7.SP.A.1- Understand that statistics can be used to gain informationabout a population by examining a sample of the population;generalizations about a population from a sample are valid only ifthe sample is representative of that population. Understand thatrandom sampling tends to produce representative samples andsupport valid inferences.7.SP.A.2- Use data from a random sample to draw inferences abouta population with an unknown characteristic of interest. Generatemultiple samples (or simulated samples) of the same size to gaugethe variation in estimates or predictions. For example, estimate themean word length in a book by randomly sampling words from thebook; predict the winner of a school election based on randomlysampled survey data. Gauge how far off the estimate or predictionmight be.7.SP.B.3-Informally assess the degree of visual overlap of twonumerical data distributions with similar variabilities, measuring thedifference between the centers by expressing it as a multiple of ameasure of variability. For example, the mean height of players onthe basketball team is 10 cm greater than the mean height ofplayers on the soccer team; on a dot plot or box plot, the separationbetween the two distributions of heights is noticeable.7.SP.B.4-Use measures of center and measures of variability fornumerical data from random samples to draw informal comparativeinferences about two populations. For example, decide whether thewords in a chapter of a 7th grade science book are generally longerthan the words in a chapter of a 4th grade science book.Maury County Public Schools(sample space).I can list possible outcomes (sample space) in a chart.I can multiply individual probabilities to find the probability of acompound event.I can explain that inferences about a population can be made byexamining a population.I can explain why the validity of a sample depends on whether thesample is representative of the population.I can explain that random sampling tends to produce representativesamples.I can create a research question, take a random sample, and makevalid conclusions.I can draw inferences about a population based on data generated bya random sample.I can generate multiple samples from the same population andanalyze the estimates or predictions based on the variation of eachsample.I can make estimates and justify predications about data and multiplesamples to check the results and gauge how close my predictionmight be.I can find the difference in the mean or median of two different datasets.I can demonstrate how two data sets that are very different can havesimilar variability.5/17/18Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by UnitSections/Topics - to be completed by individual teacher or during PDwith 7th grade math teachers Pre-assessment Section 1 Topic Section 2 Topic Section 3 Topic Quiz Section 4 Topic Section 5 Topic Section 6 Topic Quiz Section 7 Topic Section 8 Topic Section 9 Topic Unit Review Unit TestActivities/Resources/MaterialsResources Found On 7th Grade DropboxIReady:Short Tasks (Found on www.mathshell.org) MDC Lessons -Analyze Games of Chance (CD) -Designing: A Game of Chance (PS) -Evaluating Statements About Probability (CD) MDC Lessons -Comparing Data Using Statistical Measures (CD) -Sampling and Estimating: Counting TreesExtra Resources Holt Textbook All of Chapter 11 and lab- might need additional resources Online Textbook Eureka Math – Module 5, Lessons 1-12 More resources to come Holt Textbook 7-8, All of Chapter 11, and Common Core supplement workbook, may need additional resourcesOnline TextbookEureka Math – Module 5, Lessons 13-23Academic Vocabulary:Maury County Public Schools5/17/18Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by UnitUnit 8TNReady Review/Wrap Up# of Days- 25“I Can” StatementsStandardsNumber SystemsRatios and ProportionsExpressions and EquationsGeometryStatistics and ProbabilityMaury County Public Schools5/17/18Office of Instruction Pk-12
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by UnitSections/Topics - to be completed by individual teacher or during PDwith 7th grade math teachers Pre-assessment Section 1 Topic Section 2 Topic Section 3 Topic Quiz Section 4 Topic Section 5 Topic Section 6 Topic Quiz Section 7 Topic Section 8 Topic Section 9 Topic Unit Review Unit TestActivities/Resources/MaterialsResources Found On 7th Grade Dropbox Short Tasks (Found on www.mathshell.org) Ext
7th Grade Math - TN Ready Performance Standards by Unit Maury County Public Schools 5/17/18 Office of Instruction Pk-12 7th Grade Math – Curriculum Overview Q1 - 1st Nine Weeks Q2 - 2nd 9Weeks Q3 - 3rd 9