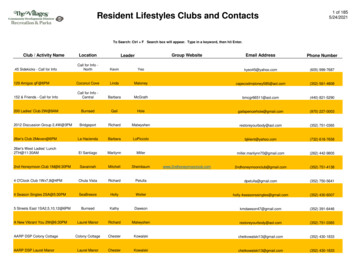
Transcription
Conducting a successful literature search:A researcher’s guide to tools, terms and techniquesFinding high-quality information can be a challenge. Sometimes you needhelp, but you aren’t able to speak directly with an expert. Reference thesecards when you need quick support—think of this as a Librarian in yourback pocket!1. Keywords, Operators & Filters2. Search Tools3. Types of Literature4. Evaluate Information5. Organize Research
Conducting a successful literature search:A researcher’s guide to tools, terms and techniques1. Keywords, operators and filtersBrainstormkeywordsExpandyour keywordsUseboolean operatorsRefineyour search resultsThese are the main ideas of yourresearch question/topic sentence.Look at the subject headings of thematerials you find and use thoseterms as applicable.Insert AND, OR, and NOT into yoursearch to broaden or narrow it.Filters in the database allow you tonarrow a search by year, content type, etc.Or look up your keywords in asubject-specific database thesaurusto find predefined terms (called“controlled vocabulary”).PTSD OR Post Traumatic StressDisorder AND soldiers NOT Navy.At the library: Consult a liaison librarian or subject specialist.For example:1
Conducting a successful literature search:A researcher’s guide to tools, terms and techniques2. Search toolsSelect the best tools:Abstract andcitation databaseShort descriptions (abstracts)of research content so youcan quickly get up to speed ona topic and determine whatcontent is worth exploring more.Full-text databaseWhen you’re ready to divedeeper into research, seek outsearchable, multidisciplinarydatabases to access the fullbreadth and depth of researchin web/PDF formats.Search box onlibrary homepageDiscover your library’s fullcatalog to view a wide array ofavailable research. *Note: Notall databases may be included,so remember to check otherdatabases, as well.Library catalogWeb search engineWhen looking for items housedphysically in the library (as wellas some electronic items).When looking for popular andwidely-available content, websearches can return a full rangeof sources. *Note: Not all resultswill pass research-level scrutiny.Institutional Repository (IR)What other research is availableto you? Check your library orwebsite to discover the latestresearch produced at yourinstitution. *Note: Format mayvary from final publication output.At the library: Find research/subject guides online.2
Conducting a successful literature search:A researcher’s guide to tools, terms and techniques3. Types of literatureYou should find:A name for other research material such as:ArticlesBooksDataGrey LiteratureJournalMonographTypes of available data:Conference proceedingPatentWritten by a researcher orscholar for a specific field,reviewed by peer scholarsbefore publicationA book on a specialized topic Equations Charts and GraphsPanels, presentations andposter sessions at a conferenceAny book accessible infull text online Chemical ReactionsWhite paperRights to an invention grantedby an official governmentagency Data SetsOther publicationReference work Maps /geographic dataDocument that often containslegislation, outlines futuretrends, or is a call foractionon a topicDissertation or thesisPublished report or datasetMagazineWritten by a journalist for amass-market audienceNewspaperEbookA collection of research,e.g., encyclopediaWritten by a journalist toinform the public abouthappenings in the worldAt the library: Get help via email and online chat.Document not published inscholarly channels, such as agovernment documentStudent research papers oftenculminating in a master’sdegree or PhD3
Conducting a successful literature search:A researcher’s guide to tools, terms and techniques4. Evaluate informationTo determine trustworthiness of the material, try the CRAAP testdeveloped by the Meriam Library at California State University, Chico1CurrencyAccuracy When was the information published How reliable is the information?and is that important to know?Relevance How important is the informationto your needs?Authority Who is the author and what aretheir credentials? Do they work for a reputableinstitution? Does it lack citations? Are there spelling errors?Purpose Is it a well-balanced independentpiece of research, or intended to sella product or idea?http://www.csuchico.edu/lins/handouts/eval websites.pdf Was the information publishedin a peer-reviewed journal?At the library: Sign up for a one-to-one research consultation.4
Conducting a successful literature search:A researcher’s guide to tools, terms and techniques5. Organize researchSave materials such as article PDFs into a documentlibrary and/or download the citation informationCitation Manager / ReferenceManager / Document LibraryAn online tool or desktop software used to organize andstore citations and full-text articles or other documents,create bibliographies, insert in-text citations into a paper,and share references with research partners.CitationThe act of explaining the source of the informationfound during the course of your research. Citation isa mandatory scholarly practice that gives credit andhelps prevent plagiarism Citations may be used inbibliographies, footnotes and within the body of yourtext. Common citation formats are APA, MLA andChicago style.Example:Crystal Renfro, The Use of Visual Tools in the AcademicResearch Process: A Literature Review, The Journal ofAcademic Librarianship, Volume 43, Issue 2, March 2017,Pages 95-99, ISSN 02.004At the library: Take an information skills workshop.5
ElsevierWe’re a global information analytics business specializing in science and health,combining content with technology, supported by operational efficiency, to turninformation into actionable knowledge. We help institutions and professionalsprogress science, advance healthcare and improve performance.Learn MoreVisit us at: https://www.elsevier.com for more information.Brought to you by Katy Kavanagh Webb, Research and Instructional ServicesLibrarian kavanaghk@ecu.edu and Elsevier’s Library Connect.Copyright 2018 Elsevier B.V.April 2018
Conducting a successful literature search: A researcher’s guide to tools, terms and techniques 1. Keywords, operators and filters Brainstorm keywords These are the main ideas of your research question/topic sentence. Expand your keywords Look at the subject headings of the materials you find and use those terms as applicable.