Transcription
Chapter9Checking Accounts andBanking Services9.1 Checking Accounts9.2 Banking Services and Fees 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning
Lesson 9.1Checking AccountsGOALS Describe the purpose of a checkingaccount and the forms associated with it. Explain how to use a checking account. Discuss the types of checking accounts.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 2
Checking Account Basics A checking account allows you to writechecks to make payments. A check is a written order to a bank to paythe amount stated to the person or businessnamed on it. A checking account is also called a demanddeposit, because the money may bewithdrawn at any time—that is, “on demand.”Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 3
(continued)Checking Account Basics Checks follow a process through the bankingsystem. The payee cashes your check. The bank that cashed the check returns it to yourbank. Your bank withdraws the money from your accountand sends it to the other bank. Your bank then stamps the back of your check,indicating that it has cleared. A canceled check is a check that has cleared youraccount.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 4
(continued)Checking Account Basics Many banks no longer send paperchecks to other banks for processing. To make processing faster and moreefficient, they exchange check informationelectronically by transmitting an image of thecheck, called a substitute check. A substitute check can be used in the sameway as an original check.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 5
(continued)Checking Account Basics You must also maintain enough money in youraccount to cover all the checks you write. A check written for more money than youraccount contains is called an overdraft. A bank that does not honor a check usually stampsthe check with the words “not sufficient funds” (NSF)and returns the check to the payee’s bank. When this occurs, the check has bounced. Your bank will charge you a fee for each NSF checkprocessed.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 6
(continued)Checking Account Basics Floating a check is writing a check andhoping to deposit money to cover itbefore the check clears. Floating a check is very risky becausetoday’s electronic systems allow checksto process very quickly. Floating a check is illegal in most states.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 7
Checking Account Advantages Convenience Safety Built-in record keeping system Access to bank servicesChapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 8
Opening a Checking Account Signature authorization form Initial depositChapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 9
Parts of a CheckCheckNumberName andAddress of MakerDatePayeeABA NumberNumeric AmountWrittenAmountMemoSignatureAccount and Routing NumbersChapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 10
Using Your Checking Account Writing checks Paying bills online Making deposits Using a checkbook register A checkbook register is a booklet used torecord checking account transactions.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 11
Bank Reconciliation The process of matching your checkbookregister with the bank statement is knownas bank reconciliation.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 12
Reconciling Your CheckingAccount1. Write ending balance from bankstatement.2. Add credits or deposits not onstatement.3. Total lines 1 and 2.4. List checks, withdrawals, anddebits made but not shown onstatement.5. Total outstanding checks/debittransactions.6. Subtract line 5 from line 3.(Result should match checkbookbalance)Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 13
Endorsing Checks A check generally cannot be cashed until it isendorsed. To endorse a check, the payee signs the toppart of the back of the check in ink. There are three major types of endorsements. Blank endorsement Special endorsement Restrictive endorsementChapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 14
Blank Endorsement A blank endorsement is the signature ofthe payee written exactly as his or hername appears on the front of the check.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 15
Special Endorsement A special endorsement, or anendorsement in full, is an endorsementthat transfers the right to cash the checkto someone else.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 16
Restrictive Endorsement A restrictive endorsement restricts orlimits the use of a check.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 17
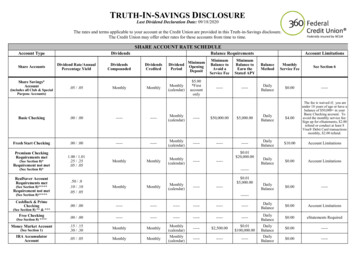
Types of Checking Accounts Joint accounts Special accounts Standard accounts Interest-bearing accounts Share accountsChapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 18
Lesson 9.2Banking Services and FeesGOALS Describe banking services available atmost financial institutions. List and explain fees charged by financialinstitutions for their services.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 19
Banking Services A full-service bank is one that offers every possiblekind of service, from savings and checking accounts tocredit cards, safe deposit boxes, loans, and ATMs. Other services commonly offered are online banking,telephone banking, certified checks, cashier’s checks,money orders, and debit cards. Most banks offer FDIC (Federal Deposit InsuranceCorporation) insurance, which protects the deposits ofcustomers against loss up to 250,000 per account.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 20
Guaranteed-payment Checks A certified check is a personal checkthat the bank guarantees or certifies tobe good. A cashier’s check, also called a bankdraft, is a check written by a bank on itsown funds. Traveler’s checks are check forms inspecific denominations that are usedinstead of cash while traveling.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 21
Money Orders Banks sell money orders to people who do notwish to use cash or do not have a checkingaccount. A money order is like a check, except that itcan never bounce. There is a charge for purchasing a moneyorder. You also can purchase money orders throughthe post office and local merchants.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 22
Debit Cards A debit card is a plastic card thatdeducts money from a checking accountalmost immediately to pay for purchases. The debit card is presented at the time ofpurchase. When a debit card is used, the amount ofthe purchase is quickly deducted fromthe customer’s checking account andpaid to the merchant.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 23
Bank Credit Cards You can apply to a full-service bank for a bankcredit card, such as a Visa or MasterCard. If you meet the requirements and are issued acard, you can use it instead of cash at anybusiness that accepts credit cards. Banks offering national credit cards usuallycharge both an annual fee for use of the cardand interest on the unpaid account balance.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 24
Overdraft Protection Overdraft protection allows you to coverchecks or withdrawals up to a specifiedamount, usually between 100 and 1,000, depending on the typical balancein your account. With overdraft protection, your checkswill be covered even if you haveinsufficient funds in your checkingaccount.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 25
Automated Teller Machines An Automated Teller Machine is often called anATM. To use ATMs, you must Have a card that is electronically coded Know your personal identification number (PIN) Getting cash is a common ATM transaction. Using a debit card you can withdraw cash from yourchecking or savings account. Using a Visa or MasterCard, you can receive a cashadvance electronically.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 26
Online and Telephone Banking Online and telephone banking services giveyou the ability to access your accounts from acomputer or telephone anytime, day or night. Services include: Transferring money from one account to another Paying bills by authorizing the bank to disbursemoney Getting account balances Seeing which checks have cleared and whichdeposits have been enteredChapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 27
(continued)Online and Telephone Banking Most banks also allow and encourageelectronic transfers of money. An electronic funds transfer (EFT) uses acomputer-based system that enables you tomove money from one account to anotherwithout writing a check or exchanging cash.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 28
Stop Payment Orders A stop-payment order is a request thatthe bank not honor a specific check. The usual reason for stopping payment isthat the check has been lost or stolen. Most banks charge a fee for stoppingpayment on a check.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 29
Safe Deposit Boxes Financial institutions offer customers asafe deposit box to store valuable itemsor documents. They charge a yearly fee based on thesize of the box. Keeping important documents and otheritems in a safe deposit box ensures thatthe items won’t be stolen, lost, ordestroyed.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 30
(continued)Safe Deposit Boxes Examples of items commonly kept in asafe deposit box include Birth, marriage, and death certificates Deeds and mortgage papers Stocks and bonds Jewelry Coin collectionsChapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 31
Loans and Trusts Financial institutions also make loans tofinance the purchase of cars, homes, homeimprovements, vacations, and other items. Banks can also provide advice for estateplanning and trusts. Banks can act as trustees of estates for minorsand others. A trustee is a person or an institution that managesproperty for the benefit of someone else under aspecial agreement.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 32
Notary Public A notary public verifies a person’s identity,witnesses the person’s signature on a legaldocument, and then “notarizes” the signatureas valid. Financial institutions typically have a person ontheir staff who is a notary public. This person provides notary services for accountholders, usually without charge. For noncustomers, however, there is typically asmall fee.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 33
Financial Services Purchasing or selling savings bonds Investment brokerage servicesChapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 34
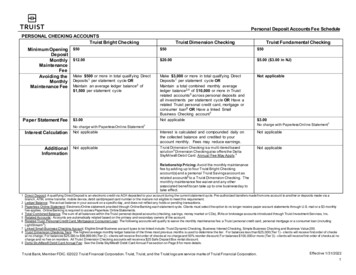
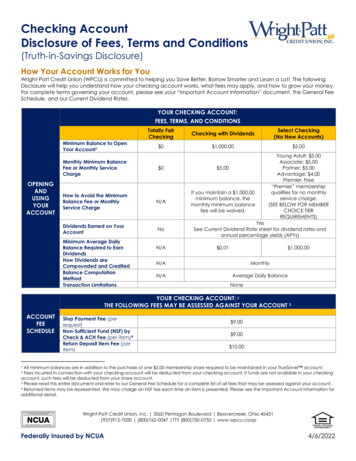
Bank Fees Banks charge fees to their customers tohelp cover their operating costs. The best way to avoid fees is to choosethe right kind of account. Shop around and find the account that isright for you. Be aware of the rules of your account, sothat you don’t violate them and be requiredto pay high fees.Chapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 35
Examples of Bank Fees Loan feesTrustee feesCheck cashing feesPer-check feesMonthly service feesOverdraft feesNSF check chargesATM transaction fees Safe deposit box feesTeller service feesMinimum balance feesFees for guaranteedpayment checks Notary service fees Online bill payment fees Fees to return canceledchecksChapter 9 2010 South-Western, Cengage LearningSLIDE 36
Chapter 9 . Checking Account Basics A checking account allows you to write checks to make payments. A . check. is a written order to a bank to pay the amount stated to the person or business named on it. A checking account is also called a . demand deposit, because the money may be withdrawn at any time—that is, "on demand."