Transcription
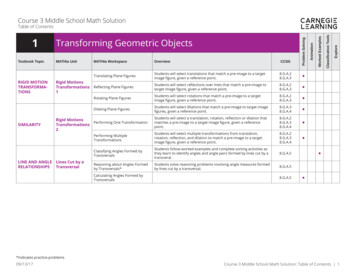
Course 3 Middle School Math SolutionRIGID ting Plane FiguresStudents will select translations that match a pre-image to a targetimage figure, given a reference point.8.G.A.28.G.A.3 Students will select reflections over lines that match a pre-image totarget image figure, given a reference point.8.G.A.28.G.A.3 Rotating Plane FiguresStudents will select rotations that match a pre-image to a targetimage figure, given a reference point.8.G.A.28.G.A.3 Dilating Plane FiguresStudents will select dilations that match a pre-image to target imagefigures, given a reference point.8.G.A.38.G.A.4 Students will select a translation, rotation, reflection or dilation thatmatches a pre-image to a target image figure, given a referencepoint.8.G.A.28.G.A.38.G.A.4 Performing MultipleTransformationsStudents will select multiple transformations from translation,rotation, reflection, and dilation to match a pre-image to a targetimage figure, given a reference point.8.G.A.28.G.A.38.G.A.4 Classifying Angles Formed byTransversalsStudents follow worked examples and complete sorting activities asthey learn to identify angles and angle pairs formed by lines cut by atransveral.8.G.A.5Reasoning about Angles Formedby Transversals*Students solve reasoning problems involving angle measures formedby lines cut by a transversal.8.G.A.5Rigid MotionsTransformations Reflecting Plane Figures1Rigid MotionsPerforming One TransformationTransformations2LINE AND ANGLE Lines Cut by aRELATIONSHIPSTransversalCalculating Angles Formed byTransversals8.G.A.5ExploreMATHia WorkspaceClassification ToolsMATHia UnitWorked ExamplesTextbook TopicTransforming Geometric ObjectsProblem Solving1AnimationTable of Contents *Indicates practice problems09/13/17Course 3 Middle School Math Solution: Table of Contents 1
Course 3 Middle School Math SolutionFROMPROPORTIONSTO LINEARRELATIONSHIPSLinear Modelsand theDistributivePropertyLinear ModelsGraphs of LinearEquations inTwo VariablesLINEARRELATIONSHIPSWritingEquations of aLineMATHia WorkspaceOverviewCCSSModeling with Integer Rates ofChangeStudents will determine linear expressions with integer coefficientsthat represent real-world contexts. They will use these expressionsto solve problems.8.F.B.4 Modeling with Fractional Rates ofChangeStudents will determine linear expressions with fraction or decimalcoefficients that represent real-world contexts. They will use theseexpressions to solve problems.8.F.B.4 Modeling using the DistributiveProperty over DivisionStudents will use the Distributive Property over Division todetermine and represent expressions for real-world contexts. Theywill use these expressions to solve problems.8.F.B.4 Graphing Given an Integer Slopeand y-InterceptStudents will write the equations of lines given an integer slope anda y-intercept.8.F.B.4 Graphing Given a Decimal Slopeand y-InterceptStudents will write the equations of lines given a decimal-value slopeand a y-intercept.8.F.B.4 Modeling Linear Equations inStandard FormStudents follow worked examples and analyze linear equations instandard form. Students identify components of linear equationsand their meaning in terms of problem situations.8.F.B.4Graphing Linear Equations usinga Given MethodStudents graph relations given in standard form by applying anindicated method: the slope-intercept method, two-intercepts method.8.F.B.4 Graphing Linear Equations usinga Chosen MethodStudents are given a relation and a choice as to which method touse to graph it. Students are then given information about the lineappropriate to the chosen method.8.F.B.4 Modeling Given Slope and a PointStudents graph relations given in standard form by applying anindicated method: the slope-intercept method, two-points method,or two-intercepts method.8.F.B.4 Calculating SlopesStudents are given a relation and a choice as to which method touse to graph it. Students are then given information about the lineappropriate to the chosen method.8.F.B.4 Modeling Given Two PointsStudents are given the ordered pairs for two points, eithermathematically or in context and are asked to identify the equationof the line that connects the points.8.F.B.4 Modeling Given an Initial PointStudents define variables and write expressions and relations todescribe linear contexts.8.F.B.4 Modeling Linear Functions usingMultiple RepresentationsStudents model problems using expressions, tables, and graphs.Students use number properties to evaluate and solve one-step andtwo-step equations.8.F.B.4 ExploreClassification ToolsMATHia UnitWorked ExamplesTextbook TopicDeveloping Functional FoundationsAnimation2Problem SolvingTable of Contents *Indicates practice problems09/13/17Course 3 Middle School Math Solution: Table of Contents 2
Course 3 Middle School Math SolutionINTRODUCTIONTO FUNCTIONSPATTERNS INBIVARIATE DATARelations andFunctionsExploreClassification ToolsWorked ExamplesMATHia UnitAnimationTextbook TopicProblem SolvingTable of ContentsMATHia WorkspaceOverviewCCSSExploring FunctionsStudents use an interactive function machine to explore mysteryfunctions. Students use the function machine and a table to identifyfunctions. They also use the machine along with sorting activities toidentify the domain and range of different functions.8.F.A.1 Exploring Graphs of FunctionsStudents use an interactive function machine and a graph to identifyand analyze function equations and graphs. Students identifyintercepts of the graphs.8.F.A.1 Classifying Relations andFunctionsStudents watch an animation and follow worked examples as theylearn how to classify relations as functions or non-functions.8.F.A.1Identifying Key Characteristics ofGraphs of FunctionsStudents will identify key characteristics from the graph of afunction, such as the intercepts, minimum and maximum x-values,minimum and maximum y-values, domain, and range.8.F.B.5Estimating Lines of Best FitStudents describe the patterns of association in scatter plots andselect the most appropriate line of best fit for a scatter plot.8.SP.A.1Using Lines of Best Fit*Students practice interpreting the meaning of lines of best fit andusing the lines to make predictions.8.SP.A.28.SP.A.3Lines of Best Fit *Indicates practice problems09/13/17Course 3 Middle School Math Solution: Table of Contents 3
Course 3 Middle School Math SolutionSolving LinearEquationsSOLVING LINEAREQUATIONSSYSTEMSOF LINEAREQUATIONSExploreMATHia WorkspaceOverviewExploring Two-Step EquationsStudents use a balance tool to explore two-step equations. They usea general strategy to solve any two-step equation.8.EE.C.7.b Solving Multi-Step EquationsStudents practice solving equations algebraically using a variety ofstrategies, including using a balance tool.8.EE.C.7.b Solving with Integers (No Type In)Students will solve equations with variables on both sides of theequals sign.8.EE.C.7.b Solving with Integers (Type In)Students will solve equations with variables on both sides of theequals sign.8.EE.C.7.b SolutionsStudents follow worked examples as they learn to identify equationswith one solution, no solutions, and infinite solutions. Students alsocheck the solutions to equations.8.EE.C.7.aSorting Equations by Number ofSolutionsStudents complete sorting activities to practice identifying linearequations with one, no, and infinite solutions.8.EE.C.7.aModeling Linear SystemsInvolving IntegersStudents will write multiple expressions with integer coefficients anduse equations to solve systems and determine break-even points inthe context of real-world problems.8.EE.C.8.a8.EE.C.8.b8.EE.C.8.c Students will write multiple expressions with decimal coefficientsand use equations to solve systems and determine break-evenpoints in the context of real-world problems.8.EE.C.8.a8.EE.C.8.b8.EE.C.8.c Students will solve systems of equations with one solution usingsubstitution in mathematical contexts.8.EE.C.8.b Linear Equationswith VariablesSolving Equations with Oneon Both SidesSolution, Infinite, and NoSystems ofModeling Linear SystemsLinear Equations Involving DecimalsSolving Linear Systems usingSubstitutionCCSSClassification ToolsMATHia UnitWorked ExamplesTextbook TopicModeling Linear EquationsAnimation3Problem SolvingTable of Contents *Indicates practice problems09/13/17Course 3 Middle School Math Solution: Table of Contents 4
Course 3 Middle School Math SolutionRational andTHE REALIrrationalNUMBER SYSTEMNumbersPYTHAGOREANTHEOREMMATHia WorkspaceOverviewIntroduction to IrrationalNumbersStudents determine perfect squares and their square roots. They userational approximations to determine decimal approximations ofsquare roots of non-perfect squares. Students watch an animationabout the real number system and classify real numbers as rationalor irrational.8.NS.A.18.NS.A.28.EE.A.2Graphing Real Numbers on aNumber LineStudents practice plotting various real numbers on a number line.Students approximate, if necessary, and plot decimals, percents,fractions, square roots, and pi.8.NS.A.18.NS.A.2 Ordering Rational and IrrationalNumbersStudents use a number line tool to plot approximate values of realnumbers and then compare and order the numbers.8.NS.A.18.NS.A.2 Exploring the PythagoreanTheoremStudents explore a variety of right triangles and answer questionsabout proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse.8.G.B.6Applying the PythagoreanStudents increase their familiarity with using the PythagoreanTheorem by analyzing worked examples.8.G.B.78.EE.A.2Pythagorean Theorem*Students solve for an unknown side length of a right triangle in realworld problems by using the Pythagorean Theorem.8.G.B.78.EE.A.2Calculating Distances on theCoordinate PlaneStudents determine distances on the coordinate plane using thePythagorean Theorem.8.G.B.88.EE.A.2The Pythagorean TheoremTheoremProblem Solving using theCCSSExploreClassification ToolsMATHia UnitWorked ExamplesTextbook TopicExpanding Number SystemsAnimation4Problem SolvingTable of Contents *Indicates practice problems09/13/17Course 3 Middle School Math Solution: Table of Contents 5
Course 3 Middle School Math SolutionEXPONENTSAND SCIENTIFICNOTATIONProperties ofWhole NumberExponentsScientificNotationVOLUME OFVolumeCURVED FIGURESMATHia WorkspaceOverviewCCSSUsing the Product Rule and theQuotient RuleStudents will simplify mathematical expressions using the Productand Quotient Rules.8.EE.A.1 Using the Power to a Power RuleStudents will simplify mathematical expressions using the Power toa Power Rule.8.EE.A.1 Using the Product to a PowerRule and the Quotient to a PowerRuleStudents will simplify mathematical expressions using the Product toa Power and the Quotient to a Power Rules.8.EE.A.1 Using Properties of exponentswith Whole Number PowersStudents will use a variety of strategies, including the Power to aPower Rule, the Product to a Power Rule, and the Quotient to aPower Rule to simplify mathematical expressions with exponents.8.EE.A.1 Simplifying Expressions withNegative and Zero ExponentsStudents will simplify mathematical expressions involving negativeexponents and exponents of 0.8.EE.A.1 Using Scientific NotationStudents write numbers in standard form as numbers in scientificnotation and write numbers in scientific notation as numbers instandard form.8.EE.A.4 Comparing Numbers usingScientific NotationStudents follow worked examples as they learn how to comparenumbers written in scientific notation.8.EE.A.3Calculating Volume of CylindersStudents will use mathematical and real-world objects to determinethe volume of cylinders.8.G.C.9 Using Volume of CylindersStudents will apply the formula for the volume of a cylinder to solvea variety of different problems.8.G.C.9 Calculating Volume of ConesStudents will use mathematical and real-world objects to determinethe volume of cones.8.G.C.9 Using Volume of ConesStudents will apply the formula for the volume of a cone to solve avariety of different problems.8.G.C.9 Calculating Volume of SpheresStudents will use mathematical and real-world objects to determinethe volume of spheres.8.G.C.9 Using Volume of SpheresStudents will apply the formula for the volume of a sphere to solve avariety of different problems.8.G.C.9 ExploreClassification ToolsMATHia UnitWorked ExamplesTextbook TopicApplying PowersAnimation5Problem SolvingTable of Contents *Indicates practice problems09/13/17Course 3 Middle School Math Solution: Table of Contents 6
3 Course 3 Middle School Math Solution: Table of Contents 2 ndicates ractice robles Course 3 Middle School Math Solution Table of Contents 2 Developing Functional Foundations Problem Solving Animation Worked Examples Classification Tools Explore Textbook Topic MATHia Unit MATHia Workspace Overview CCSS FROM










