Transcription
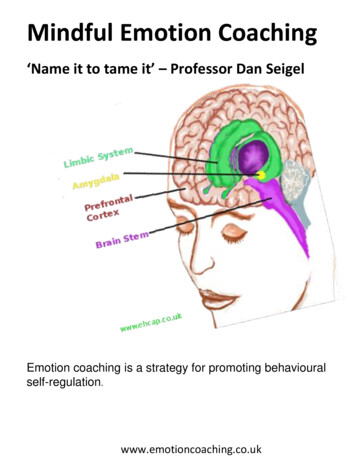
Mindful Emotion Coaching‘Name it to tame it’ – Professor Dan SeigelEmotion coaching is a strategy for promoting uk
InputIn the environmentYour brain is a like a computer It processes information you get fromyour environment and tries to makesense of it.MentalprocessingOutputWhat happens inyour mindBehaviourIt is also a SocialOrgan as it needsother brains tointeract with towork at it’s bestHow does your brain work ?Your brain is organized intodifferent areas of responsibility.E.g. senses, emotions, logicalthought and memoryThe different areas are all connectedtogether by a network of hundredsof billions of neuronsThe more you use the network –thebigger, better and faster it becomes
The emotion part of your braincalled the amygdala acts like anaccelerator on your emotions.The thinking part of your brain called the prefrontalcortex acts like a brake on these emotions.You make your best decisions when these different parts ofyour brain connect well with each other and the brain stem.Adapted from Dr Daniel Siegel The Whole Brain Child
Through non invasive scanning (body is not invadedor cut open) of very youngbabies and children the brain has cometo be seen as a ‘social organ’- normal developmentis dependent on stimulation through social interactionand is influenced by a number of other factors such sthe modification of genes in organisms, physicalhealth and diet.The importance of interaction andrelationships in human development has beenextensively researched by some of these key earlyfigures .John Bowlby, Mary Ainsworth , Mary Main andPatricia Crittendon.So .Babies are born with the basic brain structure .neuronal connections form by the firing of neuroneswhen the baby is interested (stimulated).A baby who receives loving attention will form differentneuronal pathways from a baby whose parent or caregiver is unable to be sensitive and coordinated.Connections form in our brains all the time but especiallyin the first two years of life this carries on right throughchildhood up to about the age of 25
You can calm the emotion area of your brain(amygdala) by stimulating your thinking brain orpre frontal cortexMindfulness, mindful exercises and Emotion Coachingare all ways you can build up your emotion resilience
Professor Dan Siegel talking about The HandModel of the Brain on You-Tube Make sure you look at Dan Siegel’s follow on YouTube Clip and you know all about Flipping Your Lid
The Vagus NerveOne of the ways the thinking part of yourbrain works to calm your bodily responsesand help you stay emotionally balanced is viathe vagus nerve.The vagus nerve travels from your brain stem to all the key organs in yourbody doing things such as lowering your heart and breathing rate
Emotion CoachingAccepts all feelings as normal (but not all behaviour asacceptable)Feelings can always be talked about (no matter what thebehaviour)* ‘Name it to Tame it’ is a phrase used byProfessor Dan Siegel – by naming emotionswe stimulate the thinking part of our brainwhich stimulates the vagus nerve and calmsour bodily responses
There are Core Emotions that allhumans wherever they liveexperience Humans are ‘wired’ to feel and respond to emotions such as Anger, sadness, disgust,fear and joy to survive and thrive ( Take a look at research by Paul Ekman on his researchinto emotion*) Everything we sense (experience) passes through the part of the brain that is in controlof emotional responses as wells as the part of the brain that decides how to respond(think) and what to do (behaviour).*Handy HintTake a look at the Inside Out DVD or watch this You Tube Clip and you can see how PaulEkman worked with Disneyhttps://youtu.be/oauGmJ52XmM
John Gottman’s 5 Steps of Emotion Coaching 1.2.3.4.5.Be aware of your friends’ responsesRecognize emotional times as opportunities forconnectingListen empathetically and recognising feelingsHelp verbally label emotions – this helps sooth thenervous system and recovery rateLASTLY – solve problems together what this means in practiceSTEP 1Tuning InSTEP 2Connecting with each otherSTEP 3Recognising feelings and empathisingSTEP 4Validating feelings and labellingSTEP 5Problem solvingReferences : Professor John Gottman, University of tion-to-emotion-coaching/Tuning in to Teens – Havighurst, Harley & Kehoe - Mindful,Melbourne University and Tuning in to Kids –Havighurst & Harley,Mindful, Melbourne University
Step 5: Problem-solving together Emotion Coaching is all about building and enhancing relationships rememberProblem Solving comes last make sure you explore feelings before you problem solve! When you are both calm and relaxed and where appropriate (or seek further help):–Talk about other ways of doing things–Especially talk about ways of recognising feelings earlier and finding ways ofcalming the emotion part of the brain Think about DanSiegel’s HandModel andProblem Solvewhen both yourlids are down!!‘“How were you feeling when that happened?”“What did it make you feel like?”‘Can you remember feeling this way before and what you did?”“How did you handle it last time?””What do you think you could change next time?”Rose , J., Gilbert, L., McGuire-Snieckus, R. (2015) Emotion Coaching - astrategy for promoting behavioural self-regulation in children and youngpeople in schools: A pilot study, European Journal of Social and BehaviouralSciences, 13, 1766-1790.
www.emotioncoaching.co.ukWith thanks to Olivia Morris, sixth former The Gryphon School, Sherborne forassisting with edits
Mindful Emotion Coaching www.emotioncoaching.co.uk ‘Name it to tame it’ –Professor Dan Seigel Emotion coaching










