Transcription
Click to edit Master title styleBest Practices In ClinicalSkills AssessmentColette Scott, MEdNovember 10, 20201
AgendaClickto edit Master title style Provide an overview of the state of simulation scienceand the assessment of clinical skills in healthprofessions education. Discuss the future state of simulation science in healthprofessions education. Discuss the importance of rater training and instrumentselection for evaluation.2 2
PioneersClickto edit Master title styleHoward BarrowsProgrammed/Simulated PatientsPaula StillmanThe Arizona ClinicalInterview Rating Scale(ACIRS)Ronald HardenIan HartObjective StructuredClinical Examination(OSCE)3
Click to edit Master title styleHealthcaresimulation is a rangeof activities thatshare a broad,similar purpose – toimprove the safety,effectiveness, andefficiency ofhealthcare services.Laerdal MedicalWiley OnlineSciencenode.com4usmle.org
Click to edit Master title styleEducatingand training healthcareprofessionals to bemore effective andsafe caregivers5
AdvantagesPatientSimulationClickto edit ofMastertitlestylein Clinical Skills Education Learner-centered approach to education,building on previous knowledge andexperiences Active and interactive learning without risk toan actual patient which makes for saferencounters for patients and trainees Learners witness the results of their actions inreal time Immediate feedback is provided (SPs andFaculty), and students can repeat skills untilproficient6
TelemedicineClickto edit Master title style“Telemedicine offersopportunities in a variety ofspecialties that canaugment student educationduring this time. Theprojected growth oftelemedicine necessitatesthat students learn newskills to be effectiveproviders.” (Iancu, et al 2020)7
HybridEncountersClickto editMaster title styleHybridscenariosrequire theuse of bothstandardizedpatients withhigh-fidelitymannequinsor simulators.8
Clickto editMaster title styleVirtualReality an interactive internetbased approach toproviding clinicaleducation in a safe,nonthreateningenvironment that offersincreased access andflexibility to the learner.(Dutile, et al 2010)9
Clickto edit Master titlestyleInterprofessionalEducation10
Clickto edit Mastertitle styleStandardizedPatients Individuals trained to portraya patient with a specificcondition in a realistic,standardized and repeatablewayUsed for teaching andassessment of learners History/Consultation Physical Examination Communication Skills Documentation(Gliva & Furman 2020)11
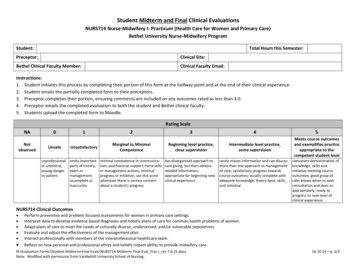
ObjectiveStructuredClick to edit Master title styleClinical Exams (OSCEs) Learners rotate through a series of timedstations Each station presents a specific clinical scenario Each station assesses one or more areas ofclinical competence (for example, history taking,communication, physical examination skills, etc.) All students are exposed to the same clinicalproblems The assessment applies a standardizedapproach, which includes standardized patients(SPs), standardized scoring tools, andstandardized exam-day logistics12
Clickto edit MasterstyleObjectiveof thetitleAssessment What is the purpose of this assessment? How will students demonstrate achievement? Variety of patient characteristics and representative conditions Age (e.g., pediatric, adult)GenderSite of care (e.g., clinic, emergency department)Organ SystemPresenting complaintExaminee level (e.g., end of course, end of year)13
SPtoTrainingClickedit Master title style Ten step process including: Portrayal of the patient Accurate completion of the ratingscale Standardized portrayal Roleplays Teaching physical exam(Gliva & Furman, 2020)14
Clickto editMaster title styleCaseDevelopmentProcessSubject Matter ExpertsSP EducatorTrainerStandardized Patient15
Post Encounter Note (PEN)Click to edit Master title styleScoring Traditionally, faculty raters are used toscore PENs For increased high stakes examreliability PEN scoring by facultyraters is slowly being replaced bycommercially available artificialintelligence16
Quality Control ofClick to edit Master title styleHuman Raters Trainer Observation andFeedback Benchmark Encounters Analysis for Drift Refresher Training Rotation of Cases17
Clickto edit Master title styleSummary Simulation methodology is a bridge betweenclassroom learning and real-life clinicalexperienceThe use of simulations is making significantcontributions to health professions educationSimulation methodology is experiential,collaborative, interactive, and learner centered1818
Click to edit Master title styleReferencesAssociation Standardized Patient Educators (ASPE) Website https://www.aspeducators.org. Terminology 2009.Committee IS. INACSL standards of best practice: simulation SM simulation design. Clin Simul Nurs. 2016;12S5–S12.Dutile C, Wright N, Beauschesne M. (2011). Virtual clinical education: Going the full distance in nursingeducation. Newborn and Infant Nursing Reviews, 11(1), 43-48.Gliva-McConvey G. et al. (eds.), Comprehensive Healthcare Simulation: Implementing Best Practices inStandardized Patient Methodology, Comprehensive Healthcare Simulation, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-03043826-5 3Iancu, A. M., Kemp, M. T., & Alam, H. B. (2020). Unmuting Medical Students’ Education: Utilizing TelemedicineDuring the COVID-19 Pandemic and Beyond (Preprint). doi:10.2196/preprints.19667Lewis KL, Bohnert CA, Gammon WL, Hölzer H, Lyman L, Smith C, Thompson T, Wallace A, Gliva-McConveyG. The association of standardized patient educators (ASPE) standards of best practice (SOBP). Adv Simul.2017;2:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41077-017-0043-4.1919
Click to edit Master title styleQuestions20
Click to edit Master title styleThank YouColette Scott MEdcscott1230@gmail.com21
Clinical Exams (OSCEs) Learners rotate through a series of timed stations Each station presents a specific clinical scenario Each station assesses one or more areas of clinical competence (for example, history taking, communication, physical examination skills, etc.) All students a