Transcription
Acupuncture:New and Old Concept for HealthcareChong-Bin Zhu, PhD, OMD, LAcAssociate ProfessorVanderbilt Center for Integrative HealthNashville, TN 37203April 25, 2014
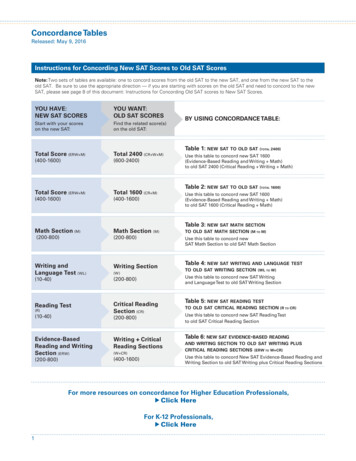
What is Acupuncture is one of the key components oftraditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is a family of procedures to stimulatepoints on the body (acupoints)—mostcommonly is the insertion of thin, solid metallicneedles. is intended to remove blockages in theflow of energy (“Qi”), restore andmaintain health is with thousands of years’ history
Types of uppingAcupointinjectionLaseracupunctureMoxibustion
Acupuncture: A New Concept forHealthCare in USCurrent health care:”mainstream” medicine—Conventional or Western MedicineAcupuncture? never heard ofit Prevention: vaccination, isolation no acupuncture Diagnosis: Not use TCM method Treatment: Not include as a routine method Healing:Not include as a routine method Insurance: No cover for prevention, no cover for acupuncture
Acupuncture: An old Concept forHealthCare in the East
How Old Is Acupuncture?Bone needles“Bian” Stone andBone needlesNew Stone Age 5000BCNew Stone Age5000BC6
Acupuncture: An old ConceptAncient NeedlesModern NeedlesGold needleSilver needleHan Dynasty, 200BC-220AD7
Acupuncture: An old Concept forHealthCare in the East Acupuncture is a key component of traditionalChinese medicine (TCM) TCM had been a main healthcare system forthousands of years before western medicineintroduced Prevention: Diet, herbal remedies, qigong, acupuncture,TuiNa Diagnosis: Use all TCM methods: yin-yang, tongue, pulse,Meridian, five elements Treatment: Acupuncture, moxibustion, herbal remedies,TuiNa, Diet, qigong Healing:All TCM modalities including acupuncture Insurance: Cover All TCM modalities includingacupuncture
What Is Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)A whole medical system that originated in China. It is based onthe concept that disease results from disruption in the flow ofqi and imbalance in the forces of yin and yang. Practicesincluding acupuncture, herbs, meditation, massage, and dietseek to aid healing by restoring the yin-yang balance and theflow of qi.--NCCAM A medical system with 3,000 year’s history for prevention,diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of illness Holistic perception of mind, body, health anddiseases Unique terminology and medical theories Individualized (personalized) medicine Comprehensive plan for healthcare
Comparison of East & WestEastEmpiricalObservations overThousands ofYears Art of Medicine Holistic View Circular Logic Energetic WestScientific Method& Case-BasedMedicine Technology ofMedicine Molecular andOrgan View Linear Logic Mechanistic10
Modalities of TCM Acupuncture, moxibustion and cuppingChinese Materia Medica and Prescription:1. Botanical Sources -Herbology(root, stem, bark, leaf, flower, fruit and seeds)2. Zoological sources( antilope/buffalo horn, chicken gizzard membrane,musk, turtle shell, oyster shell etc.)3. Mineral- (Gypsum, mirabilite, borneol, cinnabar, etc.) Tui Na/Body manipulation (massage, acupressure,corrective manipulation) Qigong/Tai’Chi Diet/nutrition
Traditional Chinese MedicineAlimentotherapy
Basic Principles of TCM Ying-Yang Qi, Xue (blood), Jing(Essence), Ye (body fluid) Zang-Fu (Internal Organ) Maridian (Channel) Five element
Yin-Yang The Tao of Universe The principle of all matters The parentage of all change The origin of birth and death--Su WenThe Tao is the One,From the One come Yin and Yang;From these two, creative energy;From energy, ten thousand things;The forms of all creation.All life embodies the yinAnd embraces the yang,Through their unionAchieving harmony.--Tao Te Ching, lePositive ChargeHeavenSpring & maleNegative ChargeEarthFall & Winter
Yin-Yang Concept describing how things function in relation to eachother and to the universe complementary opposites as parts of wholeYin-Yang imbalanceYin-Yang balanceYinYangYinYin-Yang relationship: OppositionInterdependenceMutual consumptionInter-transformationYangYin Yang
Application of Yin-YangYINYANG Structure of human bodyfront, interiorback, exterior Physiologystructurefunction Pathologyhypo-functionhyper-function Diagnosisexterior, heat, excess interior, cold, deficiency Chinese medicine cold/cool, sour, salty, bitter hot/warm, pungent, sweet Treatmentreplenish Yin/Yang deficiency, reducing excessive heat orfire with cold drug; treating excessive cold with warm drug
Application of Yin-YangEat balancedYinYang
Application of Yin-YangKeep fit physically and mentallyYangYin
Brain ogenMelatonin ineTestosteroneYangSleep/memory Yin-YangBalancedImbalanced
Qi (Chi 气)Qi --life energy, moving force (Yang)Types of Qi:Origin: Yuan Qi (prenatal-parents),Zong Qi (postnatal-breathing),Ying Qi (nourishing Qi-food)Wei Qi (defending Qi-food)Structure: Zang-Fu Qi (Qi of internal organ)Meridian QiFunction of Qi: Promoting, defending, warming,consolidating and governing, “Qi Hua” (metabolizingand transforming)
Meridian Systems--Pathways for “Qi”Flow & Links of All Systems 14 regular meridians All acupoints distributealong meridians Bridge in and out of thebody Reflect pathophysiology of the inside. Guide the treatmentLung meridian--yinLI meridian--yang
Meridians Wherethere is no free flow(blockage), there is pain.Pathogenic factorsMeridianNo free flow(blockage)Pain22
Meridians Wherethere is free flow, there isno pain.PainNo free flowPathogenic factors(blockage)MeridianAcupuncture StimulationEliminatingMeridianNormal23
Zang-Fu (脏腑)-Internal OrgansFunctional systems, not pure anatomical onesFive Zang(Yin organs)Six FuExtraordinary(Yang organs) OrgansLiver (Gan )Heart (Xin )Spleen (Pi )Lungs (Fei )Kidneys (Shen)GallbladderBrianSmall intestine MedullaStomachBoneLarge intestine VesselBladderGallbladderThree warmers UterusMind-body connection
Heart (心):The monarch of all organs Controls blood andvessels Houses mind and governsmental activity Controls sweat Opens into tongue Manifests in complexion
Kidneys (肾):Root of life, Root of Yuan Qi Store Essence and govern birth,growth, reproduction anddevelopment Produce marrow, fill up brainand control bones Govern water Control reception of Qi House Will power, Open into ears and manifest inhair
Liver(肝):The general oforgans from whom the strategy isderived Stores blood, Ensures smooth flow of Qi and blood Houses Ethereal Soul Regulating mind and mood Promoting digestion and absorption Controls sinew Opens into eyes Manifests in nails.
Peak time for each organBreakfast28
Five ElementsAnger/AnxietyWoodWaterFireInsomniaPoor appetiteMetalEarthShort breathUrinationdisorder29
Five Elements30
Acupuncture:What Conditions Commonly Treated Health maintenance and promotionPrevention—boost immune function, anti-aging, anti-oxidation Complement to western medicineTherapeutic—-- Chronic pain (headaches, joints, back, neck, sciatica, TGN,TMJ, arthritis pain )-- Emotional/mental conditions (stress, anxiety, depression,insomnia)--PMS, dysmenorrhea; menopausal syndromes; fertility--GI dysfunction--Cardiovascular conditions--Respiratory ailment (sinus allergy, asthma)--immunological/endocrinological conditions Others—sport injury, military use, cosmetic
Acupuncture:What Conditions Commonly TreatedWHO: recognizes acupuncture's common use in treatingover 100 conditions.Acupuncture: review and analysis of reports oncontrolled clinical 414 ,2002 )
Randomized controlled trialstudies
Individualized Treatment withAcupuncture/TCMInsomniaYINYANGHeart/Spleen deficiency Liver-qi stagnationPatterns:Symptoms: Excessive dream, hard toExcessive dream, hard to fallasleep, irritation, bitter taste,headache, impatience, red tonguewith yellow coating, string-pulsestay asleep, fatigue, poormemory, dizziness, paletongue with thin coating,fine and weak pulseTreatment:Replenish heart and spleen Promote liver qiPatterns:Yin deficiencySymptoms: Excessive dream, hard toLiver-fireExcessive dream, hard to fallstay asleep, fatigue, poorasleep, irritation, bitter taste,memory, dizziness, redheadache, impatience, thin/yellow,tongue, weak thin pulsecoating, rapid string-like pulseTreatment: replenish YinClear up liver fire
How Does Acupuncture Work?From TCM perspective: Unblock meridian Enhance “Qi” Modulate “Zang-Fu” Optimize “In” and “out” Balance “Yin-Yang”From biomedical perspective: Improve local condition Regulate nervous system Modulate neurotransmission Enhance immune function Regulate endocrine activity And more
Overview of Acupuncture Action--Peripheral Nervous system– A-delta fibers – smaller, fasttransmitting, myelinated fibersthat transmit sharp pain– Mechanoreceptors –Triggered by strongmechanical pressure andintense temperature– C-fibers – smallest, slowtransmitting unmyelinated nervefibers that transmit dull oraching pain.– Mechanoreceptors –Mechanical & Thermal– Chemoreceptors –Triggered by chemicalsreleased duringinflammation– A-alpha/beta fibers – largediameter, fast transmitting,myelinated sensory fibers
Overview of Acupuncture Action--Central Nervous system
Overview of Acupuncture Action--Central Nervous systemThalamus: The sensory switchboardof the brain Located in the middle of the brainSomatosensory Cortex:Receives all info on touch and pain.Somatotopically organized
Overview of Acupuncture ActionYinYangSofttissuesnervesGlandsHeart & vesslsYinYanglungsliverEndorphines, IL-1Kidney/bladderGIAcupunctureAdapted from Benarroch 2008
At the tip of a needle—localimprovementConnective tissue stretchesby physical extension(1)or acupuncture (2)Fibroblasts enlarged &flattenedRho signaling (3)ATP releaseChange cell shapeAnalgesic effect 4)Cell focal adhesionRemodeling (5)Connective tissuerelaxationLangevin HM, 2013
Acupuncture modulation on HPO/HPA axisA-β & δ fibersYu JS et al: International Review of Neurobiology, 2013
Acupuncture modulation on HPA axisSpinal CordAcupunctureA-β & δ fibersZhu CB, 2013
Neuroendocrine modulation of bloodpressure by acupunctureZhou and Longhurst 2012
Acupuncture modulation on affective disorder viaimmune system and central 5HT,NE and DAImmunological Stress(viral, bacterial, chemical.)IL-1 p38 MAPK/ERKAcupunctureMidbrain SERT, NET and DATAltered 5HT-NE-DA homeostasisIncreased risk foraffective disordersZhu CB, 2011IL-1R
Acupuncture and PainGate Control TheoryProposed by Melzack and Wall in the 1960'sAcupunctureYinYang
Acupuncture and PainGate Control TheoryProposed by Melzack and Wall in the 1960'sAcupuncturecloses the gate
Conditions that open or close the gateConditions that openthe gatePhysicalconditionsEmotionalConditionsMental conditionsConditions that closethe gateExtent of the injuryMedicationInappropriate activity levelCounter stimulation, egAcupuncture, massageAnxiety or worryPositive emotionsTensionRelaxationDepressionRestFocusing on the painIntense concentration ordistraction (meditation)BoredomInvolvement and interest inlife activities
Acupuncture and PainMolecules involved: endogenous opioid CCK 5-HT DA NE IL-1 GABA Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. Jun 2004; 1(1): 41–47.
Acupuncture and PainOpioidergic Mechanisms for Analgesic Effect ofAcupunctureHan JS, 2003
Acupuncture and PainAcupuncture up-regulates opioid receptorZhu CB, 1995
Acupuncture Analgesia Enkephalins & Dynorphins SpinalCord (Substantia Gelatinosa) Endorphins Brainstem 5HT BrainstemGray Matter)(Periaqueductal(Raphe Nuclei)
Acupuncture and PainNeurotransmitters in hippocampusZhu CB, 1995
Imaging Studies on AcupunctureSystematic review and meta-analysisActivation: information processing and control centers-supramarginal gyrus (language center), SII, pre-supplementarymotor area (pre-SMA), middle cigulate gyrus, insula, thalamus,precentral gyrusDeactivation: limbic system—amygdala, hippocampus, vmPFC,posterior cingulate cortex (PCC).Huang et al. 2012
Imaging Studies on Acupuncture“Deqi” deactivation of brainAsghar, MacPherson et al. Brair Res 3 1 5 ( 2 0 1 0 ) 1 1 1 – 1 1 8
Imaging Studies on AcupunctureActivation on DeqiDeactivation on DeqiMacPherson et al. 2006
Imaging Studies on Acupuncture“Deqi” deactivation of brainInsulaMPCMPFCBA22MTLBA43Acupoint (Liv3)Hui KS, Napadow V, Kwong K et al. 2010, JOVEMonitoring Acupuncture Effects on Human Brain by fMRI
Imaging Studies on Acupuncturecarpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) treated by acupunctureLRHealthy controlNapadow, V, etal.,Neuroimaging, 2005LRLRCTS: BaselineCTS: Post-AcupunctureHuman Brain Mapping; 28:159-131, 2006
Summary on how acupuncture worksSomatosensory art & vesslsYinBrain StemSpinal CordYanglungsliverEndorphines, IL-1Sensory signalKidney/bladderGIPeripheral organsAcupunctureAdapted from Benarroch 2008Acupuncture
StressesAcupunctureInfection/Irritation/Injuries Loss of bonemineralsIncreasecholesterolInflammation HeartDisease High BP StrokeInsulinresistanceInflammatory cytokines“Switch on”oncogenesCancer(IL-1, IL-6, TNF- , CRP )“Mess up” CNS“Chew up”Nerve cellsDiabetesAlzheimer’sAffective disordersDepressionOCDPTSDCognitive impairment Osteoporosis
Acupuncture:Keep Brain Yin-Yang ogenMelatonin eroneKeep free flow of energyKeep body healthyKeep life quality
Acupuncture, moxibustion and cupping Chinese Materia Medica and Prescription: 1. Botanical Sources -Herbology (root, stem, bark, leaf, flower, fruit and seeds) 2. Zoological sources ( antilope/buffalo horn, chicken gizzard membrane, musk, turtle shell, oyster shell etc.)