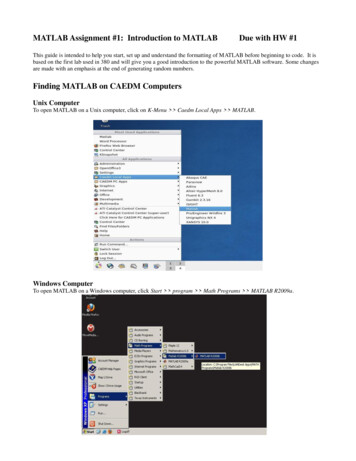
Transcription
Computer Vision with MATLABMaster ClassBruce Tannenbaum 2011 The MathWorks, Inc.1
Agenda IntroductionFeature-based registration– Automatic image registration– Rotation correction with SURF– Stereo image rectification Video processing with System objects– Tracking cars with optical flow Classification– Texture classification– Face detection Summary2
Examples of Computer Vision with MATLAB3
Computer VisionUsing images and video to detect, classify, and trackobjects or events in order to “understand” a real-worldsceneImageProcessingComputerVisionRemove noiseAdjust contrastMeasure DetectIdentifyClassifyRecognizeTrack InterpretationPedestrianBicyclistTruckCarTraffic violationAccident 4
Typical Computer Vision Challenges Variable lighting conditionsUnknown scene depth or perspectiveBackground clutterPartially hidden objects (occlusion)Differences in scale, location, and orientation5
Technical Computing with MATLABAccessExplore and DiscoverFilesData Analysisand ModelingSoftwareAlgorithmDevelopmentShareReporting andDocumentationOutputs for DesignCode and nt6
Key Products for Computer Vision Computer Vision System Toolbox - NEWImage Processing ToolboxMATLABStatistics Toolbox Additionally – Image Acquisition Toolbox– MATLAB Coder– Parallel Computing Toolbox7
Computer Vision System ToolboxDesign and simulate computer visionand video processing systems Feature detectionFeature extraction and matchingFeature-based registrationMotion estimation and trackingStereo visionVideo processingVideo file I/O, display, and graphics8
Demo: Feature-Based Registration Workflow– Feature detection– Feature extraction– Feature matching– Geometric transformationestimation with RANSAC9
Demo: Rotation Correction with SURF Workflow– Feature detection– Feature extraction– Feature matching10
Demo: Stereo Image Rectification11
Recovering Scene Depth with Stereo Cameras12
Epipolar Geometry13
Fundamental MatrixTXL FXR 014
Video Processing Video file I/O and displayVideo pre-processingMotion estimation and analysis15
Motion Estimation and Analysis Techniques– Block matching– Optical flow– Template matching– Background estimationusing Gaussian mixture models Applications Object tracking Interpolation Compression16
Demo: Using Optical Flow to Track Cars Video file I/O and displayVideo preprocessingMotion estimationSegmentation and analysis17
Useful System Objects for Video File I/O,Display, and Graphics File I/O– VideoFileReader– VideoFileWriter Display– VideoPlayer– DeployableVideoPlayer Graphics– AlphaBlender– MarkerInserter– ShapeInserter– TextInserter18
Useful System Objects for VideoPreprocessing and Statistics Preprocessing– ChromaResampler– Deinterlacer– DemosaicInterpolator Statistics (running across video frames)– Histogram– Maximum– Mean– Median– Minimum– StandardDeviation– Variance19
Different Interfaces, Different Benefits inComputer Vision System ToolboxAudienceFunctionsSystem ObjectsAlgorithmdevelopers System designersApplicationspecificalgorithmsand tools ImplementersSimulink BlocksAlgorithms thatmaintain stateEfficient ration MultidomainmodelingReal-timesystem designTarget-specificembeddedhardwareHIL, PIL20
Typical Parts of a Computer Vision Algorithm1.2.3.4.5.6.Image/video acquisitionImage/video pre-processingFeature detectionFeature extractionFeature matchingUsing features– Stabilization, mosaicking–7.Image Acquisition ToolboxImage Processing ToolboxComputer VisionSystem ToolboxStereo image rectificationFeature classificationStatistics Toolbox21
Challenge: Accurate Classification is HardHow can a computer tell that these are all chairs?22
Demo: Texture Classification Identify features appropriate for classificationExtract features for training and test dataTrain classifier with featuresTest classifier and analyze results Using KTH-TIPS database On the significance of real-world conditions for material classification,”E. Hayman, B. Caputo, M. J. Fritz, J-O. Eklund, Proc ECCV 2004“Classifying materials in the real world,” B. Caputo, E. Hayman, M. J.Fritz, J.-O. Eklundh, Image and Vision Computing, 28 (2010), 150- 163.23
Demo: Face Detection24
Statistics ToolboxPerform statistical analysis, modeling,and algorithm development Clustering– Principle components analysis– K-means– Gaussian mixture models Classification– Naïve Bayes– K-nearest neighbor search– Boosted decision trees AdaBoost, GentleBoost, LogitBoost, 25
Key Products for Computer Vision Computer Vision System Toolbox - NEWImage Processing ToolboxMATLABStatistics Toolbox Additionally – Image Acquisition Toolbox– MATLAB Coder– Parallel Computing Toolbox26
Why Use MATLAB for Computer Vision? Comprehensive environment– Analysis, algorithm development, visualization, etc. Broad library of algorithms– Computer vision– Image processing– Classification and clustering Documentation, examples, and technical supportIncreased productivity over C/C programming27
For More Information mathworks.com/products/computer-visionRelevant demos:– Barcode Recognition– Image Rectification– Traffic Warning Sign Recognition– People Tracking– Video Mosaicking DocumentationContact your sales representative28
Questions and Answers29
Why Use MATLAB for Computer Vision? Comprehensive environment – Analysis, algorithm development, visualization, etc. Broad library of algorithms – Computer vision – Image processing – Classification and clustering Documentation, examples, and technical support Incre