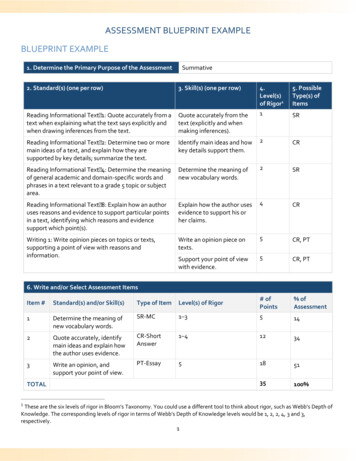
Transcription
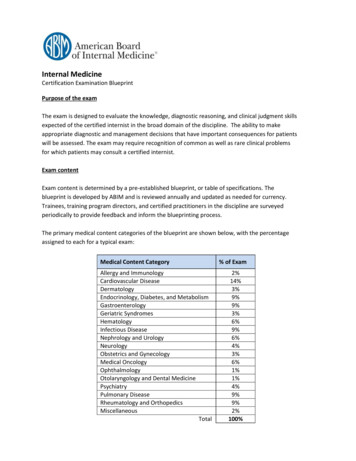
Internal MedicineCertification Examination BlueprintPurpose of the examThe exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skillsexpected of the certified internist in the broad domain of the discipline. The ability to makeappropriate diagnostic and management decisions that have important consequences for patientswill be assessed. The exam may require recognition of common as well as rare clinical problemsfor which patients may consult a certified internist.Exam contentExam content is determined by a pre-established blueprint, or table of specifications. Theblueprint is developed by ABIM and is reviewed annually and updated as needed for currency.Trainees, training program directors, and certified practitioners in the discipline are surveyedperiodically to provide feedback and inform the blueprinting process.The primary medical content categories of the blueprint are shown below, with the percentageassigned to each for a typical exam:Medical Content CategoryAllergy and ImmunologyCardiovascular DiseaseDermatologyEndocrinology, Diabetes, and MetabolismGastroenterologyGeriatric SyndromesHematologyInfectious DiseaseNephrology and UrologyNeurologyObstetrics and GynecologyMedical OncologyOphthalmologyOtolaryngology and Dental MedicinePsychiatryPulmonary DiseaseRheumatology and OrthopedicsMiscellaneousTotal% of Exam2%14%3%9%9%3%6%9%6%4%3%6%1%1%4%9%9%2%100%
Every question in the exam will fall into one of the primary medical content categories shownabove. There are also other important areas that are addressed in conjunction with this medicalcontent, and these areas are called “cross content categories.” Not all questions have a crosscontent classification; the cross-content categories are shown in the following table:Cross-Content CategoryCritical Care MedicineGeriatric MedicinePreventionWomen’s HealthClinical EpidemiologyEthicsNutritionPalliative and End-of-Life CareAdolescent MedicineOccupational MedicinePatient SafetySubstance AbuseRelative Percentage10%10%6%6%3%3%3%3%2%2%2%2%Exam formatThe exam is composed of multiple-choice questions with a single best answer, predominantlydescribing clinical scenarios. Questions ask about the work done (that is, tasks performed) byphysicians in the course of practice: Making a diagnosisOrdering and interpreting results of testsRecommending treatment or other patient careAssessing risk, determining prognosis, and applying principles from epidemiologic studiesUnderstanding the underlying pathophysiology of disease and basic science knowledgeapplicable to patient careClinical information presented may include patient photographs, radiographs, electrocardiograms,recordings of heart or lung sounds, and other media to illustrate relevant patient findings.A tutorial including examples of ABIM exam question format can be found on/internal-medicine/exam-tutorial.aspx.The primary medical categories can be expanded for additional detail to show topics that may becovered in the exam. Each primary medical content category is listed below, with the percentageof the exam assigned to this content area. Below each major category are subsection topics andtheir assigned percentages in the exam.2
Please note: The percentages below describe content of a typical exam and are approximate;actual exam content may vary.Allergy and ImmunologyAnaphylaxisAspirin idiosyncrasyStinging insect hypersensitivityDesensitization therapySerum sicknessUndifferentiated anaphylaxisAsthmaExercise- and cold-induced asthmaAllergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosisNasal polyps and aspirin sensitivityOccupational asthmaAsthma and pregnancyAsthma mimics – (including vocal cord dysfunction)Undifferentiated asthmaRhinitis, sinusitis, conjunctivitisAllergic rhinitisAcute and chronic sinusitisAllergic conjunctivitisUpper airway cough syndromeFood allergyUrticaria and angioedemaHereditary angioedemaDrug-induced urticaria and angioedemaTransfusion-related urticaria or anaphylaxisContrast-related allergySkin disordersAtopic dermatitisContact dermatitisDrug allergy other than drug-induced urticaria and angioedemaPrimary immunodeficiency disordersAntibody deficiency (common variable immunodeficiency)Cellular immunodeficiency other than humanimmunodeficiency virus (HIV) infectionComplement deficiencyPrimary humoral immunodeficiencyAllergic complications of transfusionsHemolytic transfusions reactionsTransfusion-related acute lung injuryTransfusion-related urticaria and anaphylaxis2% of Exam 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2%3
Autoimmune systemic disorders (including IgG4 related disorders) 2%MastocytosisAllergic interstitial nephritisEosinophilic esophagitisEosinophilic pneumoniaEosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss syndrome)Hypersensitivity pneumonitisCardiovascular DiseaseHypertension (NOTE: This total includes the Hypertension contentlisted under Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism;Nephrology and Urology)Essential hypertensionRenal (including renal parenchymal, renovascular)Coarctation of the aortaHypertensive urgency and emergencyUndifferentiated hypertensionPericardial diseasePericarditisPericardial effusionConstrictive pericarditisIschemic heart diseaseStable angina pectorisAcute coronary syndrome (ACS)ACS complicationsHeart failure from ischemic cardiomyopathyEvaluation of undiagnosed chest painOther ischemic heart disease (coronary artery disease, spasm)Dysrhythmias and conduction defectsConduction defectsBradyarrhythmiasTachyarrhythmiasOther dysrhythmias (cardiac resuscitation)Congenital heart disease in adultsAtrial septal defect and patent foramen ovaleBicuspid aortic valveOther congenital heart disease (patent ductus arteriosus,ventricular septal defect, pulmonic stenosis)Valvular heart diseaseAortic stenosisAortic regurgitationMitral regurgitationMitral stenosisProsthetic heart valve14% of Exam5% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2%4
Myocardial disease 2%Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)MyocarditisHypertrophic cardiomyopathy with and without obstructionRestrictive cardiomyopathyDilated cardiomyopathyCor pulmonaleUndifferentiated myocardial diseaseEndocarditis and other cardiovascular infection 2%EndocarditisInfections of the pericardial spaceEndocarditis prophylaxisUndifferentiated cardiovascular infectionVascular disease 2%Carotid artery diseaseAortaPeripheral arterial diseasePulmonary vascular diseaseVenous disease of the lower extremitiesSuperior vena cava syndrome (not due to cancer)Syncope 2%Neurocardiogenic syncope (vasovagal syncope)Situational syncope (including cough syncope, micturition syncope)Postural hypotensionPreoperative consultation 2%No testing requiredTesting indicatedLipid disorders 2%Antithrombotic therapy in cardiovascular disease 2%Miscellaneous cardiovascular disease (physical examination 2%findings, murmurs)DermatologyDermatitis (eczemas)Atopic dermatitisContact dermatitisPhotodermatitisStasis dermatitisHand dermatitisDrug eruptionsNummular dermatitisExfoliative dermatitis (erythroderma, not includingmycosis fungoides)Seborrheic dermatitis3% of Exam 2%5
Dermatologic immunologyUrticaria and angioedemaLeukocytoclastic vasculitisVascular dermatosesErythema multiformeErythema nodosumTelangiectasiaLeg ulcersAcne and rosaceaAcne vulgarisRosaceaPapulosquamous dermatosesPsoriasisPityriasis roseaLichen planusSkin and soft tissue infectionsDermatophytesHerpes zoster and varicellaViral exanthems other than varicellaCellulitisNecrotizing soft-tissue infections and gas gangreneLymphadenitis and lymphangitisEctoparasites (lice, scabies, and others)Vesiculobullous dermatosesPemphigus vulgarisDermatitis herpetiformisPigment disordersVitiligoMelasma (chloasma)Acanthosis nigricansXeroderma pigmentosaPhotosensitivity dermatosesPorphyria cutanea tardaPhotodermatitisAlopeciaNodules and tumors of the skinSeborrheic keratosisActinic keratosisWarts, corns, and skin tagsSquamous cell carcinoma of the skinBasal cell carcinoma of the skinMelanoma and neviMycosis fungoidesOther nodules or tumors of skin (dermatofibroma) 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2%6
Nutritional disorders, cutaneous manifestationsVitamin C deficiency and scurvyNiacin deficiencyOther nutritional disorders of skinDisorders of the nailsEnvironmental injury of skinFrostbiteBurnsPressure ulcersUndifferentiated dermatologyEndocrinology, Diabetes, and MetabolismAdrenal disordersPrimary aldosteronism and mineralocorticoid excessAdrenal insufficiencyPheochromocytomaThyroid disordersHyperthyroidismHypothyroidismThyroiditis (not Hashimoto's or peripartum)Thyroid nodules and thyroid cancerEuthyroid sick syndromeThyroid stormHypertension (NOTE: This total includes the Hypertensioncontent listed under Cardiovascular Disease;Nephrology and Urology)Essential hypertensionRenal artery stenosisCushing's diseaseLipid disordersHypercholesterolemiaHypertriglyceridemia (not including chylomicronemia)Chylomicronemia syndromeDiet and hyperlipidemiaOvarian disorders and female reproductive healthPolycystic ovary syndromeAmenorrheaOvarian cancerTestes and Male reproductive healthMale hypogonadismMale infertilityErectile dysfunctionTesticular carcinoma and tumorsGynecomastia 2% 2% 2% 2% 2%9% of Exam 2% 2%5% 2% 2% 2%7
Diabetes mellitusType 1 diabetes mellitusType 2 diabetes mellitusDiabetes mellitus and pregnancyComplications of diabetes mellitusDisorders of calcium metabolism and boneHypercalcemiaHypocalcemia (not including vitamin D s diseaseOsteoporosisVitamin D deficiency and osteomalaciaRenal osteodystrophyHypothalamic disordersAnterior pituitary disordersPituitary tumorsHypopituitarismPosterior pituitary and water metabolismHypernatremiaHyponatremiaEndocrine tumors and endocrine manifestations of tumorsInsulinomaVasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)-secreting tumorsZollinger-Ellison syndrome (gastrinoma)Glucagon-secreting tumorsCarcinoid syndromeMalignancy-associated hypercalcemiaEctopic adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) due to tumorSIADH from tumorUndifferentiated endocrine tumors ormanifestations of tumorsHypoglycemia not due to insulinomaPolyglandular disordersMultiple endocrine hypofunctionNutritional disordersObesityParenteral nutritionUndifferentiated nutritional disordersWomen's health endocrine issues 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2%8
GastroenterologyEsophageal diseaseGastroesophageal refluxBarrett's esophagusEsophageal carcinomaEsophageal motility disordersMedication-induced esophageal disorderEsophageal diverticulaEsophageal strictures or websGastroesophageal varicesInfectious esophagitis (Candida, herpes simplex virus,cytomegalovirus)Mallory-Weiss syndromeOther esophageal disease (eosinophilic esophagitis,esophageal rupture)Stomach or duodenal diseaseHelicobacter pylori infectionPeptic ulcer disease (other than Helicobacter pylori)Gastritis and gastropathyStomach cancerNon-ulcer dyspepsiaDisorders of gastric emptyingMenetrier’s diseaseSmall intestinal diseaseCeliac diseaseBacterial overgrowth syndromeShort bowel syndromeMesenteric ischemia and ischemic colitisCrohn's disease including Crohn's colitisGastroenteritis other than antibiotic colitisOther small intestinal disease (diarrhea [osmotic,post-surgical, bile salt-induced, nocturnal],gastric bypass complications)Colonic and anorectal diseaseColorectal cancerColon polyposis syndrome and other geneticcolon cancer syndromesScreening for colorectal cancer other thanpolyposis syndromesDiverticular diseaseUlcerative colitisIrritable bowel syndromeHemorrhoids and fissuresAntibiotic colitis9% of Exam 2% 2% 2% 2%9
Acute appendicitisRadiation colitisOther colonic or anorectal disease (constipation,fecal incontinence, neutropenic and lymphocytic colitis)Pancreatic diseaseAcute pancreatitis (including autoimmune pancreatitis)Chronic pancreatitisPancreatic carcinomaCystic fibrosisNeuroendocrine tumors of the pancreasInfections of the pancreas and pancreatic abscessUndifferentiated pancreatic diseaseBiliary tract sisCholangitisSclerosing cholangitisSphincter of Oddi dysfunctionLiver diseaseViral hepatitisLiver abscessCirrhosis and portal hypertensionDrug-induced liver disease other than acetaminophenAutoimmune hepatitisPrimary biliary cholangitisCholestasisWilson's diseaseLiver disease in pregnancyHemochromatosisHepatic vein thrombosis (Budd-Chiari syndrome)Fatty liver and nonalcoholic steatohepatitisAlcoholic hepatitisFulminant liver failureGilbert's syndromeHepatocellular carcinomaLiver transplantationUndifferentiated liver diseaseGastrointestinal complications of HIV infectionUndiagnosed gastrointestinal hemorrhageUndiagnosed upper gastrointestinal hemorrhageUndiagnosed lower gastrointestinal hemorrhageUndifferentiated gastroenterology 2% 2% 2% 2% 2% 2%10
Geriatric SyndromesPressure ulcersVenous ulcers and chronic woundsEnd-of-life and palliative care of the elderlyEthics in the elderlyAssessment of decisional capacity and competency andsurrogate decision-making in the elderlyConstipation in the elderlyDisorders of swallowing in the elderlyUrinary tract infections in the elderlyIncontinence in the elderlyDementia in the elderlyDelirium in the elderlyDizziness and vertigo in the elderlyNutrition in the elderlyOphthalmology in the elderlyCataractsAge-related macular degenerationGiant cell arteritisPsychiatry in the elderlyDepression in the elderlySleep disorders in the elderlyNeuropsychological testing of the elderlyHip fracture in the elderlyCommon foot problems in the elderlyPrinciples of the geriatric assessmentRehabilitation and the elderlyOther primary geriatric topicsClinical pharmacology and agingEpidemiology and agingNursing home careHome carePresbycusis and hearing loss in the elderlyElder mistreatmentFallsSexual function in the elderlyUndifferentiated geriatricsHematologyHypoproliferative anemiaAplastic anemiaAnemia of chronic disease or organ failure(including kidney failure)Iron deficie
Not all questions have a cross-content classification; the cross-content categories are shown in the following table: Cross-Content Category Relative Percentage Critical Care Medicine 10% Geriatric Medicine 10% Prevention 6% Women’s Health 6% Clinical Epidemiology 3% Ethics 3% Nutrition 3% Palliative and End-of-Life Care 3% Adolescent Medicine 2% Occupational Medicine 2% Patient Safety